
How many resonance structures does $N_{3}^{-}$ have?
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint: The N is having an atomic number 7 and hence the number of valence electrons in N is 7.
There is a negative charge which adds one electron to the total number of valence electrons present in $N_{3}^{-}$.
Complete answer:
So in the question we are asked how many resonance structures are possible for $N_{3}^{-}$.
We have heard the term resonance structures many times in organic chemistry classes where it is defined as the delocalization of the electrons.
Here also the resonance structures are possible due to the delocalization of the electrons between the atoms.
Resonance structures are generally when we cannot describe all the properties of the molecule with the help of a single structure. In certain polyatomic ions and in molecules we need different Lewis structures to explain the bonding in the structure and to explain the various properties of the molecule and these different structures collectively comprise a hybrid structure. The collective structures are called the resonance structures.
Let’s discuss the steps for drawing the resonance structures by solving this question.
The given ion in the question is the azide ion, which consists of three N atoms.
-First let’s calculate the number of valence electrons in the azide ion.
The atomic number of N is 7 and the electronic configuration is $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{3}}$, hence there is five valence electrons.
The total number of valence electrons in $N_{3}^{-}=3\times \left( 5 \right)+1=16$
Since there is a negative charge in the azide, one electron is added. So there are a total of 16 electrons in $N_{3}^{-}$.
-Now align the single, double and triple bonds between the three atoms and then give the remaining electrons to the atoms in such a way that all the atoms possess octet configuration.
It is very important that in a resonance structure all the atoms should possess the octet configuration.
-After satisfying the octet configuration, calculate the formal charge of each atom.
Now let’s draw the resonance structures for $N_{3}^{-}$.
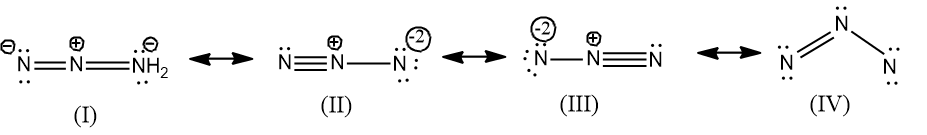
Actually four resonance structures can be drawn for $N_{3}^{-}$, but the possible structures are only three, since in the structure IV, the N in the right most end does not fulfill the criteria of octet configuration. And the structure is not feasible as they don’t have the octet configuration and the bond angle is ${{60}^{\circ }}$hence it will possess a strain.
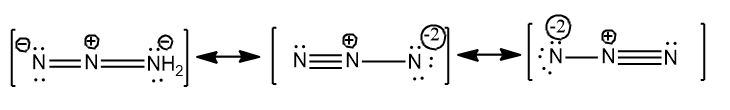
Therefore only three resonance structures are possible for $N_{3}^{-}$$N_{3}^{-}=3\times \left( 5 \right)+1=16$ and they are given below.
Note:
While drawing the resonance structures, two criteria should be satisfied:
-all the atoms should possess octet configuration in the structure.
-the structure is feasible will have the least formal charge for the atoms.
Formal charge of an atom is calculated by the formulae:
$\text{Formal}\,\text{charge=valence}\,{{\text{e}}^{\text{-}}}\text{s-Non-bonding}\,{{\text{e}}^{\text{-}}}\text{s-}\dfrac{\text{Bonding}\,{{\text{e}}^{\text{-}}}\text{s}}{\text{2}}$
There is a negative charge which adds one electron to the total number of valence electrons present in $N_{3}^{-}$.
Complete answer:
So in the question we are asked how many resonance structures are possible for $N_{3}^{-}$.
We have heard the term resonance structures many times in organic chemistry classes where it is defined as the delocalization of the electrons.
Here also the resonance structures are possible due to the delocalization of the electrons between the atoms.
Resonance structures are generally when we cannot describe all the properties of the molecule with the help of a single structure. In certain polyatomic ions and in molecules we need different Lewis structures to explain the bonding in the structure and to explain the various properties of the molecule and these different structures collectively comprise a hybrid structure. The collective structures are called the resonance structures.
Let’s discuss the steps for drawing the resonance structures by solving this question.
The given ion in the question is the azide ion, which consists of three N atoms.
-First let’s calculate the number of valence electrons in the azide ion.
The atomic number of N is 7 and the electronic configuration is $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{3}}$, hence there is five valence electrons.
The total number of valence electrons in $N_{3}^{-}=3\times \left( 5 \right)+1=16$
Since there is a negative charge in the azide, one electron is added. So there are a total of 16 electrons in $N_{3}^{-}$.
-Now align the single, double and triple bonds between the three atoms and then give the remaining electrons to the atoms in such a way that all the atoms possess octet configuration.
It is very important that in a resonance structure all the atoms should possess the octet configuration.
-After satisfying the octet configuration, calculate the formal charge of each atom.
Now let’s draw the resonance structures for $N_{3}^{-}$.

Actually four resonance structures can be drawn for $N_{3}^{-}$, but the possible structures are only three, since in the structure IV, the N in the right most end does not fulfill the criteria of octet configuration. And the structure is not feasible as they don’t have the octet configuration and the bond angle is ${{60}^{\circ }}$hence it will possess a strain.
Therefore only three resonance structures are possible for $N_{3}^{-}$$N_{3}^{-}=3\times \left( 5 \right)+1=16$ and they are given below.

Note:
While drawing the resonance structures, two criteria should be satisfied:
-all the atoms should possess octet configuration in the structure.
-the structure is feasible will have the least formal charge for the atoms.
Formal charge of an atom is calculated by the formulae:
$\text{Formal}\,\text{charge=valence}\,{{\text{e}}^{\text{-}}}\text{s-Non-bonding}\,{{\text{e}}^{\text{-}}}\text{s-}\dfrac{\text{Bonding}\,{{\text{e}}^{\text{-}}}\text{s}}{\text{2}}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




