
Select the correct option representing the excretory organs present in (i) earthworm, (ii) centipede, (iii) prawn, and (iv) flatworm.
(a) (i) Malpigian tubules (ii) Flame cell (iii) Nephridia (iv) Green gland
(b) (i) Flame cell (ii) Green gland (iii) Malpighian tubules (iv) Nephridia
(c) (i) Nephridia (ii) Malpigian tubules (iii) Green gland (iv) Flame cell
(d) (i) Green gland (ii) Nephridia (iii) Flame cell (iv) Malpigian tubules
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: Nephridia is present in the organism that is called a farmer’s friend. Malpighian tubules are present in the predatory arthropods of the class Chilopoda. The green gland is present in small aquatic crustaceans that have an exoskeleton and ten legs. The flame cell is found in the Platyhelminthes group.
Complete step by step answer:
- In earthworms, the primary waste materials are carbon dioxide and nitrogenous waste. By the mechanism of diffusion, carbon dioxide is excreted out of the body through its moist skin. Special excretory organs called nephridia excrete the nitrogenous waste out of the body.
- The excretory mechanism consists of a pair of Malpighian tubules in the centipede, extending from the midgut to the hindgut. Waste at the posterior end leaves the body via the anus.
- Prawn excretory organs are known as green or antennal glands. Because of their color, they are called green glands and the antenna gland is located at the base of the second antenna.
- A nephridium is used as an excretory organ by invertebrates such as flatworms. A ciliated flame cell is the tip of each blind tubule of the nephridium. Solutes are reabsorbed and returned to body fluids as the fluid moves down the tubule.
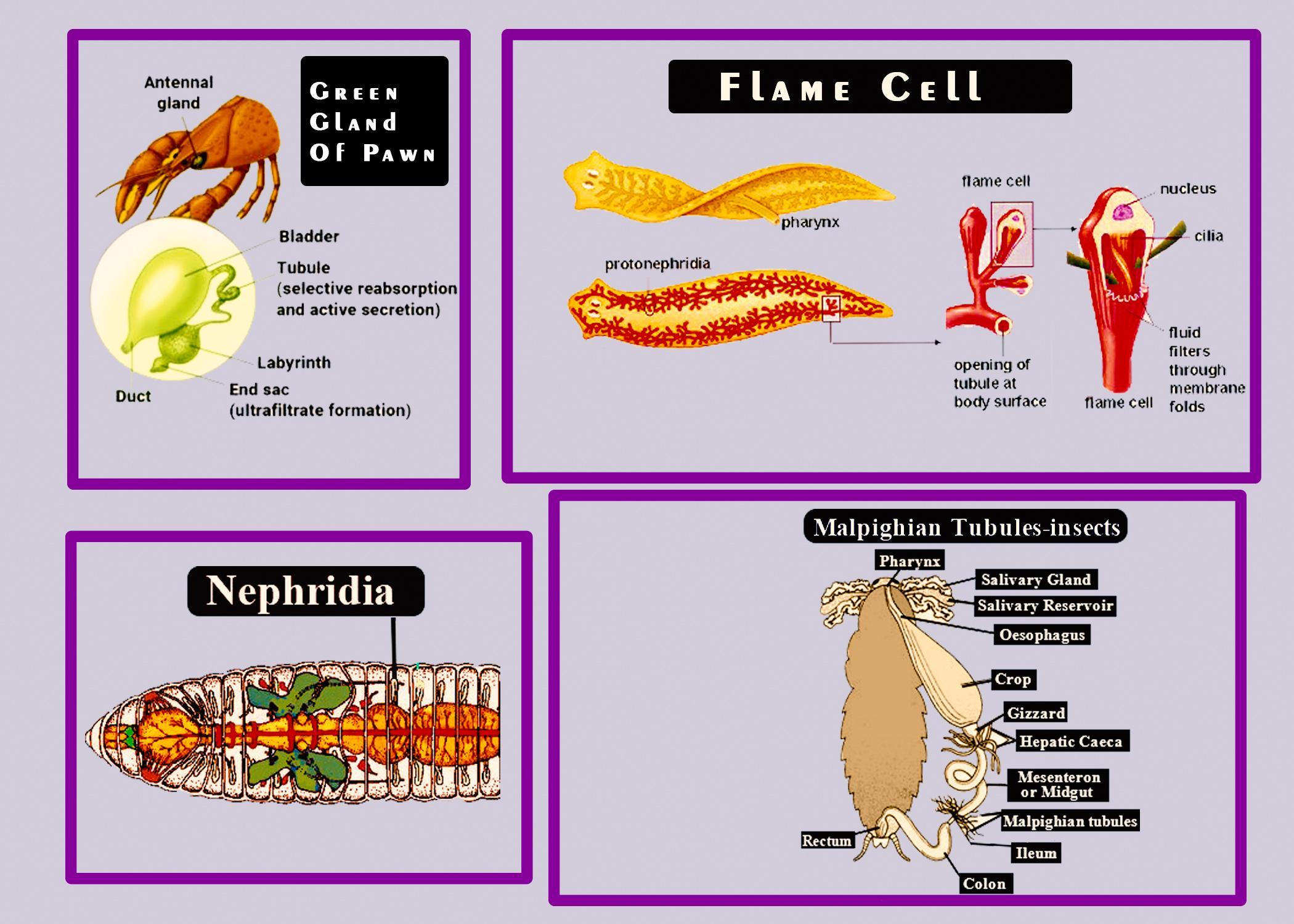
- There is a pair of nephridia on each segment of the earthworm. The fact that they have a tubule of cilia is identical to flame cells. Through a pore called the nephridiopore, excretion occurs.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(i) Nephridia (ii) Malpigian tubules (iii) Green gland (iv) Flame cell’.
Note: Planaria are freshwater-living flatworms. Their excretory system consists of two tubules attached to a duct system that is strongly branched. As they have a cluster of cilia that looks like a flickering flame when seen under the microscope, the cells in the tubules are called flame cells (or protonephridia) . Via excretory pores that open on the surface of the body, the cilia propel waste matter down the tubules and out of the body; cilia also draw water from the interstitial fluid, enabling filtration. Through reabsorption, any precious metabolites are recovered. Flame cells, including parasitic tapeworms and free-living planarians, are found in flatworms. They preserve the osmotic equilibrium of the organism as well.
