
Scala tympani is the part of
(A)Internal ear
(B)Middle ear
(C)Endolymphatic sac
(D)Brain
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: Scala tympani is the part of the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. Scala tympani is in the part which is responsible for the sound production and balance of the body. Scala tympani is also known as the Tympanic duct.
Complete answer:
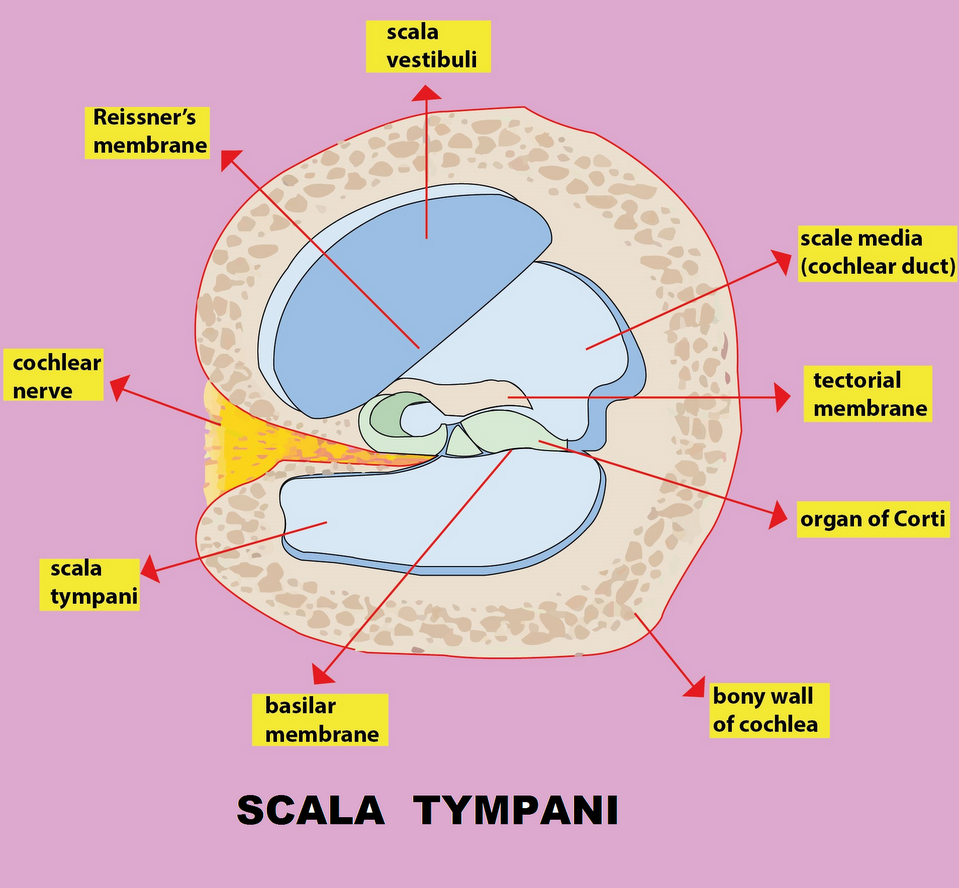
Scala tympani is the perilymph-filled cavities in the inner ear of the human. Perilymph is also known as extracellular fluid. The purpose of the perilymph-filled tympanic duct and the vestibular duct is to transduce the movement of air that causes the eardrum and the ossicles to vibrate, to the movement of liquid and therefore the membrane.
This movement is passed to the organ of Corti which is present inside the cochlear duct,
The movement of the membrane compared to the tectorial membrane causes the stereocilia to bend. They then depolarise and send impulses to the brain via the cochlear nerve. This produces a feeling of sound.
Additional Information: The peripheral hearing system consists of three parts which are the external ear, the center or middle ear, and therefore the inner ear:
The external ear consists of the pinna (also called the auricle), external auditory canal, and eardrum.
The middle ear may be a small, air-filled space containing three tiny bones called the malleus, incus, and stapes but collectively called the ossicles. The malleus connects to the eardrum linking it to the external ear and therefore the stapes (the smallest bone within the body) connects to the internal ear.
The internal or inner ear has both hearing and balance organs. The hearing part of the internal ear is named the cochlea which comes from the Greek word for ‘snail’ due to its distinctive coiled shape. The cochlea, which contains many thousands of sensory cells (called ‘hair cells’), is connected to the central hearing system by the hearing or acoustic nerve. The cochlea is stuffed with special fluids which are important to the method of hearing.
So, the correct answer is ‘Internal ear’.
Note: Hearing loss is also partial or total. This could be a result of injury or damage, genetic disorder, or physiological causes. When hearing impairment is a result of injury or damage to the external ear or middle ear, it's referred to as conductive deafness. When deafness is a result of injury or damage to the internal ear, vestibulocochlear nerve, or brain, it's referred to as sensorineural deafness.
Complete answer:
Scala tympani is the perilymph-filled cavities in the inner ear of the human. Perilymph is also known as extracellular fluid. The purpose of the perilymph-filled tympanic duct and the vestibular duct is to transduce the movement of air that causes the eardrum and the ossicles to vibrate, to the movement of liquid and therefore the membrane.
This movement is passed to the organ of Corti which is present inside the cochlear duct,
The movement of the membrane compared to the tectorial membrane causes the stereocilia to bend. They then depolarise and send impulses to the brain via the cochlear nerve. This produces a feeling of sound.
Additional Information: The peripheral hearing system consists of three parts which are the external ear, the center or middle ear, and therefore the inner ear:
The external ear consists of the pinna (also called the auricle), external auditory canal, and eardrum.
The middle ear may be a small, air-filled space containing three tiny bones called the malleus, incus, and stapes but collectively called the ossicles. The malleus connects to the eardrum linking it to the external ear and therefore the stapes (the smallest bone within the body) connects to the internal ear.
The internal or inner ear has both hearing and balance organs. The hearing part of the internal ear is named the cochlea which comes from the Greek word for ‘snail’ due to its distinctive coiled shape. The cochlea, which contains many thousands of sensory cells (called ‘hair cells’), is connected to the central hearing system by the hearing or acoustic nerve. The cochlea is stuffed with special fluids which are important to the method of hearing.
So, the correct answer is ‘Internal ear’.
Note: Hearing loss is also partial or total. This could be a result of injury or damage, genetic disorder, or physiological causes. When hearing impairment is a result of injury or damage to the external ear or middle ear, it's referred to as conductive deafness. When deafness is a result of injury or damage to the internal ear, vestibulocochlear nerve, or brain, it's referred to as sensorineural deafness.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




