
Rhombus PQRB is inscribed in \[\vartriangle ABC\] such that \[\angle B\] is one of its angles, P, Q and R lie on AB, AC and BC respectively. If \[AB = 12cm\] and \[BC = 6cm\], find the sides of rhombus PQRB.
Answer
580.5k+ views
Hint: We draw a diagram of rhombus in a triangle where the rhombus and triangle have a common angle at vertex B. Consider one side of a rhombus as a variable and find the lengths of sides of the triangle in terms of the sides of the rhombus. Prove the two triangles similar using AAA property and equate ratio of sides of two triangles.
* A rhombus is a quadrilateral having four equal and parallel sides and equal opposite angles.
* If two triangles are similar to each other, then the ratio of corresponding sides of triangles is the same for three corresponding sides.
Complete step by step answer:
Since \[\vartriangle ABC\] and rhombus PQRD have common angle B, then we draw a rhombus inside a triangle having common angle B.
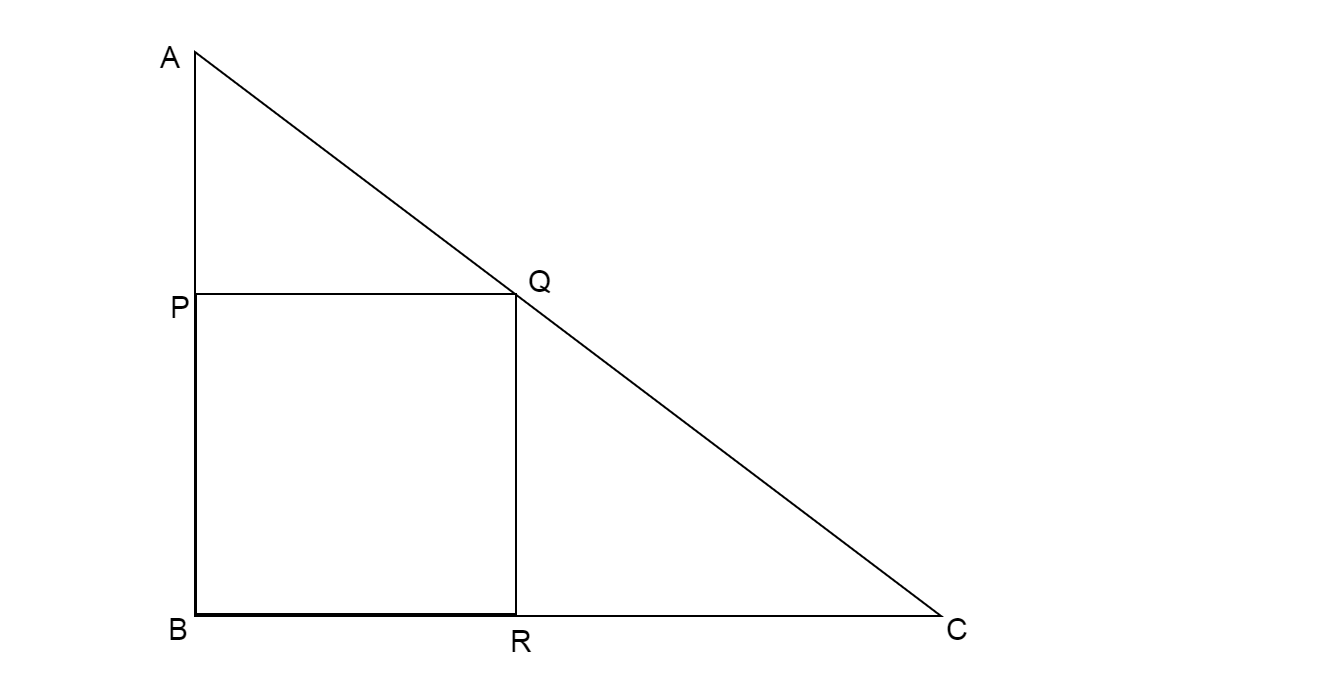
Consider one side of a rhombus as ‘$x$’
Since all sides of rhombus are equal,
\[ \Rightarrow PQ = QR = RB = BP = x\] ………………..… (1)
We know length of sides of triangle \[AB = 12cm\] and \[BC = 6cm\]
\[\because AP = AB - BP\]
\[ \Rightarrow AP = 12 - x\] ……………………….… (2)
Now we show the two triangles, \[\vartriangle ABC,\vartriangle APQ\] similar to each other.
In \[\vartriangle ABC,\vartriangle APQ\]
\[\angle APQ = \angle ABC\] (As they both are corresponding angles formed by parallel lines PQ and BR cut by transversal AB)
\[\angle AQP = \angle ACB\](As they both are corresponding angles formed by parallel lines PQ and BR cut by transversal AC)
\[\angle A = \angle A\](Common angle)
By Angle Angle Angle (AAA) property we can say triangles \[\vartriangle ABC,\vartriangle APQ\] are similar to each other.
Now using the property of similar triangles, we can write the ratio of corresponding sides of triangles equal.
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AP}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{{PQ}}{{BC}}\]
Substitute the values in the fraction from equation (1) and (2)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{12 - x}}{{12}} = \dfrac{x}{6}\]
Multiply both sides by 6
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{12 - x}}{{12}} \times 6 = \dfrac{x}{6} \times 6\]
Cancel the same factors from numerator and denominator on both sides of the equation.
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{12 - x}}{2} = x\]
Cross multiply the equations
\[ \Rightarrow 12 - x = 2x\]
Shift all variables to one side of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow 12 = 2x + x\]
\[ \Rightarrow 12 = 3x\]
Divide both sides of the equation by 3
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{12}}{3} = \dfrac{{3x}}{3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 4 = x\]
Therefore, the value of the side of Rhombus is \[x\] cm.
Also, since all sides of rhombus are equal,
\[PQ = QR = RB = NP = 4cm\]
$\therefore $ The side of Rhombus is 4cm.
Note:
Students might assume the rhombus as square and take angle B as the right angle and apply Pythagoras theorem to find the value of sides. This will yield no result. Keep in mind rhombus does not always have right angles, when it does it becomes a square, which can be a case here but we are not given anything about angles.
* A rhombus is a quadrilateral having four equal and parallel sides and equal opposite angles.
* If two triangles are similar to each other, then the ratio of corresponding sides of triangles is the same for three corresponding sides.
Complete step by step answer:
Since \[\vartriangle ABC\] and rhombus PQRD have common angle B, then we draw a rhombus inside a triangle having common angle B.

