
What is $s{p^2}$ hybridized carbon atom?
Answer
497.1k+ views
Hint: Intermixing of orbitals of slightly different energies in order to redistribute their energies resulting in the formation of new sets of orbitals of equivalent energies and shape. This process of intermixing is called hybridization while the new orbitals formed are called hybrid or hybridized orbitals.
Complete answer:
One $s$ and two $p$ orbitals hybridize to form three equivalent $s{p^2}$ hybrid orbital. In each of the three $s{p^2}$ hybrid orbital one third i.e.$33\% {\text{ s}}$ character and two third i.e. $66\% {\text{ p}}$ character is present. The three $s{p^2}$ hybrid orbitals lie in the same plane making ${120^ \circ }$ angle with each other. Therefore, molecules involving $s{p^2}$ hybridization have a bond angle of ${120^ \circ }$ and trigonal planar geometry.
The carbon atoms of alkenes or carbon atoms bonded by double bonds i.e. $C = C$ bond involves $s{p^2}$ hybridization, because the atomic number of carbon is six and its ground state electronic configuration is $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^2}$ . But in an excited state a carbon atom has four unpaired electrons. Therefore, the one $2s$ orbital and two $2p$ orbital i.e. three orbital in total gets hybridized to form three $s{p^2}$ hybrid orbital while one $2{p_z}$ orbital remains unhybridized. Hence, carbon atoms in alkenes or carbon atoms bound by double bonds are $s{p^2}$ hybridized carbon atoms.
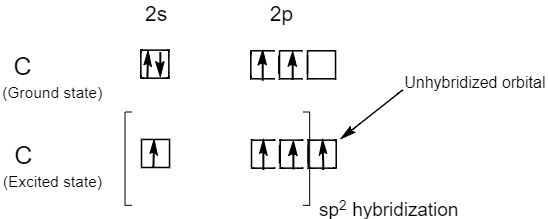
Note:
A class of hydrocarbons which is unsaturated and contains at least one carbon to carbon double bond are called alkenes. Alkenes are planar molecules with $s{p^2}$ hybridization and ${120^ \circ }$ bond angle, whereas alkynes are also a class of unsaturated hydrocarbon, containing at least one carbon to carbon triple bond. But, alkynes have linear geometry with $sp$ hybridization and ${180^ \circ }$ bond angle.
Complete answer:
One $s$ and two $p$ orbitals hybridize to form three equivalent $s{p^2}$ hybrid orbital. In each of the three $s{p^2}$ hybrid orbital one third i.e.$33\% {\text{ s}}$ character and two third i.e. $66\% {\text{ p}}$ character is present. The three $s{p^2}$ hybrid orbitals lie in the same plane making ${120^ \circ }$ angle with each other. Therefore, molecules involving $s{p^2}$ hybridization have a bond angle of ${120^ \circ }$ and trigonal planar geometry.
The carbon atoms of alkenes or carbon atoms bonded by double bonds i.e. $C = C$ bond involves $s{p^2}$ hybridization, because the atomic number of carbon is six and its ground state electronic configuration is $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^2}$ . But in an excited state a carbon atom has four unpaired electrons. Therefore, the one $2s$ orbital and two $2p$ orbital i.e. three orbital in total gets hybridized to form three $s{p^2}$ hybrid orbital while one $2{p_z}$ orbital remains unhybridized. Hence, carbon atoms in alkenes or carbon atoms bound by double bonds are $s{p^2}$ hybridized carbon atoms.

Note:
A class of hydrocarbons which is unsaturated and contains at least one carbon to carbon double bond are called alkenes. Alkenes are planar molecules with $s{p^2}$ hybridization and ${120^ \circ }$ bond angle, whereas alkynes are also a class of unsaturated hydrocarbon, containing at least one carbon to carbon triple bond. But, alkynes have linear geometry with $sp$ hybridization and ${180^ \circ }$ bond angle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




