
Select the correct option:
Identify A and B in the given figure and select the correct option.

(a) Grana thylakoid, Stroma thylakoid
(b) Stroma thylakoid, Grana thylakoid
(c) Granum, Stroma
(d) Stroma, Granum

Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: The structure involved in photosynthesis is the image depicted in the question. This double-membrane enclosed organelle has a third membrane system called thylakoids, which can be two more forms, one is also known as integral thylakoid while the other is its disc stack.
Complete step by step answer:
Two structures of the chloroplast are grana and stroma. Grana is composed of a disc-like plate that is embedded inside the stroma, while on the other hand a jelly-like colorless matrix present inside the chloroplast is called matrix. A thylakoid is a compartment that is membrane-bound inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. The area between the membranes of the thylakoid is called the thylakoid lumen. They are the site of photosynthesis reactions that are light-dependent. Grana is related by integral or stroma thylakoids that combine the stacks to create a single functional compartment.
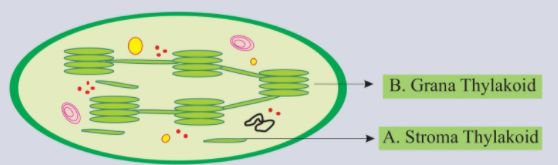
So, the correct answer is, ‘Stroma thylakoid, Grana thylakoid’.
Additional information: As it is present in the stroma, the Stroma thylakoid traps light energy for photosynthesis. Grana thylakoids (thylakoid stacks are referred to as grana).
- In botany, stroma refers to the colorless fluid inside the chloroplast covering the grana.
Grana (stacks of thylakoid) and sub- organelles or daughter cells are inside the stroma, where photosynthesis starts before the chemical changes in the stroma are completed.
- A granum (plural grana) is a thylakoid stack of discs. Chloroplasts may have between 10 and 100 grana. Grana are connected by stroma thylakoids. The distinct protein structure of Grana thylakoids and stroma thylakoids can be distinguished. Grana contributes to the wide surface area to volume ratio for chloroplasts.
Note: Photosynthesis occurs in the subcellular organelles known as the chloroplast in photosynthetic eukaryotes. It is the mechanism by which light energy is converted into chemical energy, resulting in the creation of organic compounds rich in oxygen and energy. Endosymbiotic theory suggests that chloroplasts and mitochondria (energy-producing organelles in eukaryotic cells) are descended from such organisms; photosynthetic cyanobacteria are free-living close relatives of chloroplasts.
Complete step by step answer:
Two structures of the chloroplast are grana and stroma. Grana is composed of a disc-like plate that is embedded inside the stroma, while on the other hand a jelly-like colorless matrix present inside the chloroplast is called matrix. A thylakoid is a compartment that is membrane-bound inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. The area between the membranes of the thylakoid is called the thylakoid lumen. They are the site of photosynthesis reactions that are light-dependent. Grana is related by integral or stroma thylakoids that combine the stacks to create a single functional compartment.

So, the correct answer is, ‘Stroma thylakoid, Grana thylakoid’.
Additional information: As it is present in the stroma, the Stroma thylakoid traps light energy for photosynthesis. Grana thylakoids (thylakoid stacks are referred to as grana).
- In botany, stroma refers to the colorless fluid inside the chloroplast covering the grana.
Grana (stacks of thylakoid) and sub- organelles or daughter cells are inside the stroma, where photosynthesis starts before the chemical changes in the stroma are completed.
- A granum (plural grana) is a thylakoid stack of discs. Chloroplasts may have between 10 and 100 grana. Grana are connected by stroma thylakoids. The distinct protein structure of Grana thylakoids and stroma thylakoids can be distinguished. Grana contributes to the wide surface area to volume ratio for chloroplasts.
Note: Photosynthesis occurs in the subcellular organelles known as the chloroplast in photosynthetic eukaryotes. It is the mechanism by which light energy is converted into chemical energy, resulting in the creation of organic compounds rich in oxygen and energy. Endosymbiotic theory suggests that chloroplasts and mitochondria (energy-producing organelles in eukaryotic cells) are descended from such organisms; photosynthetic cyanobacteria are free-living close relatives of chloroplasts.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




