
Sodium phenoxide when heated with CO$_2$, under pressure at 125$^\circ$C yields a product which on acetylation produces C.
The major product C would be:
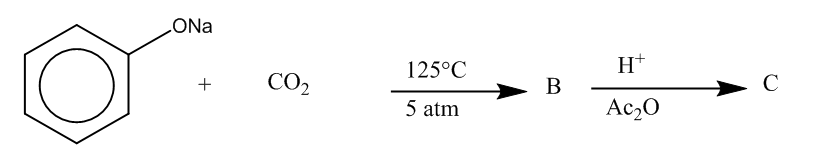
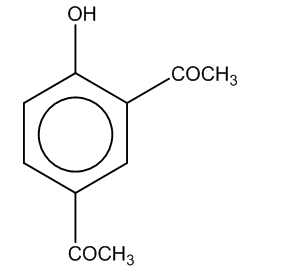
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)




Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: This question is based on the concept of acetylation reaction. As we can see in the question that B to C conversion takes place through the acetyl group. This is the Kolbe-Schmitt reaction, so now the product can be identified.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, we will move step by step for this reaction.
As we know, sodium phenoxide is the sodium salt of phenol.
The first step is when sodium phenoxide reacts with carbon-dioxide at high temp, and 5 atm to produce the salicylate i.e.
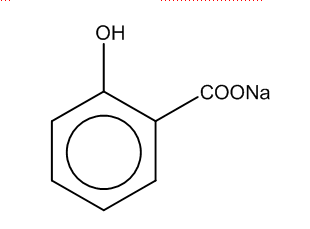
In the first step, we can see that phenol group is attached to the benzene ring, and COO- group is attached with the sodium ion.
Thus, the product formed in the first step is B.
Now, if we perform the further reaction to attain the product C, then there is a reaction of salicylate formed with the acid i.e. sulphuric acid in the presence of an acetyl group.
Thus, the product formed is
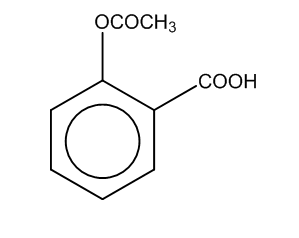
Here, we can see that –COOH group is attached at the ortho position, and the product formed is C i.e. salicylic acid.It is also known as aspirin.
The second step of this reaction is an example of acetylation reaction.
As mentioned the whole reaction i.e. from sodium phenoxide to the formation of salicylic acid is Kolbe-Schmitt reaction.
Hence, the major product formed C is
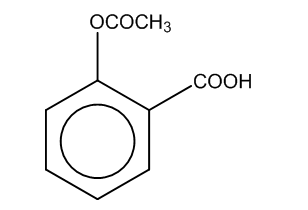
The correct option is (C).
Note: Don’t get confused while writing the complete chemical reaction, just perform it step by step as shown. There is a difference between salicylate, and salicylic acid. Salicylic acid is formed by the reaction of salicylate with sulphuric acid. So, salicylate acts as a starting material for acetylation reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, we will move step by step for this reaction.
As we know, sodium phenoxide is the sodium salt of phenol.
The first step is when sodium phenoxide reacts with carbon-dioxide at high temp, and 5 atm to produce the salicylate i.e.

In the first step, we can see that phenol group is attached to the benzene ring, and COO- group is attached with the sodium ion.
Thus, the product formed in the first step is B.
Now, if we perform the further reaction to attain the product C, then there is a reaction of salicylate formed with the acid i.e. sulphuric acid in the presence of an acetyl group.
Thus, the product formed is

Here, we can see that –COOH group is attached at the ortho position, and the product formed is C i.e. salicylic acid.It is also known as aspirin.
The second step of this reaction is an example of acetylation reaction.
As mentioned the whole reaction i.e. from sodium phenoxide to the formation of salicylic acid is Kolbe-Schmitt reaction.
Hence, the major product formed C is

The correct option is (C).
Note: Don’t get confused while writing the complete chemical reaction, just perform it step by step as shown. There is a difference between salicylate, and salicylic acid. Salicylic acid is formed by the reaction of salicylate with sulphuric acid. So, salicylate acts as a starting material for acetylation reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




