
Shearing strain is expressed by –
A) Angle of shear
B) Angle of twist
C) Decrease in volume
D) Increase in volume.
Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint: We need to understand the different mechanical properties of the solids to find the type of stress and strain involved in a situation. The given strain can be connected to one of the given parameters by understanding its usage in situations.
Complete step-by-step solution
We know that the solids can undergo mainly three types of deformation according to the direction of force applied to them. They are namely – Longitudinal or Compressional Strain, the shear strain, and the bulk strain.
The Longitudinal or compressional strain is the change in length of the material associated with the force applied perpendicular to the cross-sectional area. The ratio of the longitudinal stress to the strain produces Young’s modulus.
The Shearing strain is the change in the shape of the material due to the tangential force applied to any side of the surface of the material. The Shearing strain is expressed as the tangent of the angle made to the perpendicular to the area of the surface under consideration.
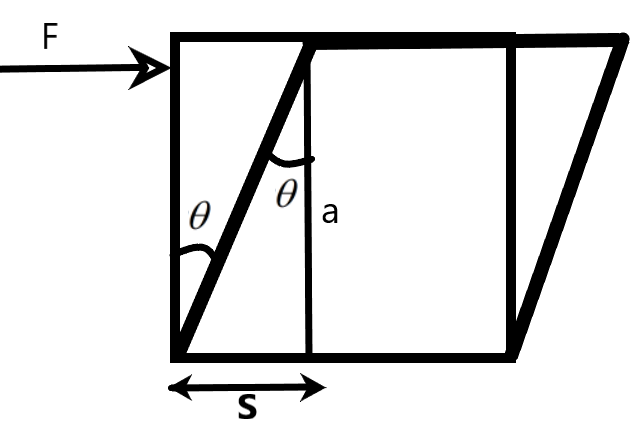
\[\begin{align}
& \text{Shearing strain, S}=a\tan \theta \\
& \text{for small angles, tan}\theta \text{=}\theta \\
& \Rightarrow \text{S}=a\theta \\
\end{align}\]
The Volume or bulk strain is the change in volume associated with the bulk pressure or stress on the material.
We get that the Shearing strain is expressed by the angle of shear.
The correct answer is A.
Note: The shearing strain is caused due to the displacement of one corner of a surface from its mean position due to the force applied tangentially on it. The tangent of the angle of shear is the ratio of this displacement to the length of the side of the material.
Complete step-by-step solution
We know that the solids can undergo mainly three types of deformation according to the direction of force applied to them. They are namely – Longitudinal or Compressional Strain, the shear strain, and the bulk strain.
The Longitudinal or compressional strain is the change in length of the material associated with the force applied perpendicular to the cross-sectional area. The ratio of the longitudinal stress to the strain produces Young’s modulus.
The Shearing strain is the change in the shape of the material due to the tangential force applied to any side of the surface of the material. The Shearing strain is expressed as the tangent of the angle made to the perpendicular to the area of the surface under consideration.

\[\begin{align}
& \text{Shearing strain, S}=a\tan \theta \\
& \text{for small angles, tan}\theta \text{=}\theta \\
& \Rightarrow \text{S}=a\theta \\
\end{align}\]
The Volume or bulk strain is the change in volume associated with the bulk pressure or stress on the material.
We get that the Shearing strain is expressed by the angle of shear.
The correct answer is A.
Note: The shearing strain is caused due to the displacement of one corner of a surface from its mean position due to the force applied tangentially on it. The tangent of the angle of shear is the ratio of this displacement to the length of the side of the material.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




