
Reagent(s) which can be used to bring about the following transformation is (are):
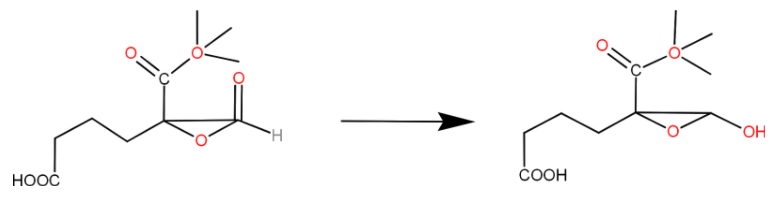
A. $LiAl{H_{4\;}}{\mathbf{in}}\;{\left( {{C_2}{H_5}} \right)_2}O$
B. $B{H_3}\;{\mathbf{in}}\;THF$
C. $NaB{H_4}\;{\mathbf{in}}\;{C_2}{H_5}OH$
D. Raney $Ni/{H_2}$ in THF

Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: We need a reducing agent which reduces the aldehyde group into its corresponding alcohols but we cannot reduce any other functional group.
Complete step by step solution:
Here in question we can see that all the functional groups remain the same as it is even after the reaction happens except the aldehyde group. Hence what we understood from this reaction is that we need an reducing agent which only reduces the aldehyde group. It cannot reduce the carboxylic group, epoxide or the esters present in it. When we use a strong reducing agent it will reduce all the functional groups. Now let us look at options one by one.
(a) $LiAl{H_{4}}$ in ${\left( {{C_2}{H_5}} \right)_2}O$: Lithium aluminium hydride in ether is strong reducing agent which can reduces all the functional group present in the question. Carboxylic acids, ketones and even ester get reduced by $LiAl{H_{4}}$. Hence we cannot use this as the reagent.
(b) $B{H_3}$ in $THF$: Borane is also a strong reducing agent which reduces carboxylic acids, esters and the aldehyde group. We need to reduce only the aldehyde group. Hence we cannot use this as the reagent.
(c) $NaB{H_4}$ in ${C_2}{H_5}OH$: Sodium borohydride in ethanol is not as strong as the lithium aluminium hydride, it can only reduce aldehyde or ketones into its corresponding alcohols. It cannot reduce carboxylic acid, esters, or the epoxide group. Hence we can use this.
(d) Raney $Ni/{H_2}$ in THF: It is also a strong reducing agent which reduces all the functional group present in the compound. Hence we cannot use this.
Therefore, option (c) is correct.
Note:
Sodium borohydride is not as reactive as lithium aluminium hydride, therefore the reduction can be done with alcohol solution or in water. It is an advantage for polar compounds which can be pretty insoluble in ether. Hydrolysis of water and acid followed by extraction is used to isolate them.
Complete step by step solution:
Here in question we can see that all the functional groups remain the same as it is even after the reaction happens except the aldehyde group. Hence what we understood from this reaction is that we need an reducing agent which only reduces the aldehyde group. It cannot reduce the carboxylic group, epoxide or the esters present in it. When we use a strong reducing agent it will reduce all the functional groups. Now let us look at options one by one.
(a) $LiAl{H_{4}}$ in ${\left( {{C_2}{H_5}} \right)_2}O$: Lithium aluminium hydride in ether is strong reducing agent which can reduces all the functional group present in the question. Carboxylic acids, ketones and even ester get reduced by $LiAl{H_{4}}$. Hence we cannot use this as the reagent.
(b) $B{H_3}$ in $THF$: Borane is also a strong reducing agent which reduces carboxylic acids, esters and the aldehyde group. We need to reduce only the aldehyde group. Hence we cannot use this as the reagent.
(c) $NaB{H_4}$ in ${C_2}{H_5}OH$: Sodium borohydride in ethanol is not as strong as the lithium aluminium hydride, it can only reduce aldehyde or ketones into its corresponding alcohols. It cannot reduce carboxylic acid, esters, or the epoxide group. Hence we can use this.
(d) Raney $Ni/{H_2}$ in THF: It is also a strong reducing agent which reduces all the functional group present in the compound. Hence we cannot use this.
Therefore, option (c) is correct.
Note:
Sodium borohydride is not as reactive as lithium aluminium hydride, therefore the reduction can be done with alcohol solution or in water. It is an advantage for polar compounds which can be pretty insoluble in ether. Hydrolysis of water and acid followed by extraction is used to isolate them.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




