
What is the reason to operate the photodiodes in reverse bias?
A. fractional change due to the photo-effects on the majority carrier dominated forward bias current is more easily measurable than the fractional change in the reverse bias current.
B. reverse bias is more efficient than forward bias.
C. fractional change due to the photo-effects on the minority carrier dominated reverse bias current is more easily measurable than the fractional change in the forward bias current.
D. reverse bias configuration result in larger amount of current (in$\mu A$)
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: A photodiode is a semiconductor device that is used to convert light into an electrical current. The current is generated when photons or light quanta are absorbed in the photodiode is very small and is in the order of $\mu A$. The current in forward bias mode is in the order of $mA$.
Complete answer:
A Photodiode is nothing but a p-n junction diode with a transparent window to allow light to fall on the diode. It operates under reverse bias.
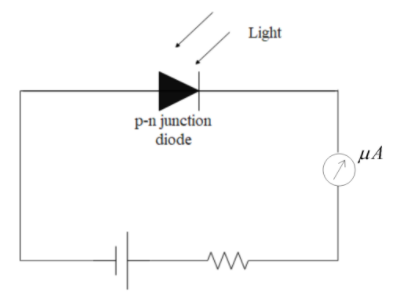
When light (photons) of energy greater than the energy gap (${{E}_{g}}$) of the semiconductor incident on the diode, then electron-hole pairs are generated due to the absorption of photons. The generation of electron-hole pairs takes place near the depletion region of the diode. Due to the electric field of the junction, electrons and holes split up before they recombine since the direction of the electric field is such that electrons reach n-side and holes reach p-side giving rise to an emf. When an external load is connected, current flows. The magnitude of the photocurrent is related to the intensity of incident light.
In forward bias current is of the order $mA$ and thus, the photocurrent cannot be observed. If a reverse bias is applied, it is easier to observe the change in the current with change in the light intensity because reverse current without light is in the order of $\mu A$, the change in reverse current due to light is also in the order of $\mu A$. That is why; it is operated in reverse bias.
Hence, option C is correct.
Note:
When light (photons) of energy greater than the energy gap (${{E}_{g}}$) of the semiconductor incident on the photodiode, then electron-hole pairs are generated due to the absorption of photons. To create an electron-hole pair, we spend some energy in the form of light or heat. When an electron and hole recombine the energy is released in the form of light (radiative recombination) or heat (non-radiative recombination) in validation of law of conservation of energy.
Complete answer:
A Photodiode is nothing but a p-n junction diode with a transparent window to allow light to fall on the diode. It operates under reverse bias.

When light (photons) of energy greater than the energy gap (${{E}_{g}}$) of the semiconductor incident on the diode, then electron-hole pairs are generated due to the absorption of photons. The generation of electron-hole pairs takes place near the depletion region of the diode. Due to the electric field of the junction, electrons and holes split up before they recombine since the direction of the electric field is such that electrons reach n-side and holes reach p-side giving rise to an emf. When an external load is connected, current flows. The magnitude of the photocurrent is related to the intensity of incident light.
In forward bias current is of the order $mA$ and thus, the photocurrent cannot be observed. If a reverse bias is applied, it is easier to observe the change in the current with change in the light intensity because reverse current without light is in the order of $\mu A$, the change in reverse current due to light is also in the order of $\mu A$. That is why; it is operated in reverse bias.
Hence, option C is correct.
Note:
When light (photons) of energy greater than the energy gap (${{E}_{g}}$) of the semiconductor incident on the photodiode, then electron-hole pairs are generated due to the absorption of photons. To create an electron-hole pair, we spend some energy in the form of light or heat. When an electron and hole recombine the energy is released in the form of light (radiative recombination) or heat (non-radiative recombination) in validation of law of conservation of energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




