
What is the solubility of cerium sulfate at \[10{}^\circ C\] ? What is the solubility of cerium sulfate at \[50{}^\circ C\] ?
Answer
509.7k+ views
Hint: We know that the solubility product of a salt is basically the product of the solubility’s or concentration of the products (ionic species) of the reaction, where the concentration of each ion is raised to the power respective to their stoichiometric coefficients in a balanced chemical equation. Sometimes, solubility of a compound gets lower with increase in temperature, cerium sulfate is one of those compounds in which its solubility decreases with increase in temperature.
Complete answer:
As we know that the solubility of cerium sulfate at \[10\] degree C is \[14g/100ml\] and its solubility at \[50\] degree C is \[6g/100ml.\] It means that only \[14\] gram of cerium sulphate will dissolve in \[100\] ml of water at \[10\] degree Celsius and only \[6\] gram of cerium sulphate will dissolve in \[100\] ml of water at $50$ degree Celsius. This shows that the solubility of cerium sulphate decreases with the increase in temperature rather. Generally, solubility of any element or compound increases with increase in temperature of the solution, but it does not happen here. Cerium sulphate is one salt whose solubility decreases with increase in temperature of the solution. The reason why the solubility of cerium sulphate decrease with increase in temperature is because the highly charged \[C{{e}^{+3}}\] and \[SO_{4}^{-2}\] ions become surrounded by a uniquely ordered sphere of water molecules, which increases the order of the system. And thus, its solubility decreases.
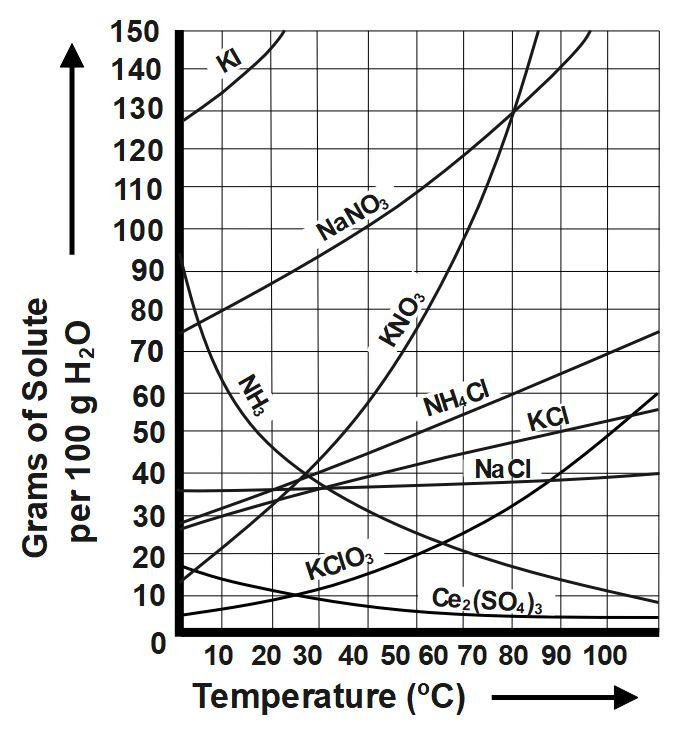
The below graph indicates solubility of cerium sulphate. The chemical formula of cerium sulphate is \[C{{e}_{2}}{{\left( S{{O}_{4}} \right)}_{3}}.\] Solubility of most of the salts increase with increase in temperature of the solution. But, there are a few salts and compounds where the solubility of them decreases with increase in temperature of the solution.
Therefore, Cerium \[(III)\] sulfate is one of the few solids that is less soluble in water at higher temperatures as it appears that \[100\] g of water will dissolve \[14\] g of the salt at \[10\text{ }{}^\circ C\] and only \[6\] g at \[50\text{ }{}^\circ C.\]
Note:
Remember that there can be different reasons for the decrease in solubility of any element or compound with increase in temperature of the solution; in this case it was due to more orderly arrangement occurring with increase in temperature. The formula of solubility product constant depends upon the number of ions produced by the ionic compounds in the water.
Complete answer:
As we know that the solubility of cerium sulfate at \[10\] degree C is \[14g/100ml\] and its solubility at \[50\] degree C is \[6g/100ml.\] It means that only \[14\] gram of cerium sulphate will dissolve in \[100\] ml of water at \[10\] degree Celsius and only \[6\] gram of cerium sulphate will dissolve in \[100\] ml of water at $50$ degree Celsius. This shows that the solubility of cerium sulphate decreases with the increase in temperature rather. Generally, solubility of any element or compound increases with increase in temperature of the solution, but it does not happen here. Cerium sulphate is one salt whose solubility decreases with increase in temperature of the solution. The reason why the solubility of cerium sulphate decrease with increase in temperature is because the highly charged \[C{{e}^{+3}}\] and \[SO_{4}^{-2}\] ions become surrounded by a uniquely ordered sphere of water molecules, which increases the order of the system. And thus, its solubility decreases.

The below graph indicates solubility of cerium sulphate. The chemical formula of cerium sulphate is \[C{{e}_{2}}{{\left( S{{O}_{4}} \right)}_{3}}.\] Solubility of most of the salts increase with increase in temperature of the solution. But, there are a few salts and compounds where the solubility of them decreases with increase in temperature of the solution.
Therefore, Cerium \[(III)\] sulfate is one of the few solids that is less soluble in water at higher temperatures as it appears that \[100\] g of water will dissolve \[14\] g of the salt at \[10\text{ }{}^\circ C\] and only \[6\] g at \[50\text{ }{}^\circ C.\]
Note:
Remember that there can be different reasons for the decrease in solubility of any element or compound with increase in temperature of the solution; in this case it was due to more orderly arrangement occurring with increase in temperature. The formula of solubility product constant depends upon the number of ions produced by the ionic compounds in the water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