Malpighian tubules are found lining the intestines of certain arthropod species. They are typically found in pairs, and insect species differ in the number of tubules. For osmotic balance reabsorption and maintenance, Malpighian tubules are convoluted, which lifts the region of their surface and are lined with microvilli.
'Green Gland' is one of the pairs of excretory organs emptying at the base of the antennae on either side of the head area of decapod crustaceans. Prawns have green excretion glands.
Complete step by step answer:
- In earthworms, the primary waste materials are carbon dioxide and nitrogenous waste. By the mechanism of diffusion, carbon dioxide is excreted out of the body through its moist skin. Special excretory organs called nephridia excrete the nitrogenous waste out of the body.
- The excretory mechanism consists of a pair of Malpighian tubules in the centipede, extending from the midgut to the hindgut. Waste at the posterior end leaves the body via the anus.
- Prawn excretory organs are known as green or antennal glands. Because of their color, they are called green glands and the antenna gland is located at the base of the second antenna.
- A nephridium is used as an excretory organ by invertebrates such as flatworms. A ciliated flame cell is the tip of each blind tubule of the nephridium. Solutes are reabsorbed and returned to body fluids as the fluid moves down the tubule.

- There is a pair of nephridia on each segment of the earthworm. The fact that they have a tubule of cilia is identical to flame cells. Through a pore called the nephridiopore, excretion occurs.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(i) Nephridia (ii) Malpigian tubules (iii) Green gland (iv) Flame cell’.
Note: Planaria are freshwater-living flatworms. Their excretory system consists of two tubules attached to a duct system that is strongly branched. As they have a cluster of cilia that looks like a flickering flame when seen under the microscope, the cells in the tubules are called flame cells (or protonephridia) . Via excretory pores that open on the surface of the body, the cilia propel waste matter down the tubules and out of the body; cilia also draw water from the interstitial fluid, enabling filtration. Through reabsorption, any precious metabolites are recovered. Flame cells, including parasitic tapeworms and free-living planarians, are found in flatworms. They preserve the osmotic equilibrium of the organism as well.
Malpighian tubules are found lining the intestines of certain arthropod species. They are typically found in pairs, and insect species differ in the number of tubules. For osmotic balance reabsorption and maintenance, Malpighian tubules are convoluted, which lifts the region of their surface and are lined with microvilli.
'Green Gland' is one of the pairs of excretory organs emptying at the base of the antennae on either side of the head area of decapod crustaceans. Prawns have green excretion glands.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




