
Pyrosilicates is also called as:
(A) Chain silicates
(B) sorosilicates
(C) sheet silicates
(D) cyclic silicates
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: The basic building block of silicate minerals is the ${{[Si{{O}_{4}}]}^{4-}}$ tetrahedron. Silicate minerals containing chains are termed as insolicates. In single chains ${{(Si{{O}_{3}}^{2-})}_{n}}$ , the silicon to oxygen ratio 1:3. While in double chains ${{(S{{i}_{4}}{{O}_{11}}^{6-})}_{n}}$ , the silicon to oxygen ratio 4:11.
Complete step by step solution:
Silicates are the mineral containing silicon and oxygen in tetrahedral ${{[Si{{O}_{4}}]}^{4-}}$ units, in which silicon atoms are bonded to four oxygen atoms in a tetrahedral fashion. In silicates, either distance, the units are present or many such units are joined together via corners by sharing 1, 2, 3, or 4 oxygen atoms per silicate unit.
Some of the examples of silicates are feldspar, zeolites, mica, and asbestos. The important man-made silicates are glass and cement.
When silicate chains are linked together, they form chain, ring, sheet, or three-dimensional structures. The negative charge on the silicate structure is neutralized by positively charged metal ions. If all four corners are shared with other tetrahedral units, their dimensional networks are formed.
Depending on the way the tetrahedral units are linked, the silicates are classified into the following types:
(1) Orthosilicates
(2) Pyrosilicates
(3) Cyclic silicates
(4) Chain silicates
(5) Double chain silicates
(6) Silicon sheets or phyllosilicates
(7) Three-dimensional silicates
Pyro silicates: these type of silicates contain $S{{i}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}^{6-}$ ions which are formed by joining two tetrahedral ${{[Si{{O}_{4}}]}^{4-}}$ units and this ${{[Si{{O}_{4}}]}^{4-}}$ share one oxygen atom at one corner. The pyrosilicate ion is less basic than orthosilicate ion and only one mineral in nature contains pyrosilicate ion. Example: thortveitite - $S{{c}_{2}}S{{i}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$
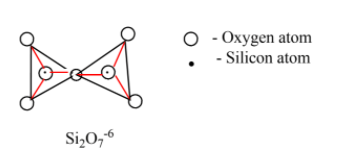
Based on the structure of the above pyrosilicates are also known as soro silicates or disilicates.
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note: Silicates are common minerals in the earth crust since silicon and oxygen are abundant elements. The oxygen to silicon ratio represents the degree of polymerization. Grater will be the degree of polymerization that decreases the oxygen to silicon ratio. The basic silicates minerals readily react with weak acids.
Complete step by step solution:
Silicates are the mineral containing silicon and oxygen in tetrahedral ${{[Si{{O}_{4}}]}^{4-}}$ units, in which silicon atoms are bonded to four oxygen atoms in a tetrahedral fashion. In silicates, either distance, the units are present or many such units are joined together via corners by sharing 1, 2, 3, or 4 oxygen atoms per silicate unit.
Some of the examples of silicates are feldspar, zeolites, mica, and asbestos. The important man-made silicates are glass and cement.
When silicate chains are linked together, they form chain, ring, sheet, or three-dimensional structures. The negative charge on the silicate structure is neutralized by positively charged metal ions. If all four corners are shared with other tetrahedral units, their dimensional networks are formed.
Depending on the way the tetrahedral units are linked, the silicates are classified into the following types:
(1) Orthosilicates
(2) Pyrosilicates
(3) Cyclic silicates
(4) Chain silicates
(5) Double chain silicates
(6) Silicon sheets or phyllosilicates
(7) Three-dimensional silicates
Pyro silicates: these type of silicates contain $S{{i}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}^{6-}$ ions which are formed by joining two tetrahedral ${{[Si{{O}_{4}}]}^{4-}}$ units and this ${{[Si{{O}_{4}}]}^{4-}}$ share one oxygen atom at one corner. The pyrosilicate ion is less basic than orthosilicate ion and only one mineral in nature contains pyrosilicate ion. Example: thortveitite - $S{{c}_{2}}S{{i}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$

Based on the structure of the above pyrosilicates are also known as soro silicates or disilicates.
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note: Silicates are common minerals in the earth crust since silicon and oxygen are abundant elements. The oxygen to silicon ratio represents the degree of polymerization. Grater will be the degree of polymerization that decreases the oxygen to silicon ratio. The basic silicates minerals readily react with weak acids.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