Consider one side of a rhombus as ‘$x$’
Since all sides of rhombus are equal,
\[ \Rightarrow PQ = QR = RB = BP = x\] ………………..… (1)
We know length of sides of triangle \[AB = 12cm\] and \[BC = 6cm\]
\[\because AP = AB - BP\]
\[ \Rightarrow AP = 12 - x\] ……………………….… (2)
Now we show the two triangles, \[\vartriangle ABC,\vartriangle APQ\] similar to each other.
In \[\vartriangle ABC,\vartriangle APQ\]
\[\angle APQ = \angle ABC\] (As they both are corresponding angles formed by parallel lines PQ and BR cut by transversal AB)
\[\angle AQP = \angle ACB\](As they both are corresponding angles formed by parallel lines PQ and BR cut by transversal AC)
\[\angle A = \angle A\](Common angle)
By Angle Angle Angle (AAA) property we can say triangles \[\vartriangle ABC,\vartriangle APQ\] are similar to each other.
Now using the property of similar triangles, we can write the ratio of corresponding sides of triangles equal.
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AP}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{{PQ}}{{BC}}\]
Substitute the values in the fraction from equation (1) and (2)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{12 - x}}{{12}} = \dfrac{x}{6}\]
Multiply both sides by 6
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{12 - x}}{{12}} \times 6 = \dfrac{x}{6} \times 6\]
Cancel the same factors from numerator and denominator on both sides of the equation.
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{12 - x}}{2} = x\]
Cross multiply the equations
\[ \Rightarrow 12 - x = 2x\]
Shift all variables to one side of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow 12 = 2x + x\]
\[ \Rightarrow 12 = 3x\]
Divide both sides of the equation by 3
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{12}}{3} = \dfrac{{3x}}{3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 4 = x\]
Therefore, the value of the side of Rhombus is \[x\] cm.
Also, since all sides of rhombus are equal,
\[PQ = QR = RB = NP = 4cm\]
$\therefore $ The side of Rhombus is 4cm.
Note:
Students might assume the rhombus as square and take angle B as the right angle and apply Pythagoras theorem to find the value of sides. This will yield no result. Keep in mind rhombus does not always have right angles, when it does it becomes a square, which can be a case here but we are not given anything about angles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

The Equation xxx + 2 is Satisfied when x is Equal to Class 10 Maths

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What is Contraception List its four different methods class 10 biology CBSE




