
Respiratory enzymes are present in
(a)Mitochondria
(b)Chloroplast
(c)Golgi bodies
(d)Lysosome
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: This specific organelle plays a major role in cellular respiration through the production of ATP by using chemical energy found in glucose. Additionally, it is also responsible for generating clusters of iron and sulphur, which are important cofactors of many enzymes.
Complete answer:
The main function of mitochondria during aerobic respiration is to produce ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. The main substrate such as the respiratory enzymes and electron carriers for the electron transport system are located within the inner mitochondrial membrane and the enzymes that are required for the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) are located in the matrix. A pool of chemical energy (ATP, NADH, and ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$ ) are generated in the mitochondrial matrix during Krebs cycle, from the oxidation of pyruvate that is the end product of glycolysis.
The enzymes of the Krebs cycle are basically membrane proteins found within the matrix of the mitochondria except for succinate dehydrogenase which is an integral membrane protein locked to the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Additional information:
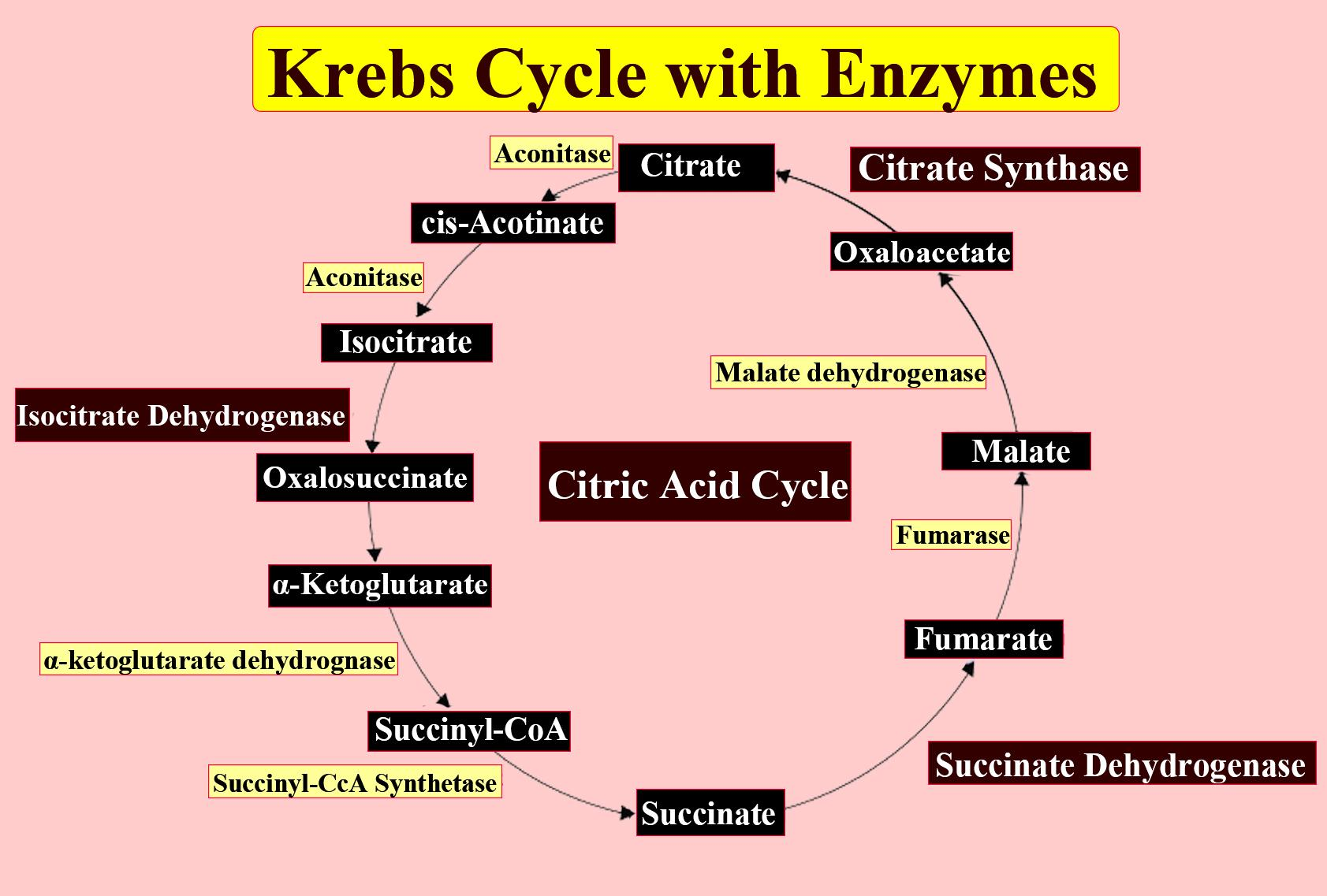
The TCA cycle is the main pathway that provides a unifying point for many metabolites, which feed in at various points. The eight different steps are as follows:
Step 1: Acetyl CoA (two carbon molecule) and oxaloacetate (4 carbon molecule) together form citrate (6 carbon molecule).
