
What is the shape of the wavefront in each of the following cases :
A) Light diverging from a point source.
B) Light emerging from a convex lens when a point source is placed at its focus.
C) The portion of the wavefront of light from a distance star intercepted by the earth.
Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint: A wavefront is a line or surface within a two or three dimensional medium through which waves are passing, being the locus of all adjacent points at which the disturbances are in phase.
Complete step by step answer:
The wavefront is defined as the locus of all points where the wave has the same phase of the sinusoid.
The term wavefront is meaningful for fields that, at each point, vary sinusoidally in time with single temporal frequency.
Wave Fronts usually move with time.
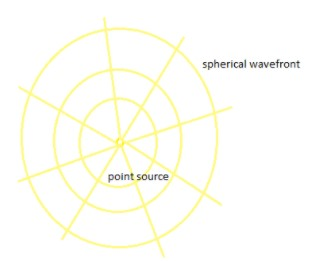
Case (A) - Light diverging from a point source :- The point source emits the spherical wavefront as the light diverges from a point source in all directions.
Case (B)- Light emerging from a convex lens when a point source is placed at its focus :- The shape of the wavefront in case of a light emerging out of a convex lens, when a point source is placed at its focus is a plane.
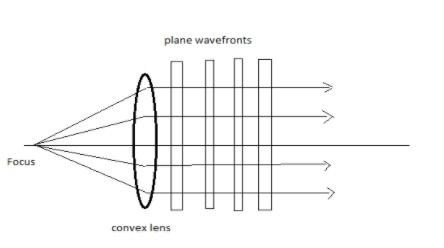
The plane wavefront consists of parallel grids.
Case (C)- The portion of the wavefront of light from a distance star intercepted by the earth :- Since a small area on the surface of a large sphere is nearly planar, so the portion of the wavefront of light from a distance star intercepted by the earth is a plane wavefront.
Note: At large distances from a small source in a uniform medium, the fronts are small parts of a sphere of very large radius and they can be considered as planes.
The sunlight from the sun reaches earth with a plane wavefront.
Complete step by step answer:
The wavefront is defined as the locus of all points where the wave has the same phase of the sinusoid.
The term wavefront is meaningful for fields that, at each point, vary sinusoidally in time with single temporal frequency.
Wave Fronts usually move with time.
Case (A) - Light diverging from a point source :- The point source emits the spherical wavefront as the light diverges from a point source in all directions.

Case (B)- Light emerging from a convex lens when a point source is placed at its focus :- The shape of the wavefront in case of a light emerging out of a convex lens, when a point source is placed at its focus is a plane.

The plane wavefront consists of parallel grids.
Case (C)- The portion of the wavefront of light from a distance star intercepted by the earth :- Since a small area on the surface of a large sphere is nearly planar, so the portion of the wavefront of light from a distance star intercepted by the earth is a plane wavefront.
Note: At large distances from a small source in a uniform medium, the fronts are small parts of a sphere of very large radius and they can be considered as planes.
The sunlight from the sun reaches earth with a plane wavefront.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




