
How do you show the breakdown of a phospholipid into its components?
Answer
554.4k+ views
Hint: Phospholipids are the type of lipid-containing phosphoric acid group. It forms the outermost layer of an animal cell that is the plasma membrane.
Complete answer:
Lipids are hydrophobic biomolecules that play an important role in living organisms. The functions of lipids are the storage of energy for the long term, protection, insulation, and lubrication. It can also act as a precursor for hormones as well as is a primary component of the cell membrane. Lipids are divided into four major groups: triglycerides (include fats and oils), phospholipids, steroids, and waxes. All of these have a common characteristic that they are hydrophobic and cannot mix in water.
Phospholipids are a group of complex lipids containing a glycerol molecule attached to two fatty acids either saturated or unsaturated and a phosphate group with a nitrogen base. Glycerol is three-carbon alcohol where the two fatty acids are attached to carbon one and two while the phosphate group with nitrogen base is attached to the third carbon of the glycerol molecule. Phospholipids have a polar head made up of glycerol molecule and phosphate group with nitrogen attached that is hydrophilic and can mix in water; and a nonpolar tail that are two chains of fatty acids that are hydrophobic.
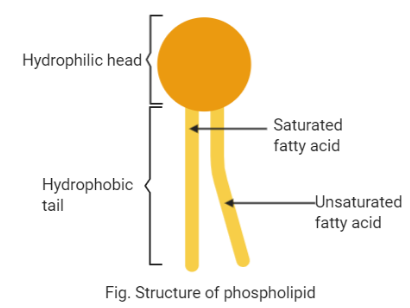
Hence, phospholipids in the cell membrane are arranged in a bilayer in such a way that the hydrophilic part interacts with the water containing environment and the hydrophobic part of the phospholipid is not in contact with water.
Hence, we can say that when a phospholipid is broken down it will dissociate into a glycerol molecule, a phosphate group with one organic group mostly nitrogen, and two chains of fatty acids.
Note:
Phospholipids are of two types glycerophospholipid and sphingophospholipids. Sphingophospholipids are eighteen carbon compounds containing sphingosine alcohol, a phosphate group attached to a nitrogen base called choline. The only example of sphingophospholipid is sphingomyelin.
Complete answer:
Lipids are hydrophobic biomolecules that play an important role in living organisms. The functions of lipids are the storage of energy for the long term, protection, insulation, and lubrication. It can also act as a precursor for hormones as well as is a primary component of the cell membrane. Lipids are divided into four major groups: triglycerides (include fats and oils), phospholipids, steroids, and waxes. All of these have a common characteristic that they are hydrophobic and cannot mix in water.
Phospholipids are a group of complex lipids containing a glycerol molecule attached to two fatty acids either saturated or unsaturated and a phosphate group with a nitrogen base. Glycerol is three-carbon alcohol where the two fatty acids are attached to carbon one and two while the phosphate group with nitrogen base is attached to the third carbon of the glycerol molecule. Phospholipids have a polar head made up of glycerol molecule and phosphate group with nitrogen attached that is hydrophilic and can mix in water; and a nonpolar tail that are two chains of fatty acids that are hydrophobic.

Hence, phospholipids in the cell membrane are arranged in a bilayer in such a way that the hydrophilic part interacts with the water containing environment and the hydrophobic part of the phospholipid is not in contact with water.
Hence, we can say that when a phospholipid is broken down it will dissociate into a glycerol molecule, a phosphate group with one organic group mostly nitrogen, and two chains of fatty acids.
Note:
Phospholipids are of two types glycerophospholipid and sphingophospholipids. Sphingophospholipids are eighteen carbon compounds containing sphingosine alcohol, a phosphate group attached to a nitrogen base called choline. The only example of sphingophospholipid is sphingomyelin.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




