
Sanger’s reagent is used for the identification of:
A) N-terminal of peptide chain
B) C-terminal of peptide chain
C) Side chain of amino acids
D) Molecular weight of the peptide chain
E) Number of amino acids in peptide chain
Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint: To solve this we must know that Sanger’s reagent is also known as 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene or dinitrofluorobenzene. It is abbreviated as DNBF. It is named after the scientist Frederick Sanger who first used it to detect free amino acids in insulin. Sanger’s reagent can be helpful for the sequencing of proteins.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that Sanger’s reagent is also known as 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene or dinitrofluorobenzene. It is abbreviated as DNBF. It is named after the scientist Sanger who used it to detect free amino acids in insulin.
Sanger’s reagent is prepared by the reaction of 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene with potassium fluoride in nitrobenzene. Sanger’s reagent appears as solid yellow coloured crystals.Sanger’s reagent is used for determining the N-terminal amino acid in polypeptide chains, in particular insulin. Sanger’s reagent reacts with amino groups in amino acids to produce dinitrophenyl amino acids. These dinitrophenyl amino acids are stable under acid hydrolysis conditions that break peptide bonds.
The structure of Sanger’s reagent is as follows:
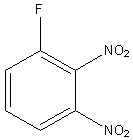
Thus, Sanger’s reagent is used for the identification of N-terminal of peptide chain.
Thus, the correct option is (A) N-terminal of peptide chain.
Note: The pressure applied to a pure solvent so that it does not pass into the given solution by osmosis is known as the osmotic pressure. Remember to calculate the van’t Hoff factor correctly. van’t Hoff factor is the number of ions a compound can form when dissolved in water.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that Sanger’s reagent is also known as 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene or dinitrofluorobenzene. It is abbreviated as DNBF. It is named after the scientist Sanger who used it to detect free amino acids in insulin.
Sanger’s reagent is prepared by the reaction of 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene with potassium fluoride in nitrobenzene. Sanger’s reagent appears as solid yellow coloured crystals.Sanger’s reagent is used for determining the N-terminal amino acid in polypeptide chains, in particular insulin. Sanger’s reagent reacts with amino groups in amino acids to produce dinitrophenyl amino acids. These dinitrophenyl amino acids are stable under acid hydrolysis conditions that break peptide bonds.
The structure of Sanger’s reagent is as follows:

Thus, Sanger’s reagent is used for the identification of N-terminal of peptide chain.
Thus, the correct option is (A) N-terminal of peptide chain.
Note: The pressure applied to a pure solvent so that it does not pass into the given solution by osmosis is known as the osmotic pressure. Remember to calculate the van’t Hoff factor correctly. van’t Hoff factor is the number of ions a compound can form when dissolved in water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




