
Refer the given figure of a typical cell and select the option that incorrectly matches the cell modification with its functions?
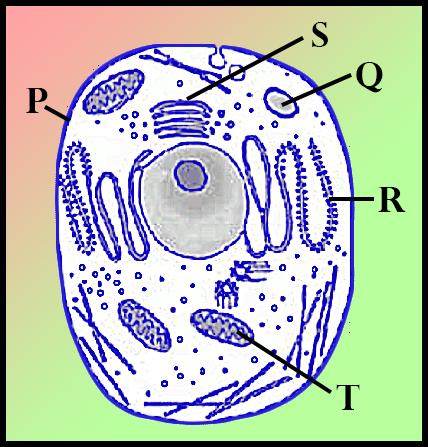
(a) In a free moving cell-like WBC, Structure P will be more elastic and pliable.
(b) A cell that is extensively involved in secreting substances such as enzymes, structures R, and S will be highly developed.
(c) A cell that is extensively involved in protein synthesis, will have a large number of structure S.
(d) A cell that needs lots of energy will have an abundant number of structures T.

Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Animal cells are the essential unit of life in organisms of the kingdom Animalia. they're eukaryotic cells, meaning that they have a true nucleus and specialized structures called organelles that perform different functions.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given diagram, P represents the Plasma membrane, Q represents Lysosome, R represents Rough endoplasmic reticulum, S represents the Golgi apparatus and T represents Mitochondria.
The Golgi apparatus also called the Golgi complex, Golgi body or simply the Golgi is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. The Golgi apparatus is involved in lipid transport and lysosome formation. It is also involved in the transportation of proteins or enzymes formed by the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes are a cell structure that makes protein. Protein is essential for various cell functions, such as repairing damage or directing chemical processes. Ribosomes are found floating within the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(b) A cell that is extensively involved in secreting substances such as enzymes, structures R, and S will be highly developed.’
Additional Information:
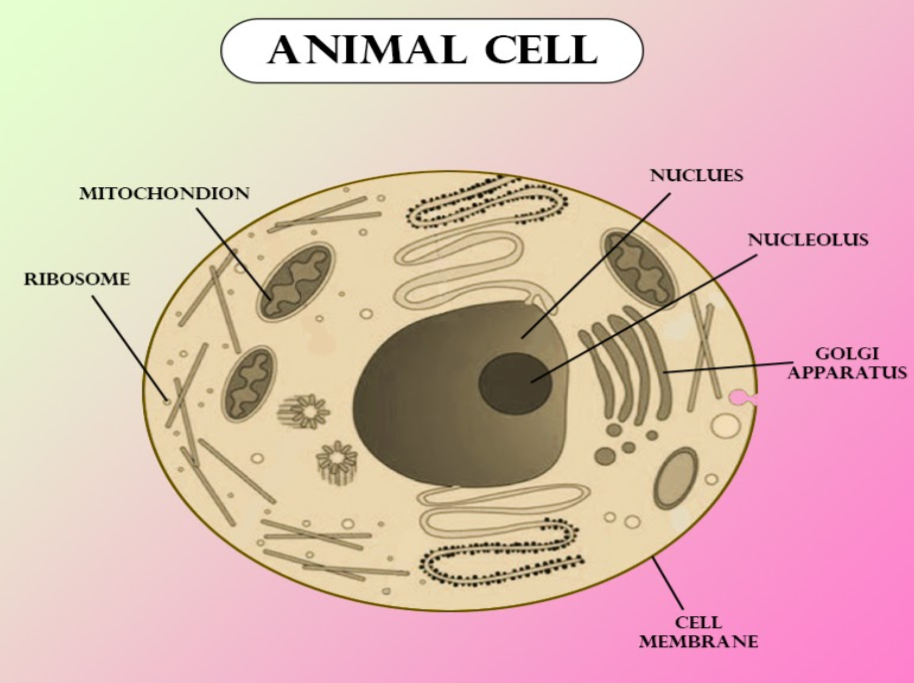
A typical animal cell comprises below-mentioned cell organelles:
Cell Membrane: A thin membrane layer of protein and fats surrounding the cell. Its primary role is to guard the cell against its surroundings.
Nuclear Membrane: A double-membrane structure that surrounds the nucleus and is also known as the nuclear envelope.
Nucleus: It is an organelle that contains several other sub-organelles like nucleolus, nucleosomes, and chromatins. It also contains DNA and other genetic materials.
Centrosome: It is a very small organelle found near to the nucleus which features a thick center with radiating tubules. The centrosomes are where microtubules are produced.
Lysosome (Cell Vesicles): They are round organelles surrounded by a membrane and comprising digestive enzymes that help in digestion, excretion, and within the cell renewal process.
Mitochondria: They are spherical or rod-shaped organelles that have a double membrane. They are the powerhouse of a cell as they play a crucial role in releasing energy.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): This cellular organelle consists of a thin, winding network of membranous sacs originating from the nucleus.
Note: An animal cell is usually irregular with round shape. This is primarily because of the absence of the cell wall, which is the characteristic feature of plant cells. Furthermore, animal cells don't have plastids as animals aren't autotrophs.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given diagram, P represents the Plasma membrane, Q represents Lysosome, R represents Rough endoplasmic reticulum, S represents the Golgi apparatus and T represents Mitochondria.
The Golgi apparatus also called the Golgi complex, Golgi body or simply the Golgi is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. The Golgi apparatus is involved in lipid transport and lysosome formation. It is also involved in the transportation of proteins or enzymes formed by the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes are a cell structure that makes protein. Protein is essential for various cell functions, such as repairing damage or directing chemical processes. Ribosomes are found floating within the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.

So, the correct answer is, ‘(b) A cell that is extensively involved in secreting substances such as enzymes, structures R, and S will be highly developed.’
Additional Information:
A typical animal cell comprises below-mentioned cell organelles:
Cell Membrane: A thin membrane layer of protein and fats surrounding the cell. Its primary role is to guard the cell against its surroundings.
Nuclear Membrane: A double-membrane structure that surrounds the nucleus and is also known as the nuclear envelope.
Nucleus: It is an organelle that contains several other sub-organelles like nucleolus, nucleosomes, and chromatins. It also contains DNA and other genetic materials.
Centrosome: It is a very small organelle found near to the nucleus which features a thick center with radiating tubules. The centrosomes are where microtubules are produced.
Lysosome (Cell Vesicles): They are round organelles surrounded by a membrane and comprising digestive enzymes that help in digestion, excretion, and within the cell renewal process.
Mitochondria: They are spherical or rod-shaped organelles that have a double membrane. They are the powerhouse of a cell as they play a crucial role in releasing energy.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): This cellular organelle consists of a thin, winding network of membranous sacs originating from the nucleus.
Note: An animal cell is usually irregular with round shape. This is primarily because of the absence of the cell wall, which is the characteristic feature of plant cells. Furthermore, animal cells don't have plastids as animals aren't autotrophs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




