
How many sigma and pi bonds are present in propene molecules?
Answer
554.1k+ views
Hint: Here the first thing we get from "propene" usually all bonds between atoms in most of the organic compounds contains one sigma bond each of them. Whenever it is a single bond it contains only sigma bonds. These multiple bonds double and triple however we can understand how it contains sigma and pi bonds. Therefore double bonds have one each and triple bonds have one sigma bond as well as two pi bonds.
Complete step-by-step answer:We all know that propene structural formula is given by \[C{{H}_{2}}=CH-C{{H}_{3}}\]
Propene has \[8\sigma \] sigma bonds ( \[C-C\] bonds and all \[C-H\] bonds) and \[1\pi \] pi bond \[{{C}_{1}}-{{C}_{2}}\]
Whereas
Single Bond = \[8\sigma \] bond.
Double Bond = \[8\sigma \] bond + \[1\pi \] bond.
Triple Bond = \[8\sigma \] bond + \[2\pi \] bond.
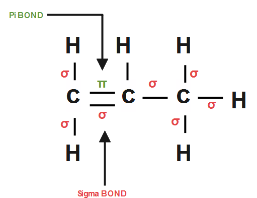
So therefore we have \[8\sigma \] sigma bond as well as \[1\pi \] pi bond in a propene molecule.
Note: Note that the \[\pi \] bonding in the orbital is always lower in energy than nonbonding p orbital. Therefore each and every carbon Centre as shown has two electrons in lower energy efficiency and bonding of π orbital the energy of each and every system is being lowered overall and its thus more and more stable, regardless of anion, radical or cation.
Meanwhile the stability of alkyl carbocation is all due to conjugated \[\pi \] electrons. The double bond doesn’t really exist in nature or that environment. Instead of that it is a group of three adjacent, non-hybridized, overlapping p orbitals we call it as a conjugated \[\pi \] electron. We can clearly state that the interaction between all of three p orbitals from three carbon resulting in a really stable cation. It all deprives us of ups and downs to where the location of the electron deficient our carbon atom is.
Complete step-by-step answer:We all know that propene structural formula is given by \[C{{H}_{2}}=CH-C{{H}_{3}}\]
Propene has \[8\sigma \] sigma bonds ( \[C-C\] bonds and all \[C-H\] bonds) and \[1\pi \] pi bond \[{{C}_{1}}-{{C}_{2}}\]
Whereas
Single Bond = \[8\sigma \] bond.
Double Bond = \[8\sigma \] bond + \[1\pi \] bond.
Triple Bond = \[8\sigma \] bond + \[2\pi \] bond.

So therefore we have \[8\sigma \] sigma bond as well as \[1\pi \] pi bond in a propene molecule.
Note: Note that the \[\pi \] bonding in the orbital is always lower in energy than nonbonding p orbital. Therefore each and every carbon Centre as shown has two electrons in lower energy efficiency and bonding of π orbital the energy of each and every system is being lowered overall and its thus more and more stable, regardless of anion, radical or cation.
Meanwhile the stability of alkyl carbocation is all due to conjugated \[\pi \] electrons. The double bond doesn’t really exist in nature or that environment. Instead of that it is a group of three adjacent, non-hybridized, overlapping p orbitals we call it as a conjugated \[\pi \] electron. We can clearly state that the interaction between all of three p orbitals from three carbon resulting in a really stable cation. It all deprives us of ups and downs to where the location of the electron deficient our carbon atom is.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




