
Smallest cell organelle which is called cell engine is:
(a) Ribosome
(b) Lysosome
(c) Vacuoles
(d) Endoplasmic reticulum
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: They are minute particles consisting of RNA and associated proteins that function to synthesize proteins. They are needed for many cellular functions which mainly includes repairing damage or directing chemical processes.
Complete answer:
Ribosomes are the engines of cells as they make all the cell’s proteins, which carry out the cell’s functions. They occur as both free particles in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and as particles attached to the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotic cells. Cells have many ribosomes, and the number mainly depends on how active a particular cell is in synthesizing proteins. The translation is the process through which the ribosome produces proteins.
Within the ribosome, the rRNA molecules govern the catalytic steps of protein synthesis. The procedure includes stitching together amino acids to make a protein molecule. Therefore, rRNA is also called a ribozyme or catalytic RNA to reflect this function.
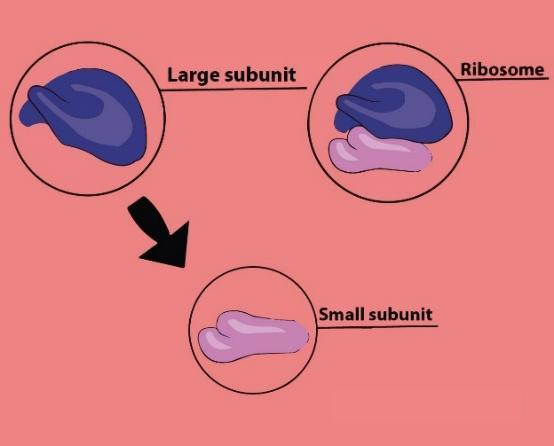
Additional information: Ribosomes are the sites at which information is carried in the form of genetic code and is converted into protein molecules. Each ribosome unit is composed of two subunits, a larger one and a smaller one, each of which has a characteristic shape. Ribosome subunits
are typically referred to in terms of their sedimentation rate, which is measured in Svedberg units (S), in a centrifugal field.
So, the correct answer is ‘(a) Ribosome’.<.b>
Note: Ribosomes act as catalysts in two extremely important biological processes called peptidyl transfer(peptidyl transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the addition of an amino acid residue in order to grow the polypeptide chain in protein synthesis) and peptidyl hydrolysis.
Complete answer:
Ribosomes are the engines of cells as they make all the cell’s proteins, which carry out the cell’s functions. They occur as both free particles in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and as particles attached to the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotic cells. Cells have many ribosomes, and the number mainly depends on how active a particular cell is in synthesizing proteins. The translation is the process through which the ribosome produces proteins.

Within the ribosome, the rRNA molecules govern the catalytic steps of protein synthesis. The procedure includes stitching together amino acids to make a protein molecule. Therefore, rRNA is also called a ribozyme or catalytic RNA to reflect this function.
Additional information: Ribosomes are the sites at which information is carried in the form of genetic code and is converted into protein molecules. Each ribosome unit is composed of two subunits, a larger one and a smaller one, each of which has a characteristic shape. Ribosome subunits
are typically referred to in terms of their sedimentation rate, which is measured in Svedberg units (S), in a centrifugal field.
So, the correct answer is ‘(a) Ribosome’.<.b>
Note: Ribosomes act as catalysts in two extremely important biological processes called peptidyl transfer(peptidyl transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the addition of an amino acid residue in order to grow the polypeptide chain in protein synthesis) and peptidyl hydrolysis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




