
Rhizopus reproduces by the method of-
(a) Regeneration
(b) Spore formation
(c) Budding
(d) Fragmentation
Answer
529.5k+ views
Hint: Rhizopus is a saprotrophic fungus that attacks the variety of foodstuffs. Soft rot or leak disease of strawberry, apple, jackfruit, etc. is due to Rhizopus. They reproduce using special single- cell structures that are dispersed through different media. They develop within special structures.
Complete answer:
Rhizopus comes under a class of zygomycetes. This class of fungi reproduces through spore formation. Asexual reproduction occurs through spores. These are the single- celled specialized structures that separate from the organism, get dispersed, and germinate to produce new mycelium after falling on a suitable substrate. The spores produced during asexual reproduction in fungi are formed by mitotic divisions and are thus termed as mitospores. Mitospores are non- motile. They are called sporangiospores as the spores are formed inside sporangia that are borne at the tips of special hyphae called sporangiophores. Sexual reproduction occurs through conjugation. Because of it, these are also called conjugation fungi. Sporangiospores are thin- walled non- motile spores produced endogenously in a sporangium due to favorable conditions, which after liberation gives rise to new mycelium.
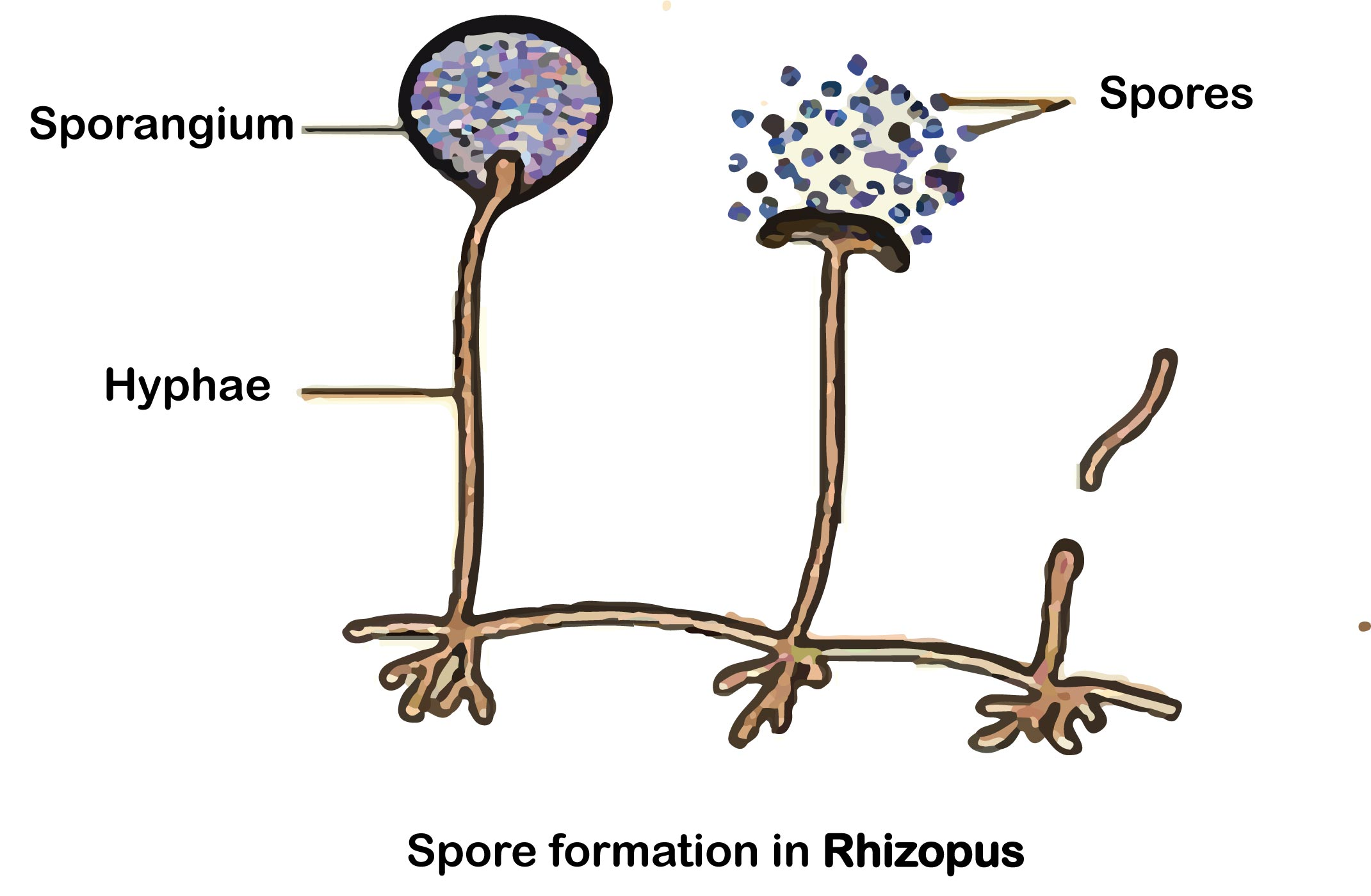
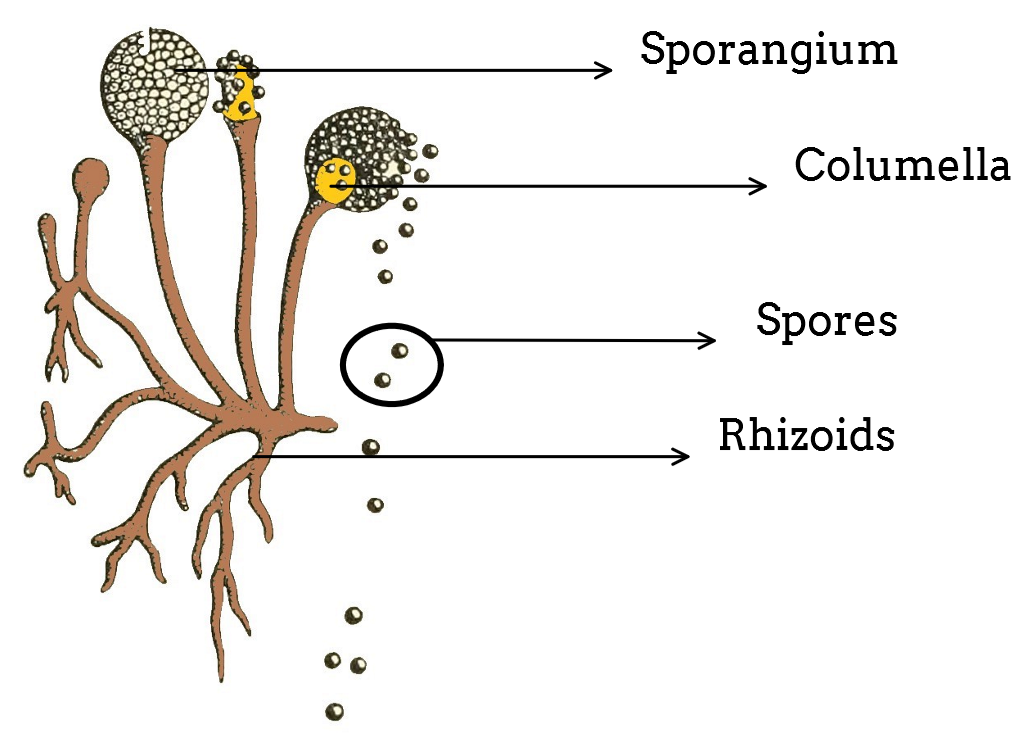
So, the answer is, “Spore formation.”
Additional Information:
- Sexual reproduction produces a resting spore that is a diploid spore and zygospore. Because of the presence of a zygospore, the group of fungi is called zygomycetes.
- Zygospore is the site of meiosis and does not give rise to new mycelium directly. Instead it produces a new sporangium called germ sporangium.
