
Secondary constriction is also called as
(a)Nucleo-chromosome
(b)Nucleolar organizer
(c)SAT chromosome
(d)None of the above
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: These are the chromosomal regions crucial for the formation of the nucleolus and located on the short arms of the chromosomes. Secondary constrictions are the constricted or the narrow region found at any point of the chromosome other than that of the centromere, also known as primary constriction.
Complete answer:
Secondary constriction is also called the nucleolar organizers. Secondary constrictions are the narrow areas and consist of two types: joints and the Nucleolar Organizing Region (NOR). Joints are areas involved in the breaking and fusion of chromosome segments while the NOR or nucleolar organizer region in secondary constriction is capable of forming nucleolus in the interphase of the cell cycle
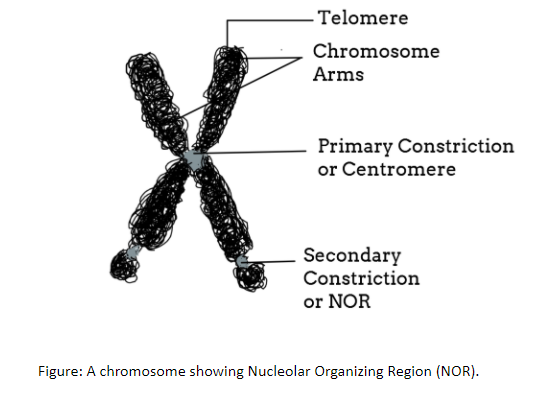
Additional Information: -In 1969, Herbert Lubs discovered secondary constriction on the bottom end of the long arm of the X chromosome.
-‘Chromosomal satellite’ is the term given to that part of the end of the chromosome that is separated from the rest of the chromosome by a secondary constriction.
-Due to secondary constriction, a knob-like structure is formed at the end of the chromosome called a satellite chromosome (SAT chromosome).
- In a non-dividing cell, the nucleolar organizer is associated with the nucleolus in the assembly of ribosomes.
-The nucleolar organizer consists of numerous tandem (one in front of the other) repeats of a single gene
-The nucleolus is a distinct structure present in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Primarily, it participates in assembling the ribosomes, alteration of tRNA, and sensing cellular stress.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Nucleolar organizer.’
Note: The nucleolus is a distinct structure present in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Primarily, it participates in assembling the ribosomes, alteration of tRNA, and sensing cellular stress. The nucleolus is composed of RNA and proteins.
Complete answer:
Secondary constriction is also called the nucleolar organizers. Secondary constrictions are the narrow areas and consist of two types: joints and the Nucleolar Organizing Region (NOR). Joints are areas involved in the breaking and fusion of chromosome segments while the NOR or nucleolar organizer region in secondary constriction is capable of forming nucleolus in the interphase of the cell cycle

Additional Information: -In 1969, Herbert Lubs discovered secondary constriction on the bottom end of the long arm of the X chromosome.
-‘Chromosomal satellite’ is the term given to that part of the end of the chromosome that is separated from the rest of the chromosome by a secondary constriction.
-Due to secondary constriction, a knob-like structure is formed at the end of the chromosome called a satellite chromosome (SAT chromosome).
- In a non-dividing cell, the nucleolar organizer is associated with the nucleolus in the assembly of ribosomes.
-The nucleolar organizer consists of numerous tandem (one in front of the other) repeats of a single gene
-The nucleolus is a distinct structure present in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Primarily, it participates in assembling the ribosomes, alteration of tRNA, and sensing cellular stress.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Nucleolar organizer.’
Note: The nucleolus is a distinct structure present in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Primarily, it participates in assembling the ribosomes, alteration of tRNA, and sensing cellular stress. The nucleolus is composed of RNA and proteins.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




