
Select the incorrect statement(s) about cilia and flagella
(a)Cilia and flagella give a cartwheel appearance
(b)Axoneme is made up of nine microtubule triplets at the periphery
(c)They show ‘9+2’ microtubule organization
(d)Both (a) and (b)
Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint Cilia and flagella are cell organelles that are structurally alike but dissimilar within the length and functions. Cilia are found in organisms like paramecium whereas flagella are often present in bacteria and sperm cells. Cilia are shorter and numerous than flagella.
Complete answer:
Cilia and flagella are the foremost common organelles for locomotion in unicellular organisms. Organisms containing cilia can move faster and more proficiently. Most prokaryotic and eukaryotic microorganisms contain flagella, but they do vary from each other structurally and functionally. Although the 9 + 2 pattern is the basic pattern of nearing all cilia and flagella, the axonemes of certain protozoans and a few insect sperm show some interesting variations. The simplest axoneme, comprising three doublet microtubules and none central singlets (3 + 0) is present in Daplius, a parasitic protozoan. Its flagellum beats slowly (1.5 beats/s) during a helical pattern. Other axonemes contain 6 + 0 or 9 + 0 arrangements of microtubules. These unusual cilia and flagella, which are all motile, exhibit that the central pair of singlet microtubules isn't needed for axonemal beating which means fewer than nine outer doublets can sustain motility, but at a lower frequency. The axoneme is the apical part of cilia and flagella where the structure comprises only A and B microtubules within the periphery. The C microtubule from the basal body resists at the cell membrane alone.
Additional information:
Cilia Overview are-
-The organelle cilia are present in eukaryotic cells.
-They are of two types: motile cilia and non-motile cilia.
- The non-motile cilia are called primary cilia and work as sensory organelles.
- Cilia are structurally identical to flagella.
- Microorganisms like paramecium comprise cilia for motion.
Flagella Overview are-
1. They help an organism in movement.
2. They function as sensory organs to recognize temperature and pH changes.
3. Some eukaryotes utilized flagellum to enhance reproduction rates.
4. Recent scientists have evidenced that flagella are also utilized as a secretory organelle. For example in Chlamydomonas.
So, the correct answer is 'Axoneme is made up of nine microtubule triplets at the periphery'.