Note: Sporangiospore is a means of asexual reproduction that should not be confused with oospores, ascospores, and basidiospores which are means of sexual reproduction. These sexual spores form different classes of fungi and develop special stalks bearing them.
Complete answer:
Rhizopus comes under a class of zygomycetes. This class of fungi reproduces through spore formation. Asexual reproduction occurs through spores. These are the single- celled specialized structures that separate from the organism, get dispersed, and germinate to produce new mycelium after falling on a suitable substrate. The spores produced during asexual reproduction in fungi are formed by mitotic divisions and are thus termed as mitospores. Mitospores are non- motile. They are called sporangiospores as the spores are formed inside sporangia that are borne at the tips of special hyphae called sporangiophores. Sexual reproduction occurs through conjugation. Because of it, these are also called conjugation fungi. Sporangiospores are thin- walled non- motile spores produced endogenously in a sporangium due to favorable conditions, which after liberation gives rise to new mycelium.


So, the answer is, “Spore formation.”
Additional Information:
- Sexual reproduction produces a resting spore that is a diploid spore and zygospore. Because of the presence of a zygospore, the group of fungi is called zygomycetes.
- Zygospore is the site of meiosis and does not give rise to new mycelium directly. Instead it produces a new sporangium called germ sporangium.
Note: Sporangiospore is a means of asexual reproduction that should not be confused with oospores, ascospores, and basidiospores which are means of sexual reproduction. These sexual spores form different classes of fungi and develop special stalks bearing them.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




