
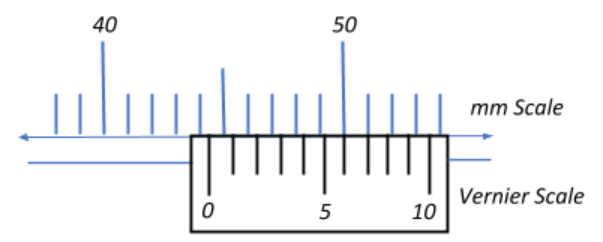
What is the reading on the Vernier scale?
A. 44.6 mm
B. 44.5 mm
C. 48.5 mm

Answer
582k+ views
Hint: Recall that each division on the main scale represents 1mm and each division on the Vernier scale represents 0.1mm. The division to which the zero on the Vernier scale is closest to is the main scale reading, and the division of the Vernier scale that first coincides with a division on the main scale gives the Vernier scale reading. Add these two together to obtain an effective reading.
Formula used: Final reading = Main scale reading + Vernier scale reading
Complete step by step answer:
A Vernier Calliper is an instrument that is used to make very accurate linear measurements. A calliper usually consists of an inner jaw and an outer jaw. The outer jaw holds the object whose dimensions we have to measure and measures the external diameter or width of an object, while the inner jaw is smaller and is used to measure the internal diameter of an object. It consists of the main scale which is the mm scale, and the Vernier scale that slides over the main scale and gives interpolated readings to a precision of 0.1mm. The interpolated reading is obtained by observing which line of the Vernier scale coincides with a line on the main scale.
Let us now examine the image of the Vernier calliper given to us. We can obtain the resultant reading in just two steps:
1. To obtain the main scale reading: Each division on the main scale represents 1mm. We see that the zero of the Vernier scale is closest to the fourth division after 40, i.e., the $44^{th}$ division, which is indicative of 44mm. Hence the main scale reading is 44mm.
2. To obtain the Vernier scale reading: Each division on the Vernier scale represents 0.1mm. We look closely for the line where the divisions of the main scale and the Vernier scale coincide. In case there are two or more points of coincidence we only consider the division of first coincidence. From the image, we see that the first coinciding Vernier division is the $6^{th}$ division. This is indicative of 0.6mm.
To this end, the effective reading will be the sum of the main scale and Vernier scale readings and is equivalent to 44mm+0.6mm = 44.6mm.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Note that the readings that we obtained are without accounting for any zero error.
Zero error can be understood as the condition where the Callipers register a reading when there should not be any reading or when the main scale and the Vernier scale are supposed to read 0 and coincide with each other but do not do so. It can be of two types: when the Vernier scale is towards numbers greater than 0 on the main scale then the error is positive, whereas if the Vernier scale is towards the plain region before 0 on the main scale then the zero error is negative.
Therefore, the effective reading would hence be Main scale reading + Vernier scale reading-(zero error).
Formula used: Final reading = Main scale reading + Vernier scale reading
Complete step by step answer:
A Vernier Calliper is an instrument that is used to make very accurate linear measurements. A calliper usually consists of an inner jaw and an outer jaw. The outer jaw holds the object whose dimensions we have to measure and measures the external diameter or width of an object, while the inner jaw is smaller and is used to measure the internal diameter of an object. It consists of the main scale which is the mm scale, and the Vernier scale that slides over the main scale and gives interpolated readings to a precision of 0.1mm. The interpolated reading is obtained by observing which line of the Vernier scale coincides with a line on the main scale.
Let us now examine the image of the Vernier calliper given to us. We can obtain the resultant reading in just two steps:
1. To obtain the main scale reading: Each division on the main scale represents 1mm. We see that the zero of the Vernier scale is closest to the fourth division after 40, i.e., the $44^{th}$ division, which is indicative of 44mm. Hence the main scale reading is 44mm.
2. To obtain the Vernier scale reading: Each division on the Vernier scale represents 0.1mm. We look closely for the line where the divisions of the main scale and the Vernier scale coincide. In case there are two or more points of coincidence we only consider the division of first coincidence. From the image, we see that the first coinciding Vernier division is the $6^{th}$ division. This is indicative of 0.6mm.
To this end, the effective reading will be the sum of the main scale and Vernier scale readings and is equivalent to 44mm+0.6mm = 44.6mm.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Note that the readings that we obtained are without accounting for any zero error.
Zero error can be understood as the condition where the Callipers register a reading when there should not be any reading or when the main scale and the Vernier scale are supposed to read 0 and coincide with each other but do not do so. It can be of two types: when the Vernier scale is towards numbers greater than 0 on the main scale then the error is positive, whereas if the Vernier scale is towards the plain region before 0 on the main scale then the zero error is negative.
Therefore, the effective reading would hence be Main scale reading + Vernier scale reading-(zero error).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




