
Sieve tube elements and companion cells are connected by
A. Plasmodesmata
B. Pit fields
C. Aquaporins
D. Gap junctions
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: Sieve tube elements and companion cells are two major units of phloem tissue. The phloem is a vascular tissue and is involved in food transport throughout the plant. The sieve tube elements and companion cells are interconnected by channel-forming cells.
Complete answer:The phloem is one of the two conducting tissues of the plant. It helps with food conduction and storage. The phloem is made up of four major elements. These elements are sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma, and phloem sclerenchyma.
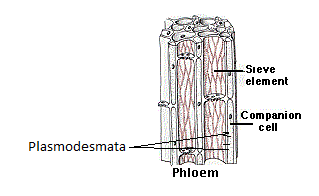
The sieve tubes are the most active food conducting elements of the phloem tissue. It is made up of hollow cylindrical cells. These cells are arranged longitudinally making long tube-like structures. The cells have thin cellulose walls.
The companion cells are spindle-shaped cells associated with the sieve tube elements and aid food conduction. They are also elongated cells and are found attached to the adjacent sieve tube cells. The companion cells also have thin cell walls. They aid in the maintenance of the pressure gradient in the sieve tubes. Both the companion cells and the sieve tube cells are derived from the same mother cell.
Now, both these cells are connected by channel-forming cells called plasmodesmata. The plasmodesmata form porous channels between the two cells by traversing the thin cell walls of both sieve tube element cells and companion cells. These channels promote easy content transfer.
Now, let us study other options.
Pit fields are little potions in the cell walls. The adjacent plant cells are connected by pit fields that help in the exchange of fluids and communication between cells.
Aquaporins are membrane proteins. They help in the transfer of water and other solutes across the membranes of the plant cells.
Gap junctions are just like the plasmodesmata but are found in animal cells.
Hence, option A is the correct answer.
Note: The plasmodesmata are formed due to entrapment of endoplasmic reticulum across the middle lamella during the synthesis of the new cell wall just after cell division. Eventually, these pores make cytoplasmic connections between cells. But plasmodesmata can also be forced into existing cells.
Complete answer:The phloem is one of the two conducting tissues of the plant. It helps with food conduction and storage. The phloem is made up of four major elements. These elements are sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma, and phloem sclerenchyma.
The sieve tubes are the most active food conducting elements of the phloem tissue. It is made up of hollow cylindrical cells. These cells are arranged longitudinally making long tube-like structures. The cells have thin cellulose walls.
The companion cells are spindle-shaped cells associated with the sieve tube elements and aid food conduction. They are also elongated cells and are found attached to the adjacent sieve tube cells. The companion cells also have thin cell walls. They aid in the maintenance of the pressure gradient in the sieve tubes. Both the companion cells and the sieve tube cells are derived from the same mother cell.
Now, both these cells are connected by channel-forming cells called plasmodesmata. The plasmodesmata form porous channels between the two cells by traversing the thin cell walls of both sieve tube element cells and companion cells. These channels promote easy content transfer.

Now, let us study other options.
Pit fields are little potions in the cell walls. The adjacent plant cells are connected by pit fields that help in the exchange of fluids and communication between cells.
Aquaporins are membrane proteins. They help in the transfer of water and other solutes across the membranes of the plant cells.
Gap junctions are just like the plasmodesmata but are found in animal cells.
Hence, option A is the correct answer.
Note: The plasmodesmata are formed due to entrapment of endoplasmic reticulum across the middle lamella during the synthesis of the new cell wall just after cell division. Eventually, these pores make cytoplasmic connections between cells. But plasmodesmata can also be forced into existing cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




