
Reduction of aromatic nitro compounds using Sn and HCl gives:
Answer
522.1k+ views
Hint: Consider an arbitrary aromatic nitro compound and try to write the reaction mechanism with Sn/HCl. Tin reacts with HCl and forms Tin(IV) chloride. Hence, we can say that ${{H}^{+}}$ ions are releases which react with the nitro functional group of the aromatic compound.
Complete answer:
Nitration of aromatic compounds is used to add nitrogen atoms to the aromatic compound in the form of nitro ($-N{{O}_{2}}$) group. The nitrating mixture consists of hot conc. nitric acid also called hot fuming nitric acid and conc. sulphuric acid.
Sulphuric acid is a stronger acid than nitric acid. Sulphuric acid protonated nitrogen present in the nitric acid. This leads to the formation of nitroso ion($N{{O}_{2}}^{+}$).
Nitroso ion is then added to the benzene ring through electrophilic substitution reaction. This is how aromatic nitro compounds are formed.
We will now consider an aromatic nitro compound and write its reaction with Sn/HCl.
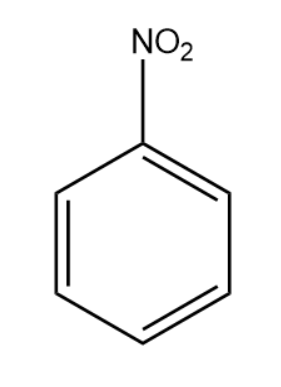
Tin reacts with hydrochloric acid to form Tin(IV) chloride. The ${{H}^{+}}$ ions present react with the nitro group of the aromatic compound.
The oxygen from the nitro group is released in the form of water molecules. In place of oxygen atoms, hydrogen gets substituted leading to formation of aromatic amine.
The reaction is given below:
\[2{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{O}_{2}}\text{ }+\text{ }3Sn\text{ }+\text{ }12HCl\text{ }\to \text{ }2{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}\text{ }+\text{ }3SnC{{l}_{4}}\text{ }+\text{ }4{{H}_{2}}O\]
The product formed is aniline which is an aromatic primary amine.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (A).
Note:
Electrophilic aromatic substitution is an organic reaction in which the hydrogen that is attached to an organic system is replaced by incoming electrophile.
Some of the important electrophilic aromatic substitutions include aromatic nitration, aromatic halogenation, aromatic sulfonation, and alkylation and acylation through Friedel-Crafts reaction mechanism.
Complete answer:
Nitration of aromatic compounds is used to add nitrogen atoms to the aromatic compound in the form of nitro ($-N{{O}_{2}}$) group. The nitrating mixture consists of hot conc. nitric acid also called hot fuming nitric acid and conc. sulphuric acid.
Sulphuric acid is a stronger acid than nitric acid. Sulphuric acid protonated nitrogen present in the nitric acid. This leads to the formation of nitroso ion($N{{O}_{2}}^{+}$).
Nitroso ion is then added to the benzene ring through electrophilic substitution reaction. This is how aromatic nitro compounds are formed.
We will now consider an aromatic nitro compound and write its reaction with Sn/HCl.

Tin reacts with hydrochloric acid to form Tin(IV) chloride. The ${{H}^{+}}$ ions present react with the nitro group of the aromatic compound.
The oxygen from the nitro group is released in the form of water molecules. In place of oxygen atoms, hydrogen gets substituted leading to formation of aromatic amine.
The reaction is given below:
\[2{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{O}_{2}}\text{ }+\text{ }3Sn\text{ }+\text{ }12HCl\text{ }\to \text{ }2{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}\text{ }+\text{ }3SnC{{l}_{4}}\text{ }+\text{ }4{{H}_{2}}O\]
The product formed is aniline which is an aromatic primary amine.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (A).
Note:
Electrophilic aromatic substitution is an organic reaction in which the hydrogen that is attached to an organic system is replaced by incoming electrophile.
Some of the important electrophilic aromatic substitutions include aromatic nitration, aromatic halogenation, aromatic sulfonation, and alkylation and acylation through Friedel-Crafts reaction mechanism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




