
Shaving mirrors are:
A. Convex mirrors
B. Concave mirrors
C. Plane mirrors
D. None of these
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: The concave mirror gives the magnified image of an object. The convex mirror gives the image smaller than the object. Whereas the plane mirror gives an image of the same size as an object.
Complete step by step answer:
Commonly, there are three types of mirrors. They are the concave mirror, convex mirror, and plane mirror. Concave and convex mirrors have a spherical surface that gives magnified and diminished images of an object respectively. But plane mirrors have a flat surface that gives an image of the actual size of an object but reversed from right to left. Each type of mirror has its own applications. For shaving, we prefer to view the magnified clear image. Concerning the properties of these three mirrors, we can use a concave mirror for shaving.
Therefore, shaving mirrors are concave mirrors.
Additional information:
Concave and convex mirrors are called spherical mirrors. Because the reflecting surface of these mirrors is spherical. To learn about the spherical surface of the mirror, we should learn some important points related to the surface.
1.Vertex or midpoint: It is the midpoint in the spherical surface. Object to the vertex is the smallest distance between the mirror and object than the edges. From this point, we can understand that the concave mirror is curved inwards.
2.Centre of curvature: On considering the spherical surface as an imaginary sphere, we get a centre point that is called the centre of curvature. The distance between the centre of curvature and all the points in the reflecting surface gives the same length.
3.Principal focus: If we draw the line connecting the vertex and the centre of curvature, the principal focus is the midpoint of the line.
4.Focal length$f$: Distance between the mirror and the principal focus. To find the Focal length,
\[\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{{{d_ \circ }}} + \dfrac{1}{{{d_i}}}\].
Where, ${d_o}$=distance between the object from the mirror
${d_i}$= distance between the image and the mirror
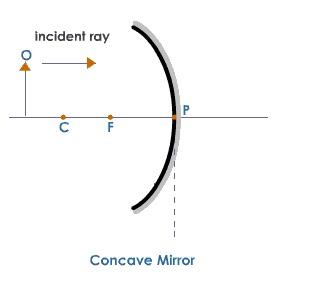
The nature of the image in the concave mirror can be found in three cases.
case1: When the object is at the centre of curvature, it gives the same size as an object, real and an inverted image
case2: When the object is between the centre of curvature and principal focus, it gives magnified, real and an inverted image.
case3: When the object is farther from the mirror than the centre of curvature, it gives small, real, and an inverted image.
case4: When the object is inside the principal focus, it gives the magnified, virtual, and erect image. The focal length for the virtual image gives negative value, this indicates that the image is behind the mirror.
Note:
To know the nature of the mirror, we should know the properties. While using a shaving mirror, the object is either between the principal focus and centre of curvature or farther from the centre of curvature.
Complete step by step answer:
Commonly, there are three types of mirrors. They are the concave mirror, convex mirror, and plane mirror. Concave and convex mirrors have a spherical surface that gives magnified and diminished images of an object respectively. But plane mirrors have a flat surface that gives an image of the actual size of an object but reversed from right to left. Each type of mirror has its own applications. For shaving, we prefer to view the magnified clear image. Concerning the properties of these three mirrors, we can use a concave mirror for shaving.
Therefore, shaving mirrors are concave mirrors.
Additional information:
Concave and convex mirrors are called spherical mirrors. Because the reflecting surface of these mirrors is spherical. To learn about the spherical surface of the mirror, we should learn some important points related to the surface.
1.Vertex or midpoint: It is the midpoint in the spherical surface. Object to the vertex is the smallest distance between the mirror and object than the edges. From this point, we can understand that the concave mirror is curved inwards.
2.Centre of curvature: On considering the spherical surface as an imaginary sphere, we get a centre point that is called the centre of curvature. The distance between the centre of curvature and all the points in the reflecting surface gives the same length.
3.Principal focus: If we draw the line connecting the vertex and the centre of curvature, the principal focus is the midpoint of the line.
4.Focal length$f$: Distance between the mirror and the principal focus. To find the Focal length,
\[\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{{{d_ \circ }}} + \dfrac{1}{{{d_i}}}\].
Where, ${d_o}$=distance between the object from the mirror
${d_i}$= distance between the image and the mirror

The nature of the image in the concave mirror can be found in three cases.
case1: When the object is at the centre of curvature, it gives the same size as an object, real and an inverted image
case2: When the object is between the centre of curvature and principal focus, it gives magnified, real and an inverted image.
case3: When the object is farther from the mirror than the centre of curvature, it gives small, real, and an inverted image.
case4: When the object is inside the principal focus, it gives the magnified, virtual, and erect image. The focal length for the virtual image gives negative value, this indicates that the image is behind the mirror.
Note:
To know the nature of the mirror, we should know the properties. While using a shaving mirror, the object is either between the principal focus and centre of curvature or farther from the centre of curvature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




