
Sclerenchyma is a simple permanent tissue with thick secondary lignified cell walls. In which of the following cells the secondary cell walls are present?
(a) The cells contain cytoplasm only.
(b) The cells with protoplast.
(c) The cells which are living at maturity.
(d) The cells which are non-living at maturity.
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: It matures with surrounding tissues and provides more permanent support than collenchyma, maintaining the established morphology of plants. The cells are rigid and non-stretchable and are usually found in non-growing regions of plant bodies, such as the bark or mature stems.
Complete answer:
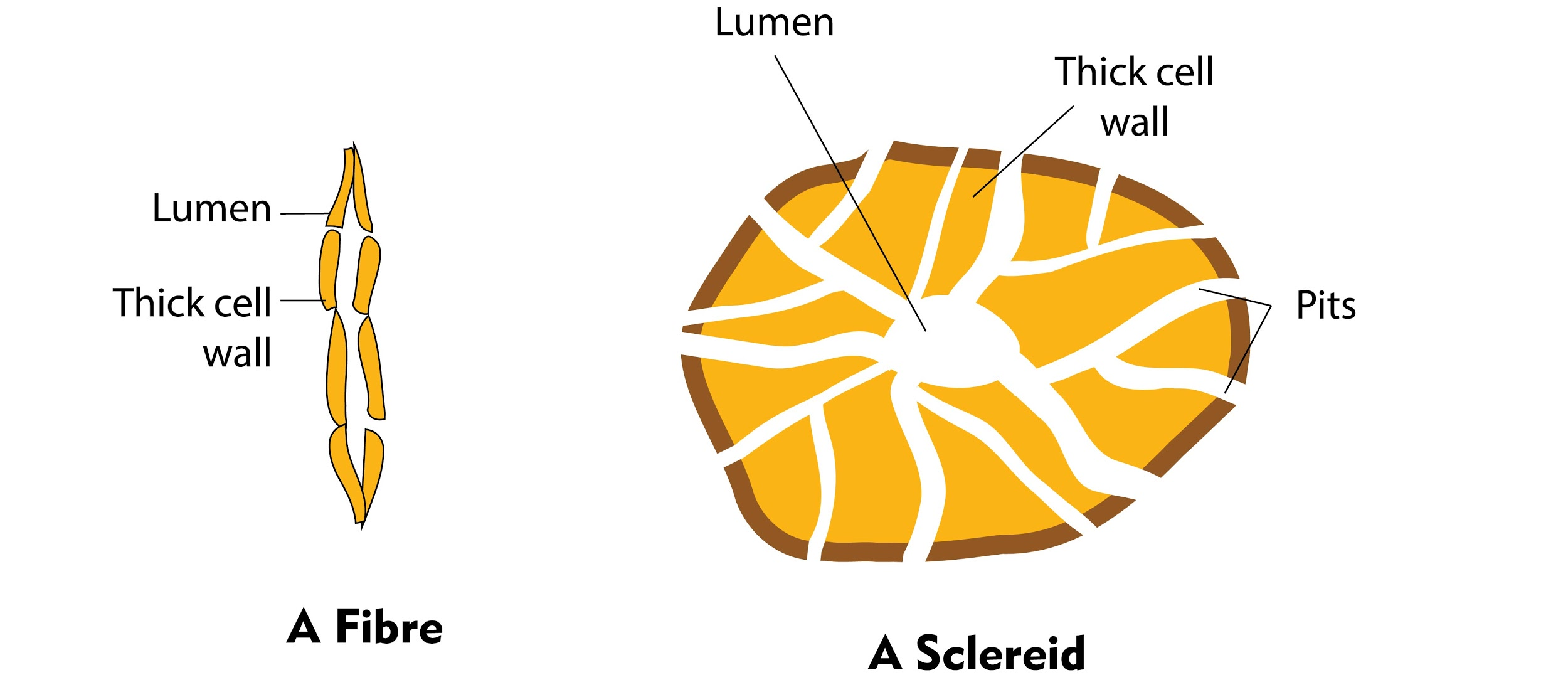
It is a straightforward permanent tissue that represents a group of permanent cells that are structurally and functionally similar for example a gathering of comparable permanent cells that are responsible for a common function. Simple permanent tissues are of three kinds: Parenchyma, Collenchyma, and Sclerenchyma. Sclerenchyma is a thick-walled, lignified permanent tissue that is portrayed by the absence of a living protoplast. Consequently, it is viewed as dead. Its main function is mechanical support.
Additional Information: The support of sclerenchyma is involved in sclereids and filaments. This tissue decreases shrinking; however, it is vigorously expensive for the plant to make. Sclerenchyma develops with the encompassing tissues and offers more permanent support than collenchyma, keeping up the setup morphology of the plant. Fibers have tapered ends, can be numerous centimeters long, and involve the pack tops and sheaths normal for vascular groups, particularly in monocotyledonous plants. The bundle sheath may form bundle sheath expansions by spreading to the epidermis, particularly in grass leaves.
So, the correct answer is ‘The cells which are non-livings at maturity’.
Note: When sclerenchyma tissue is mature, then it is formed by dead cells that have heavily thickened walls containing lignin and high cellulose content (60%–80%), and it serves the function of providing structural support in plants. The sclerenchyma cells possess two kinds of cell walls: primary and secondary walls. The secondary wall is very thick and highly lignified (15%–35%) and imparts a great rigidity and hardness to the cell and tissue.
Complete answer:
It is a straightforward permanent tissue that represents a group of permanent cells that are structurally and functionally similar for example a gathering of comparable permanent cells that are responsible for a common function. Simple permanent tissues are of three kinds: Parenchyma, Collenchyma, and Sclerenchyma. Sclerenchyma is a thick-walled, lignified permanent tissue that is portrayed by the absence of a living protoplast. Consequently, it is viewed as dead. Its main function is mechanical support.
Additional Information: The support of sclerenchyma is involved in sclereids and filaments. This tissue decreases shrinking; however, it is vigorously expensive for the plant to make. Sclerenchyma develops with the encompassing tissues and offers more permanent support than collenchyma, keeping up the setup morphology of the plant. Fibers have tapered ends, can be numerous centimeters long, and involve the pack tops and sheaths normal for vascular groups, particularly in monocotyledonous plants. The bundle sheath may form bundle sheath expansions by spreading to the epidermis, particularly in grass leaves.
So, the correct answer is ‘The cells which are non-livings at maturity’.
Note: When sclerenchyma tissue is mature, then it is formed by dead cells that have heavily thickened walls containing lignin and high cellulose content (60%–80%), and it serves the function of providing structural support in plants. The sclerenchyma cells possess two kinds of cell walls: primary and secondary walls. The secondary wall is very thick and highly lignified (15%–35%) and imparts a great rigidity and hardness to the cell and tissue.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




