
What is the relationship among amplitude, crest, and trough ?
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: In order to answer this question, we will study the basic anatomy of a wave. This way, we can know all the basic components of a wave and also give information about their relation with each other.
Complete answer:
Now, the first thing we start off is by looking at what exactly is a wave? As we all are aware of the wave-particle duality. It states that a particle can also be represented in the form of a wave.Therefore, a wave can be interpreted as a transfer of energy through a point from one point to another. The examples of waves are: the water waves, the sound waves, the radio waves, etc.
Also there are two different forms of waves, a TRANSVERSE wave which moves in the perpendicular direction to the motion of the wave (eg: vibrating guitar string or electromagnetic waves) and a LONGITUDINAL wave which moves in the direction parallel to the motion of the wave (eg: A slinky wave that you push and pull).
Now, we will look at the components of the wave with the help of the following diagram:
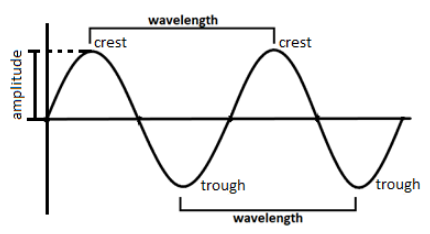
Here, we take an example of a transverse wave for our better understanding. In a transverse wave, the locations where the maximum displacement occurs in the positive or upwards direction is known as CREST and the maximum displacement that occurs in the negative or downward direction is known as the TROUGH. Also, the magnitude of this maximum displacement that occurs in the positive or the negative direction of the axis is the AMPLITUDE of the wave with which it travels. There is one more property of the wave, the WAVELENGTH, which is the distance of one complete wave cycle, i.e., the distance between two consecutive crests or two consecutive troughs is equivalent to one wavelength.
Now looking at the relationship between the crest, the trough and the wavelength, we can write that the amplitude is the magnitude of the wave in the positive direction from the axis at which the crest occurs and similarly, the magnitude of the wave from the axis in the negative direction at which the trough occurs is the wave amplitude in the negative direction.
Note: In longitudinal waves, the areas at which the maximum occurs are known as compressions and Rarefactions similar to that of the crest and the trough in the transverse waves.The magnitude of the displacement between the crest and the trough from the axis is the double of the amplitude of the wave.
Complete answer:
Now, the first thing we start off is by looking at what exactly is a wave? As we all are aware of the wave-particle duality. It states that a particle can also be represented in the form of a wave.Therefore, a wave can be interpreted as a transfer of energy through a point from one point to another. The examples of waves are: the water waves, the sound waves, the radio waves, etc.
Also there are two different forms of waves, a TRANSVERSE wave which moves in the perpendicular direction to the motion of the wave (eg: vibrating guitar string or electromagnetic waves) and a LONGITUDINAL wave which moves in the direction parallel to the motion of the wave (eg: A slinky wave that you push and pull).
Now, we will look at the components of the wave with the help of the following diagram:

Here, we take an example of a transverse wave for our better understanding. In a transverse wave, the locations where the maximum displacement occurs in the positive or upwards direction is known as CREST and the maximum displacement that occurs in the negative or downward direction is known as the TROUGH. Also, the magnitude of this maximum displacement that occurs in the positive or the negative direction of the axis is the AMPLITUDE of the wave with which it travels. There is one more property of the wave, the WAVELENGTH, which is the distance of one complete wave cycle, i.e., the distance between two consecutive crests or two consecutive troughs is equivalent to one wavelength.
Now looking at the relationship between the crest, the trough and the wavelength, we can write that the amplitude is the magnitude of the wave in the positive direction from the axis at which the crest occurs and similarly, the magnitude of the wave from the axis in the negative direction at which the trough occurs is the wave amplitude in the negative direction.
Note: In longitudinal waves, the areas at which the maximum occurs are known as compressions and Rarefactions similar to that of the crest and the trough in the transverse waves.The magnitude of the displacement between the crest and the trough from the axis is the double of the amplitude of the wave.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




