
Spherical wave fronts, emanating from a point source, strike a plane reflecting surface. What will happen to these wave fronts, immediately after reflection?
Answer
505.8k+ views
Hint: The locus of all points of the medium that vibrate in the same phase is known as a wave front. Wave fronts may be one of three styles, depending on the shape of the light source. A wave front is a line or surface in the direction of wave motion that has the same phase of disturbances at all points. If a wave front diverges, the energy conveyed by the wave spreads over a bigger and bigger region, and thus, the intensity decreases. The force of a plane wave is steady since plane wave fronts neither converge or diverge.
Complete answer:
Depending on the source of light, wave fronts may be one of three types: cylindrical wave front, spherical wave front, and plane wavefront are the three types of wave fronts.
Spherical Wave Front: When a point source emits waves in three dimensions in an isotropic medium, the wave fronts are spheres centred on the source. A spherical wave front is one such wave front.
Cylindrical wave front: When the source of light is linear, all the points equidistant from the linear source lie on the surface of a cylinder. This type of wave front is called a cylindrical wave front.
Plane wave front: The wave front obtained when a fraction of a spherical or cylindrical wave front originates from a distant source such as infinity is known as a plane wave front.
Spherical Wave Front diagram:
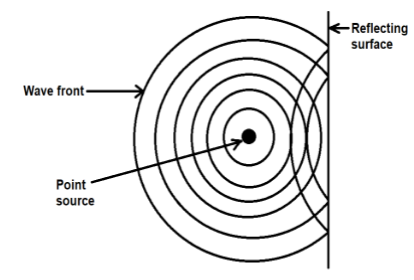
When light is emerging from a point source, the wave fronts are observed to be spherical in shape. In spherical wave front, amplitude of light waves, \[A \propto \dfrac{1}{{{r_1}}}\]. And Intensity of light waves, $I \propto \dfrac{1}{{{r_1}^2}}$. The wave front will remain spherical after reflection from the surface but their direction of propagation will be revered.
Note: The term "wave regular" refers to a perpendicular drawn to the surface of a wave front at any point in the direction of light propagation. A ray of light is the direction in which light travels. As a result, a wave normal is the same as a light beam. The appearance of wave fronts can be altered with the use of a lens.
Complete answer:
Depending on the source of light, wave fronts may be one of three types: cylindrical wave front, spherical wave front, and plane wavefront are the three types of wave fronts.
Spherical Wave Front: When a point source emits waves in three dimensions in an isotropic medium, the wave fronts are spheres centred on the source. A spherical wave front is one such wave front.
Cylindrical wave front: When the source of light is linear, all the points equidistant from the linear source lie on the surface of a cylinder. This type of wave front is called a cylindrical wave front.
Plane wave front: The wave front obtained when a fraction of a spherical or cylindrical wave front originates from a distant source such as infinity is known as a plane wave front.
Spherical Wave Front diagram:

When light is emerging from a point source, the wave fronts are observed to be spherical in shape. In spherical wave front, amplitude of light waves, \[A \propto \dfrac{1}{{{r_1}}}\]. And Intensity of light waves, $I \propto \dfrac{1}{{{r_1}^2}}$. The wave front will remain spherical after reflection from the surface but their direction of propagation will be revered.
Note: The term "wave regular" refers to a perpendicular drawn to the surface of a wave front at any point in the direction of light propagation. A ray of light is the direction in which light travels. As a result, a wave normal is the same as a light beam. The appearance of wave fronts can be altered with the use of a lens.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




