
Sketch the emergent wavefront.
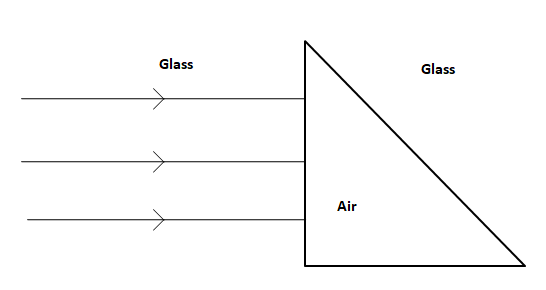

Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Wavefront is defined as the locus of all the particles of a medium vibrating in the same phase at a given instant. The shape of a given wavefront depends upon the formation of disturbance. Huygens’s principle gave a brief description of the wavefront and used to find the new position of the given wavefront at any instant if its present status is known.
Complete step by step answer:
Here we consider the example of prism to sketch the emergent wavefront. Consider a plane wavefront PQ incident on a glass prism ABC having a small angle of refraction. According to Huygens’s principle, each point on a wavefront PQ acts as a new disturbance center. These centers of disturbances send out secondary wavelets. The different secondary wavelets will travel different distances through a prism.
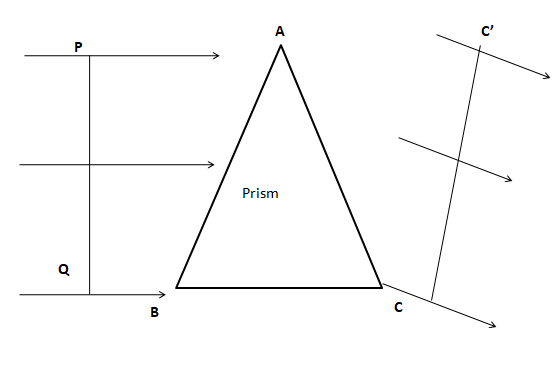
From point P, suppose the secondary wavelet will travel almost the whole distance in air before its incident on a prism A. After traveling a very small distance in the prism, this wavelet emerges and travels in the air. The time during which the wavelets travel from B to C in glass prism is equal to BC/v. Where v is the speed of light in the glass, at the same time, the wavelet from P will travel almost the whole distance in the air and reaches point C’ such that AC’ > BC. Thus points C’ and C are in the same phase. Join CC’, we get a plane wavefront CC,’ which is known as the emergent plane wavefront.
Note:
According to Huygens’s principle:
i) Each source of light is a center of disturbance from which waves spread in all directions. All particles are equidistant from the source and vibrating in the same phase lies on a wavefront surface.
ii) Every point on a wavefront is a source of new disturbance that produces secondary wavelets. These wavelets travel with the speed of light in all directions in that medium.
Complete step by step answer:
Here we consider the example of prism to sketch the emergent wavefront. Consider a plane wavefront PQ incident on a glass prism ABC having a small angle of refraction. According to Huygens’s principle, each point on a wavefront PQ acts as a new disturbance center. These centers of disturbances send out secondary wavelets. The different secondary wavelets will travel different distances through a prism.

From point P, suppose the secondary wavelet will travel almost the whole distance in air before its incident on a prism A. After traveling a very small distance in the prism, this wavelet emerges and travels in the air. The time during which the wavelets travel from B to C in glass prism is equal to BC/v. Where v is the speed of light in the glass, at the same time, the wavelet from P will travel almost the whole distance in the air and reaches point C’ such that AC’ > BC. Thus points C’ and C are in the same phase. Join CC’, we get a plane wavefront CC,’ which is known as the emergent plane wavefront.
Note:
According to Huygens’s principle:
i) Each source of light is a center of disturbance from which waves spread in all directions. All particles are equidistant from the source and vibrating in the same phase lies on a wavefront surface.
ii) Every point on a wavefront is a source of new disturbance that produces secondary wavelets. These wavelets travel with the speed of light in all directions in that medium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




