
What is radial distribution function? Draw this function for the $1s,2s,3s,2p,3p\text{ }and\text{ 4}p$ in a hydrogen atom.
Answer
542.1k+ views
Hint: Radial distribution function tells us about the regions having high and low electron density and we can easily draw the probability curves for the orbitals of hydrogen atom if we know the number of regions of high probability i.e. n and zero probability i.e. l. For s-orbitals; n=n and
L=$n-1$ and for p-orbitals; n=$n-1$ and l=$n-1$. Now answer the statement.
Complete answer:
First of all, let’s discuss what a radial distribution function is. By the radial distribution function, we mean the probability of finding the electron within a small radial space around the nucleus.
Radial distribution function is also known as the radial probability distribution .
It depends upon the probability density and the volume of the shell.
The mathematical expression for the radial distribution function is as;
Probability=${{\Psi }^{2}}\times 4\pi {{r}^{2}}dr=4\pi {{r}^{2}}dr{{\Psi }^{2}}$
Here, gives the probability density for an electron in a given volume , r is the radius and dr is the thickness of the shell.
We can draw the radial distribution curves for the given orbitals if we know the regions of high probability of electrons and zero probability of electrons.
For s-orbitals;
Number of regions of high probability is represented by n and is =$n$.
Here, n represents the principal quantum number i.e. the shell to which the electron belongs.
Number of regions zero probability i.e. node is represented by l and is =$n-1$.
For p-orbitals;
Number of regions of high probability is represented by n and is =$n-1$.
Here, n represents the principal quantum number i.e. the shell to which the electron belongs.
Number of regions zero probability i.e. node is represented by l and is =$n-2$.
Now, the radial probability curves for the $1s,2s,3s,2p,3p\text{ }and\text{ 4}p$ in a hydrogen atom are as follows:-
(1) $1s$ orbital
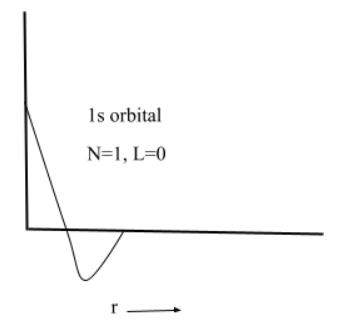
Here, n represents the number of regions of high probability and l represents the number of nodes i.e. the region where probability of finding the electrons is zero.
(2) $2s$
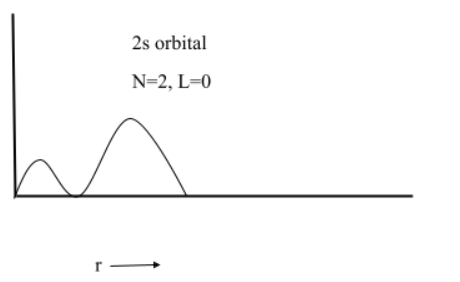
(3) $3s$
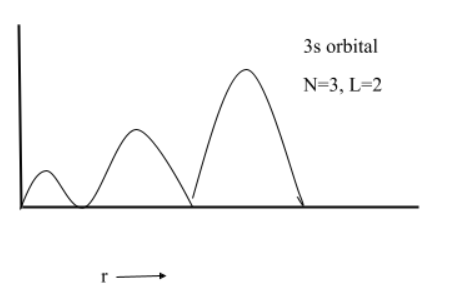
(4) $2p$
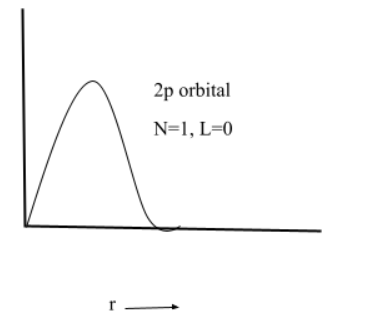
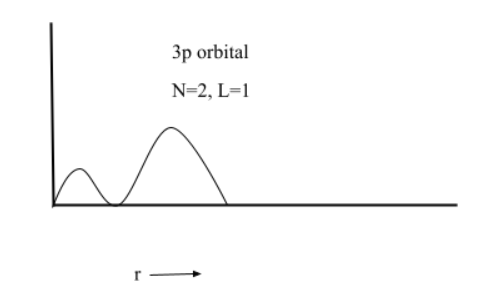
(5) $3p$
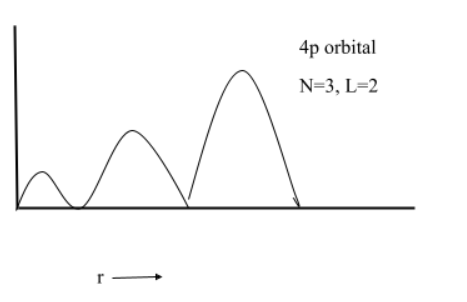
(6) $4p$
Note:
The peak of the curve gives the distance from the nucleus where the probability of finding the electrons is maximum and this distance is called the distance of maximum probability or the radius of maximum probability.
L=$n-1$ and for p-orbitals; n=$n-1$ and l=$n-1$. Now answer the statement.
Complete answer:
First of all, let’s discuss what a radial distribution function is. By the radial distribution function, we mean the probability of finding the electron within a small radial space around the nucleus.
Radial distribution function is also known as the radial probability distribution .
It depends upon the probability density and the volume of the shell.
The mathematical expression for the radial distribution function is as;
Probability=${{\Psi }^{2}}\times 4\pi {{r}^{2}}dr=4\pi {{r}^{2}}dr{{\Psi }^{2}}$
Here, gives the probability density for an electron in a given volume , r is the radius and dr is the thickness of the shell.
We can draw the radial distribution curves for the given orbitals if we know the regions of high probability of electrons and zero probability of electrons.
For s-orbitals;
Number of regions of high probability is represented by n and is =$n$.
Here, n represents the principal quantum number i.e. the shell to which the electron belongs.
Number of regions zero probability i.e. node is represented by l and is =$n-1$.
For p-orbitals;
Number of regions of high probability is represented by n and is =$n-1$.
Here, n represents the principal quantum number i.e. the shell to which the electron belongs.
Number of regions zero probability i.e. node is represented by l and is =$n-2$.
Now, the radial probability curves for the $1s,2s,3s,2p,3p\text{ }and\text{ 4}p$ in a hydrogen atom are as follows:-
(1) $1s$ orbital

Here, n represents the number of regions of high probability and l represents the number of nodes i.e. the region where probability of finding the electrons is zero.
(2) $2s$

(3) $3s$

(4) $2p$

(5) $3p$

(6) $4p$

Note:
The peak of the curve gives the distance from the nucleus where the probability of finding the electrons is maximum and this distance is called the distance of maximum probability or the radius of maximum probability.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




