
What is the sine, cosine and tangent of 270 degrees?
Answer
536.1k+ views
Hint: Express ${{270}^{\circ }}\text{ into }\left( {{270}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)$ . Then we should use the following two identities for sin and cosine respectively, $\sin \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)=-\cos \theta \text{ and }\cos \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)=\sin \theta $ . To find the tangent, we must remember that $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }$ . In case the value of tangent is undefined, verify using the graph of $y=\tan \theta \text{ at }\theta ={{270}^{\circ }}$ to check whether it is $+\infty \text{ or }-\infty $ .
Complete step by step solution:
For sine of 270 degrees:
We can write ${{270}^{\circ }}\text{ as }\left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)$ . Or, in equation form
$\sin \left( {{270}^{\circ }} \right)=\sin \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)...\left( i \right)$
We know the trigonometric identity $\sin \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)=-\cos \theta $.
If we put $\theta ={{0}^{\circ }}$ and keep in mind the fact that $\cos {{0}^{\circ }}=1$ , we get
$\sin \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)=-\cos {{0}^{\circ }}=-1...\left( ii \right)$
Now substituting the value of $\sin \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)$ in equation (i), we get
$\sin \left( {{270}^{\circ }} \right)=-1$
Hence, the sine of 270 degrees is -1.
For cosine of 270 degrees:
We can write ${{270}^{\circ }}\text{ as }\left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)$ . Or, in equation form
$\cos \left( {{270}^{\circ }} \right)=\cos \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)...\left( iii \right)$
We know the trigonometric identity $\cos \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)=\sin \theta $.
If we put $\theta ={{0}^{\circ }}$ and keep in mind the fact that $\sin {{0}^{\circ }}=0$ , we get
$\cos \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)=\sin {{0}^{\circ }}=0...\left( iv \right)$
Now substituting the value of $\cos \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)$ in equation (iii), we get
$\cos \left( {{270}^{\circ }} \right)=0$
Hence, the cosine of 270 degrees is 0.
For tangent of 270 degrees:
We are well aware of the identity that
$\tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }$
Thus, we can write
$\tan {{270}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{\sin {{270}^{\circ }}}{\cos {{270}^{\circ }}}$
We can write ${{270}^{\circ }}\text{ as }\left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)$ . Or, in equation form
$\tan \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{\sin \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)}{\cos \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)}$
We can now substitute the values of $\sin \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)\text{ and }\cos \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)$ from equation (ii) and equation (iv) respectively. Thus, we have,
$\tan \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{-1}{0}$ , which is N.D. or undefined.
Now, to check whether the value is $+\infty \text{ or }-\infty $ , we should use the graph of $y=\tan \left( x \right)\text{ at }x={{270}^{\circ }}$
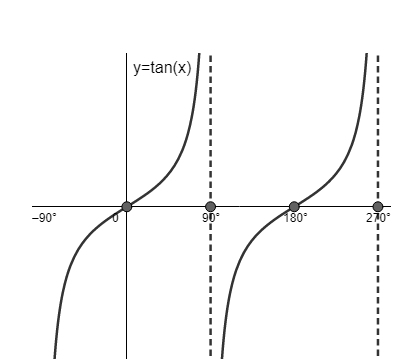
From this graph, we can clearly see that $y=\tan \left( x \right)\text{ approaches }+\infty \text{ at }x={{270}^{\circ }}$ .
\[\therefore \tan \left( {{270}^{\circ }} \right)=+\infty \]
Hence, the tangent of 270 degrees is positive infinity.
Note: We can express 270 degrees into multiple forms, such as, $\left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right),\left( {{180}^{\circ }}+{{90}^{\circ }} \right)\text{ or }\left( {{360}^{\circ }}-{{90}^{\circ }} \right)$ . All of these forms could be used separately to find the trigonometric values of ${{270}^{\circ }}$ . We should remember not to assume $\left( \dfrac{-1}{0} \right)\text{ as -}\infty $ when we are trying to find the tangent of ${{270}^{\circ }}$.
Complete step by step solution:
For sine of 270 degrees:
We can write ${{270}^{\circ }}\text{ as }\left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)$ . Or, in equation form
$\sin \left( {{270}^{\circ }} \right)=\sin \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)...\left( i \right)$
We know the trigonometric identity $\sin \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)=-\cos \theta $.
If we put $\theta ={{0}^{\circ }}$ and keep in mind the fact that $\cos {{0}^{\circ }}=1$ , we get
$\sin \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)=-\cos {{0}^{\circ }}=-1...\left( ii \right)$
Now substituting the value of $\sin \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)$ in equation (i), we get
$\sin \left( {{270}^{\circ }} \right)=-1$
Hence, the sine of 270 degrees is -1.
For cosine of 270 degrees:
We can write ${{270}^{\circ }}\text{ as }\left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)$ . Or, in equation form
$\cos \left( {{270}^{\circ }} \right)=\cos \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)...\left( iii \right)$
We know the trigonometric identity $\cos \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+\theta \right)=\sin \theta $.
If we put $\theta ={{0}^{\circ }}$ and keep in mind the fact that $\sin {{0}^{\circ }}=0$ , we get
$\cos \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)=\sin {{0}^{\circ }}=0...\left( iv \right)$
Now substituting the value of $\cos \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)$ in equation (iii), we get
$\cos \left( {{270}^{\circ }} \right)=0$
Hence, the cosine of 270 degrees is 0.
For tangent of 270 degrees:
We are well aware of the identity that
$\tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }$
Thus, we can write
$\tan {{270}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{\sin {{270}^{\circ }}}{\cos {{270}^{\circ }}}$
We can write ${{270}^{\circ }}\text{ as }\left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)$ . Or, in equation form
$\tan \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{\sin \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)}{\cos \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)}$
We can now substitute the values of $\sin \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)\text{ and }\cos \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)$ from equation (ii) and equation (iv) respectively. Thus, we have,
$\tan \left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{-1}{0}$ , which is N.D. or undefined.
Now, to check whether the value is $+\infty \text{ or }-\infty $ , we should use the graph of $y=\tan \left( x \right)\text{ at }x={{270}^{\circ }}$

From this graph, we can clearly see that $y=\tan \left( x \right)\text{ approaches }+\infty \text{ at }x={{270}^{\circ }}$ .
\[\therefore \tan \left( {{270}^{\circ }} \right)=+\infty \]
Hence, the tangent of 270 degrees is positive infinity.
Note: We can express 270 degrees into multiple forms, such as, $\left( {{270}^{\circ }}+{{0}^{\circ }} \right),\left( {{180}^{\circ }}+{{90}^{\circ }} \right)\text{ or }\left( {{360}^{\circ }}-{{90}^{\circ }} \right)$ . All of these forms could be used separately to find the trigonometric values of ${{270}^{\circ }}$ . We should remember not to assume $\left( \dfrac{-1}{0} \right)\text{ as -}\infty $ when we are trying to find the tangent of ${{270}^{\circ }}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




