
What role does Cytochrome C Oxidase play in Aerobic Respiration?
Answer
497.7k+ views
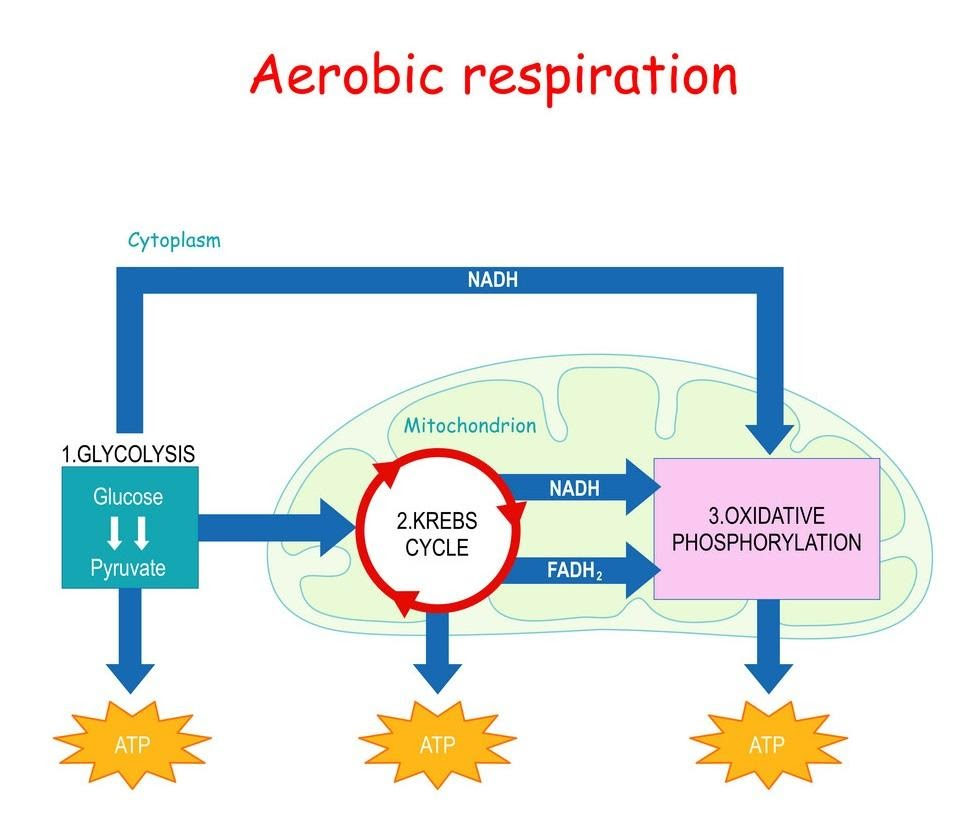
Hint: Cytochrome C Oxidase which is also called as Complex $IV$ of mitochondrial chain (respiratory) plays a crucial role in energy production in Aerobic respiration. It is the last step in the electron transport chain that is ETS. Its major role is to transfer electrons from carbon to oxygen forming water. C to ${O_2}$ form ${H_2}O$. So, Cytochrome C oxidase is a membrane bound enzyme in respiratory chain.
Complete answer-
Cytochrome C Oxidase is an important participant in life supporting the organelle in function of ATP synthesis. Cytochrome C Oxidase is basically composed of thirteen subunits. From which three are copper ions, and also, they have-zinc, magnesium and two heme groups.
Cytochrome C Oxidase as the last step in ETS, is considered as the termination in the inner mitochondrial membrane, where it reduces oxygen (molecular) to free water, which allows ATP production. Meanwhile, copper chaperons are required for assembling the Cytochrome C Oxidase complex.
Let us know about Cytochrome C Oxidase in detail- Cytochrome C Oxidase is a membrane protein large in structure and is encoded by mitochondrial genome. Cytochrome C Oxidase is blocked by the activity of cyanide which results in the blockage of ATP synthesis in the mitochondrial matrix. The leftover ${O_2}$ is consumed by cells and then mediated by cyanide-insensitive quinol also known as alternative oxidase.
Note:
The Cytochrome c Oxidase other than being present in the mitochondrial matrix is also found in bacteria and archaea. There are defects involved in genetic mutations which alter the $COX$ complex which affect the ATP synthesis. Such disorders are detected in early childhood with high energy demands. Such as in organs- heart, muscle and brain. A dysfunctional cytochrome C oxidase is severe if altered.
Complete answer-
Cytochrome C Oxidase is an important participant in life supporting the organelle in function of ATP synthesis. Cytochrome C Oxidase is basically composed of thirteen subunits. From which three are copper ions, and also, they have-zinc, magnesium and two heme groups.
Cytochrome C Oxidase as the last step in ETS, is considered as the termination in the inner mitochondrial membrane, where it reduces oxygen (molecular) to free water, which allows ATP production. Meanwhile, copper chaperons are required for assembling the Cytochrome C Oxidase complex.
Let us know about Cytochrome C Oxidase in detail- Cytochrome C Oxidase is a membrane protein large in structure and is encoded by mitochondrial genome. Cytochrome C Oxidase is blocked by the activity of cyanide which results in the blockage of ATP synthesis in the mitochondrial matrix. The leftover ${O_2}$ is consumed by cells and then mediated by cyanide-insensitive quinol also known as alternative oxidase.

Note:
The Cytochrome c Oxidase other than being present in the mitochondrial matrix is also found in bacteria and archaea. There are defects involved in genetic mutations which alter the $COX$ complex which affect the ATP synthesis. Such disorders are detected in early childhood with high energy demands. Such as in organs- heart, muscle and brain. A dysfunctional cytochrome C oxidase is severe if altered.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