Note: The difference between cilia and flagella is quite apparent. They vary structurally and possess several patterns of movement. There also are different variations of cilia and flagella that perform various functions. Despite their different names, flagella and cilia have an equivalent axoneme structure, including nine doublet microtubules arranged during a revolve around two central singlet microtubules.
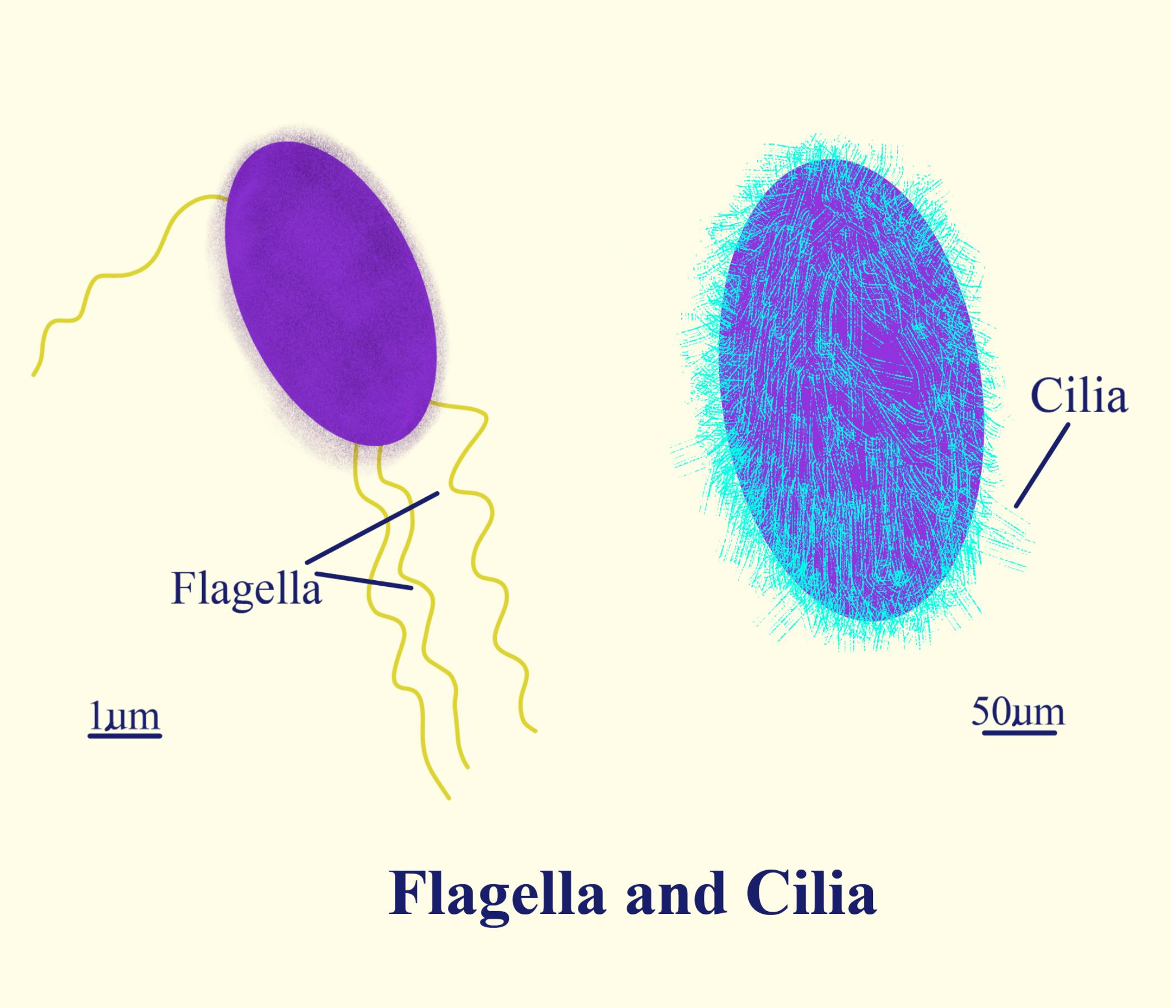
Complete answer:
Cilia and flagella are the foremost common organelles for locomotion in unicellular organisms. Organisms containing cilia can move faster and more proficiently. Most prokaryotic and eukaryotic microorganisms contain flagella, but they do vary from each other structurally and functionally. Although the 9 + 2 pattern is the basic pattern of nearing all cilia and flagella, the axonemes of certain protozoans and a few insect sperm show some interesting variations. The simplest axoneme, comprising three doublet microtubules and none central singlets (3 + 0) is present in Daplius, a parasitic protozoan. Its flagellum beats slowly (1.5 beats/s) during a helical pattern. Other axonemes contain 6 + 0 or 9 + 0 arrangements of microtubules. These unusual cilia and flagella, which are all motile, exhibit that the central pair of singlet microtubules isn't needed for axonemal beating which means fewer than nine outer doublets can sustain motility, but at a lower frequency. The axoneme is the apical part of cilia and flagella where the structure comprises only A and B microtubules within the periphery. The C microtubule from the basal body resists at the cell membrane alone.
Additional information:
Cilia Overview are-
-The organelle cilia are present in eukaryotic cells.
-They are of two types: motile cilia and non-motile cilia.
- The non-motile cilia are called primary cilia and work as sensory organelles.
- Cilia are structurally identical to flagella.
- Microorganisms like paramecium comprise cilia for motion.
Flagella Overview are-
1. They help an organism in movement.
2. They function as sensory organs to recognize temperature and pH changes.
3. Some eukaryotes utilized flagellum to enhance reproduction rates.
4. Recent scientists have evidenced that flagella are also utilized as a secretory organelle. For example in Chlamydomonas.
So, the correct answer is 'Axoneme is made up of nine microtubule triplets at the periphery'.
Note: The difference between cilia and flagella is quite apparent. They vary structurally and possess several patterns of movement. There also are different variations of cilia and flagella that perform various functions. Despite their different names, flagella and cilia have an equivalent axoneme structure, including nine doublet microtubules arranged during a revolve around two central singlet microtubules.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