Step 2: Citrate is then converted to isocitrate that is an isomer of citrate
Step 3: Alpha-ketoglutarate (a five carbon molecule) is formed after oxidation of citrate which results in the release of carbon dioxide. Also one NADH molecule is formed. Isocitrate dehydrogenase is responsible for catalysing this step.
Step 4: Alpha-ketoglutarate is oxidised to form a 4 carbon molecule that binds to coenzyme A forming succinyl CoA. Under this step a second molecule of NADH is produced and a second molecule of carbon dioxide.
Step 5: Succinyl CoA is converted to succinate (4 carbon molecules) and one GTP molecule is produced.
Step 6: Succinate is then converted into fumarate (4 carbon molecules) and a molecule of ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$ is produced.
Step 7: Fumarate from the above step is converted to malate (another 4 carbon molecules).
Step 8: Malate is converted into oxaloacetate and a third molecule of NADH is produced.
So, the correct answer is ‘Mitochondria’.
Notes: Krebs cycle is regulated in a variety of ways including:
Metabolites: Negative feedback on the enzymes is provided by the products of the cycle that catalyse it. For example, NADH inhibits the majority of the enzymes found in the cycle.
Citrate: It acts like an inhibitor in the case of phosphofructokinase, a key enzyme in glycolysis. This in turn reduces the rate of production of pyruvate and therefore of acetyl-coA.
Calcium: Calcium is also known to accelerate the Krebs cycle by stimulating the link reaction.
Complete answer:
The main function of mitochondria during aerobic respiration is to produce ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. The main substrate such as the respiratory enzymes and electron carriers for the electron transport system are located within the inner mitochondrial membrane and the enzymes that are required for the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) are located in the matrix. A pool of chemical energy (ATP, NADH, and ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$ ) are generated in the mitochondrial matrix during Krebs cycle, from the oxidation of pyruvate that is the end product of glycolysis.
The enzymes of the Krebs cycle are basically membrane proteins found within the matrix of the mitochondria except for succinate dehydrogenase which is an integral membrane protein locked to the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Additional information:
The TCA cycle is the main pathway that provides a unifying point for many metabolites, which feed in at various points. The eight different steps are as follows:
Step 1: Acetyl CoA (two carbon molecule) and oxaloacetate (4 carbon molecule) together form citrate (6 carbon molecule).
Step 2: Citrate is then converted to isocitrate that is an isomer of citrate
Step 3: Alpha-ketoglutarate (a five carbon molecule) is formed after oxidation of citrate which results in the release of carbon dioxide. Also one NADH molecule is formed. Isocitrate dehydrogenase is responsible for catalysing this step.
Step 4: Alpha-ketoglutarate is oxidised to form a 4 carbon molecule that binds to coenzyme A forming succinyl CoA. Under this step a second molecule of NADH is produced and a second molecule of carbon dioxide.
Step 5: Succinyl CoA is converted to succinate (4 carbon molecules) and one GTP molecule is produced.
Step 6: Succinate is then converted into fumarate (4 carbon molecules) and a molecule of ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$ is produced.
Step 7: Fumarate from the above step is converted to malate (another 4 carbon molecules).
Step 8: Malate is converted into oxaloacetate and a third molecule of NADH is produced.

So, the correct answer is ‘Mitochondria’.
Notes: Krebs cycle is regulated in a variety of ways including:
Metabolites: Negative feedback on the enzymes is provided by the products of the cycle that catalyse it. For example, NADH inhibits the majority of the enzymes found in the cycle.
Citrate: It acts like an inhibitor in the case of phosphofructokinase, a key enzyme in glycolysis. This in turn reduces the rate of production of pyruvate and therefore of acetyl-coA.
Calcium: Calcium is also known to accelerate the Krebs cycle by stimulating the link reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




