
Spirogyra is a
(a)Freshwater and free-floating alga
(b)Marine and free-floating alga
(c)Freshwater and locomotory alga
(d)None of the above
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: Spirogyra is also known as the pond silk/water silk. Spirogyra has a distinctively spiral chloroplast. Most of the aquatic animals eat spirogyra.
Complete answer:
Spirogyra is a filamentous plus free-floating algae generally observed in freshwater such as ponds, lakes. They perform photosynthesis. The size of the spirogyra ranges from 10µm to 100µm of width and the length ranges to centimeters. They are commonly observed in eutrophic water (the water which is excessively high in the mineral and nutrient content).
Additional Information:
-Spirogyra can undergo vegetative, sexual as well as asexual reproduction.
-Under appropriate conditions, spirogyra will undergo vegetative reproduction.
Vegetative reproduction: In vegetative reproduction, the spirulina will undergo fragmentation. After vegetative reproduction, the fragments will undergo several divisions, and later it will form into a new filament. Each fragment will develop into a new filament.
Asexual reproduction: It is observed in some spirogyra by azygospores, akinetes, aplanospores.
-Azygospores are formed when the gametes that will not undergo fusion and thereby will develop into filaments.
-The shrinkage of protoplasts and will form a wall all over it. This will form an aplanospores.
-Akinetes are also produced similarly as that of aplanospores but, it differs in having a thicker cell wall made of cellulose and pectin.
Sexual reproduction: The male and female gametes are of the same size. They will undergo conjugation. This is otherwise called as isogamous.
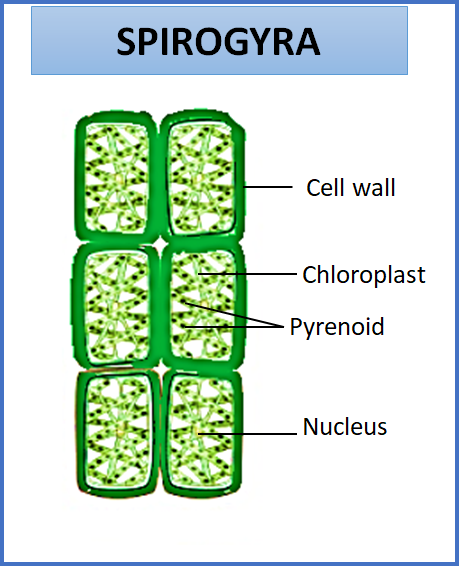
So, the correct answer is, ‘freshwater and free-floating alga’.
Note:
The whole protoplasts are called gametes. These are otherwise called aplanogamete which is formed during the final growing season of the spirulina. The zygote of the spirulina is haploid (2n) and they will undergo meiosis to form 4 haploid (n) nucleus. The zygote divides rapidly in the germ tube and it forms the spirulina.
Complete answer:
Spirogyra is a filamentous plus free-floating algae generally observed in freshwater such as ponds, lakes. They perform photosynthesis. The size of the spirogyra ranges from 10µm to 100µm of width and the length ranges to centimeters. They are commonly observed in eutrophic water (the water which is excessively high in the mineral and nutrient content).
Additional Information:
-Spirogyra can undergo vegetative, sexual as well as asexual reproduction.
-Under appropriate conditions, spirogyra will undergo vegetative reproduction.
Vegetative reproduction: In vegetative reproduction, the spirulina will undergo fragmentation. After vegetative reproduction, the fragments will undergo several divisions, and later it will form into a new filament. Each fragment will develop into a new filament.
Asexual reproduction: It is observed in some spirogyra by azygospores, akinetes, aplanospores.
-Azygospores are formed when the gametes that will not undergo fusion and thereby will develop into filaments.
-The shrinkage of protoplasts and will form a wall all over it. This will form an aplanospores.
-Akinetes are also produced similarly as that of aplanospores but, it differs in having a thicker cell wall made of cellulose and pectin.
Sexual reproduction: The male and female gametes are of the same size. They will undergo conjugation. This is otherwise called as isogamous.

So, the correct answer is, ‘freshwater and free-floating alga’.
Note:
The whole protoplasts are called gametes. These are otherwise called aplanogamete which is formed during the final growing season of the spirulina. The zygote of the spirulina is haploid (2n) and they will undergo meiosis to form 4 haploid (n) nucleus. The zygote divides rapidly in the germ tube and it forms the spirulina.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




