
Sigmoid growth curve is represented by
(a) $\dfrac{dN}{dt}=rN$
(b) \[\dfrac{dN}{dt}=rN(1-\dfrac{n}{k})\]
(c)$Nt={{N}_{o}}+B+I-D-E$
(d) $\dfrac{dN}{dt}=1-\dfrac{N}{K}$
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Change in the population size is equal to the product of the intrinsic rate of increase and population size with one less than from the ratio of population size and carrying capacity.
Complete answer:
The sigmoid growth curve shows that growth is continuous population growth in an environment where resources are unlimited and it is a density-independent growth.
$\dfrac{dN}{dt}=rN(1-\frac{N}{K})$
Where,
$\dfrac{dN}{dt}$ = change in the population
r= intrinsic rate of increase
N= population size
K= carrying capacity.
Additional Information: -Under favorable conditions, bacteria reproduce asexually by binary fission every 20 minutes.
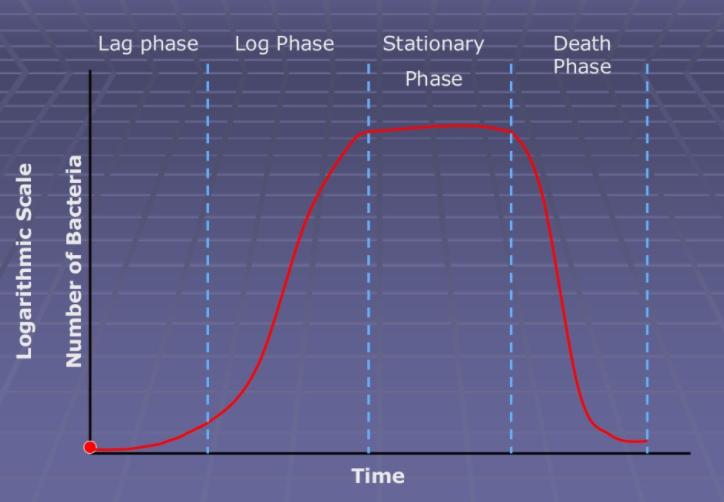
-The bacterial growth cycle is divided into four phases- lag phase, log phase, stationary phase, and decline phase.
-Lag phase
-This phase is one to four hours long.
-In this phase, bacteria adapt themselves to growth conditions.
-This phase is marked by the synthesis of RNA, enzymes and other molecules take place.
-In this phase, bacteria are maturing but not yet able to divide.
-Log phase
-This phase is also known as an exponential phase of eight hours long.
-This phase is marked by cell doubling where the new bacteria appearing per unit time is proportional to the population at that time.
-In this phase few waste products are produced.
-Due to the medium is soon depleted of nutrients and enriched with wastes, the exponential growth cannot continue indefinitely.
-Stationary phase
-This phase lasts long for a few hours or even days.
-This phase is a growth-limiting factor because of the depletion of a nutrient and the formation of inhibitory products.
-In this phase, the newly formed cells per time are equal to the dying cells per time.
-Decline phase
-This phase lasts long for a few hours or days
-In this phase, the bacteria run out of nutrients and die although the number of cells remains constant.
-After a certain period, all the cells die and culture becomes sterile.
So, the correct answer is,\['\dfrac{dN}{dt}=rN(1-\dfrac{N}{K})'\]
Note: -The maximum cell size is seen at the end of the lag phase.
-The log phase is the time when the cell is most active metabolically and is preferred for industrial purposes.
Complete answer:
The sigmoid growth curve shows that growth is continuous population growth in an environment where resources are unlimited and it is a density-independent growth.
$\dfrac{dN}{dt}=rN(1-\frac{N}{K})$
Where,
$\dfrac{dN}{dt}$ = change in the population
r= intrinsic rate of increase
N= population size
K= carrying capacity.

Additional Information: -Under favorable conditions, bacteria reproduce asexually by binary fission every 20 minutes.
-The bacterial growth cycle is divided into four phases- lag phase, log phase, stationary phase, and decline phase.
-Lag phase
-This phase is one to four hours long.
-In this phase, bacteria adapt themselves to growth conditions.
-This phase is marked by the synthesis of RNA, enzymes and other molecules take place.
-In this phase, bacteria are maturing but not yet able to divide.
-Log phase
-This phase is also known as an exponential phase of eight hours long.
-This phase is marked by cell doubling where the new bacteria appearing per unit time is proportional to the population at that time.
-In this phase few waste products are produced.
-Due to the medium is soon depleted of nutrients and enriched with wastes, the exponential growth cannot continue indefinitely.
-Stationary phase
-This phase lasts long for a few hours or even days.
-This phase is a growth-limiting factor because of the depletion of a nutrient and the formation of inhibitory products.
-In this phase, the newly formed cells per time are equal to the dying cells per time.
-Decline phase
-This phase lasts long for a few hours or days
-In this phase, the bacteria run out of nutrients and die although the number of cells remains constant.
-After a certain period, all the cells die and culture becomes sterile.
So, the correct answer is,\['\dfrac{dN}{dt}=rN(1-\dfrac{N}{K})'\]
Note: -The maximum cell size is seen at the end of the lag phase.
-The log phase is the time when the cell is most active metabolically and is preferred for industrial purposes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




