
Soap and detergents are the sources of organic pollutants like
(a) Glycerol
(b) Polyphosphates
(c) Sulfonated hydrocarbon
(d) All of the above
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint:The pollutants in the soap and detergents are the chemical compounds that are used in their formation and these can be both organic and inorganic compounds containing carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, phosphorus, etc.
Complete answer:Glycerol, Polyphosphates, and Sulfonated hydrocarbon, all these can be pollutants in the soaps and detergents. The fats and oils that are required for manufacturing soaps are extracted from the plants and animals and three fatty acid molecules are added per molecule of fat to make it a triglyceride.
Some common alkalis that are used in soap making are sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide. In the case of detergents, the materials that are used in their formation are Petrochemicals, sulfur trioxide, Oleochemicals, ethylene oxide, sulphuric acid, and alkalis like potassium and sodium.
All these organic and inorganic chemicals can be pollutants because when these are released in water bodies, they make that water unsuitable for the organisms living there and also affect the fertility of soils decreasing the net productivity and in turn, the ecosystems consisting of the small plants and animals are also affected. The reaction of formation and chemical structure of soap has been given below –
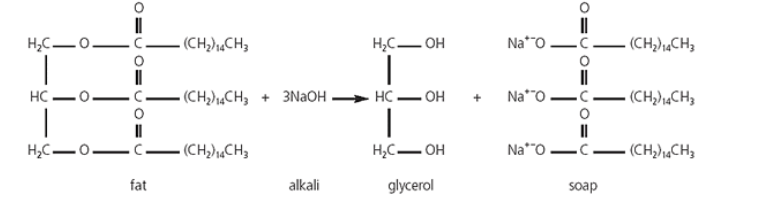
So, the correct answer is ‘All of the above’.
Note:Organic pollution occurs when an excess of organic matter is present in the sewage or manure enters the water bodies. Due to the presence of a large amount of organic matter in water bodies like ponds, the number of decomposers increases in that ecosystem. For decomposing all the organic matter present in the water, these decomposers grow rapidly and use a great amount of available oxygen causing a reduction in oxygen content of the water which becomes a reason for the death of the other aquatic organism.
Complete answer:Glycerol, Polyphosphates, and Sulfonated hydrocarbon, all these can be pollutants in the soaps and detergents. The fats and oils that are required for manufacturing soaps are extracted from the plants and animals and three fatty acid molecules are added per molecule of fat to make it a triglyceride.
Some common alkalis that are used in soap making are sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide. In the case of detergents, the materials that are used in their formation are Petrochemicals, sulfur trioxide, Oleochemicals, ethylene oxide, sulphuric acid, and alkalis like potassium and sodium.
All these organic and inorganic chemicals can be pollutants because when these are released in water bodies, they make that water unsuitable for the organisms living there and also affect the fertility of soils decreasing the net productivity and in turn, the ecosystems consisting of the small plants and animals are also affected. The reaction of formation and chemical structure of soap has been given below –

So, the correct answer is ‘All of the above’.
Note:Organic pollution occurs when an excess of organic matter is present in the sewage or manure enters the water bodies. Due to the presence of a large amount of organic matter in water bodies like ponds, the number of decomposers increases in that ecosystem. For decomposing all the organic matter present in the water, these decomposers grow rapidly and use a great amount of available oxygen causing a reduction in oxygen content of the water which becomes a reason for the death of the other aquatic organism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




