
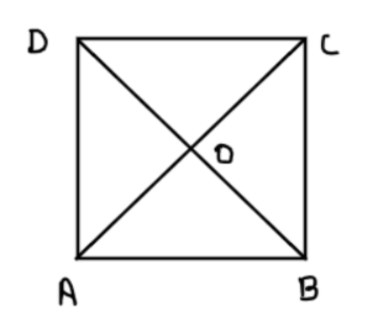
Show that the diagonals of a square are equal and bisect each other at right angles.
Answer
622.5k+ views
Hint - Think of various triangle congruence postulates to apply the CPCT concept.
We have been given that we have a square ABCD. We need to prove that its diagonals are equal and they bisect each other at \[90^\circ \].
We need to prove that $AC = BD$ and $AC{\text{ and BD}}$ bisect each other at right angles.
Proof:
Let’s consider two triangles $\vartriangle ABC{\text{ and }}\vartriangle {\text{BAD}}$
$AB = AB$ (Common line segment in both the triangles)
$BC = AD$ (Opposite sides of a square are always equal)
$\angle ABC = \angle BAD = 90^\circ $ (Two adjacent sides of a square always make $90^\circ $ angle between them)
Hence clearly the two triangles mentioned above are congruent, that is $\vartriangle ABC \cong \vartriangle BAD$ by SAS (Side Angle Side) postulate.
Now using CPCT (Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles), we can say that
$AC = BD$
Hence proved that the diagonals of a square are equal.
Now let’s prove that they bisect at right angles.
In $\vartriangle OAD{\text{ and }}\vartriangle {\text{OCB}}$
$AD = CB$ (Opposite sides of a square are equal)
$\angle OAD = \angle OCB$ (As AD is parallel to BC so alternate interior angles are equal)
$\angle ODA = \angle OBC$ (As AD is parallel to BC so alternate interior angles are equal)
Hence clearly the two triangles $\vartriangle OAD{\text{ and }}\vartriangle {\text{OCB}}$ are congruent, by ASA (Angle Side Angle) postulate.
Now using CPCT (Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles), we can say that
$OA = OC$…………………………… (1)
Similarly, we can prove that $OB = OD$………………… (2)
Now from the figure above it is clear that AC and BD bisect each other.
Now in $\vartriangle OBA{\text{ and }}\vartriangle {\text{ODA}}$
$OB = OD$ (Using equation (2))
$BA = DA$ (Sides of a square are equal)
$OA = OA$ (Common line to both the triangles)
This $\vartriangle OBA{\text{ and }}\vartriangle {\text{ODA}}$ are congruent to each other using SSS (Side Side Side) postulate.
Hence using CPCT we can say that $\angle AOB = \angle AOD$………………… (3)
Now $\angle AOB + \angle AOD = 180^\circ $ as BD is a straight line.
Using equation (3) we can say that the above reduces to
$2\angle AOB = 180^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow \angle AOB = \angle AOD = 90^\circ $
Hence, clearly we can say that the diagonals bisect each other at right angles.
Hence Proved.
Note- Such problems are always based upon the concept of triangle congruence so all we need is to pick up correct triangles and apply the concept of triangle congruence using different postulates to eventually use CPCT (Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles) for the equality of other sides and angles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




