
Sporangiospores of Mucor are
A. Polyploid
B. Triploid
C. Diploid
D. Haploid
Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint: The Mucor genus consists of about 80 species. They are found growing over decaying fruits and vegetables, jellies, soil, etc. They form mat-like appearances and are called molds. Mostly they reproduce by vegetative or asexual mode. Sexual reproduction is also present.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The vegetative body of Mucor is eucarpic having cottony and highly branched mycelium. Mycelia are thread-like structures that contain reproductive or vegetative cells. They ramify all over the substrate over which they grow. Absorption of nutrients and anchorage is provided by hyphae. The walls of hyphae are made of chitin and other polysaccharides like purines, proteins, etc. The protoplast is covered by the plasma membrane which lies inner of the chitin cell wall.
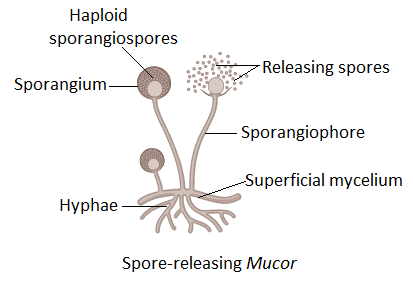
Reproduction occurs through fragmentation if the vegetative mode is used. The mother mycelium breaks into fragments and is capable of growing into individual Mucor. Sporangiospores are formed during the asexual mode of reproduction. They are formed inside the sporangium.
When favorable conditions arrive, the vegetative hyphae elongate to form aerial unbranched hyphae. This is called Sporangiophore. Sporangiophores develop singly on the upper side of the superficial mycelium. On attaining a certain height, the nuclei and cytoplasm are pushed towards the apical side of hyphae or sporangiophore. This causes hyphae to swell up and enlarge. This structure develops to form a round sporangium. The sporangium contains uninucleate and haploid sporangiospores. When the haploid spores mature, dehiscence of sporangium occurs which releases them into the air.
Hence, option D) is the right answer.
Note: Mucor is commonly found growing on the dung of animals. These are not able to infect humans and animals as they cannot tolerate endothermic conditions. Some of the strains are thermotolerant and may cause opportunistic infections. They may cause autolysis of infected cells.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The vegetative body of Mucor is eucarpic having cottony and highly branched mycelium. Mycelia are thread-like structures that contain reproductive or vegetative cells. They ramify all over the substrate over which they grow. Absorption of nutrients and anchorage is provided by hyphae. The walls of hyphae are made of chitin and other polysaccharides like purines, proteins, etc. The protoplast is covered by the plasma membrane which lies inner of the chitin cell wall.

Reproduction occurs through fragmentation if the vegetative mode is used. The mother mycelium breaks into fragments and is capable of growing into individual Mucor. Sporangiospores are formed during the asexual mode of reproduction. They are formed inside the sporangium.
When favorable conditions arrive, the vegetative hyphae elongate to form aerial unbranched hyphae. This is called Sporangiophore. Sporangiophores develop singly on the upper side of the superficial mycelium. On attaining a certain height, the nuclei and cytoplasm are pushed towards the apical side of hyphae or sporangiophore. This causes hyphae to swell up and enlarge. This structure develops to form a round sporangium. The sporangium contains uninucleate and haploid sporangiospores. When the haploid spores mature, dehiscence of sporangium occurs which releases them into the air.
Hence, option D) is the right answer.
Note: Mucor is commonly found growing on the dung of animals. These are not able to infect humans and animals as they cannot tolerate endothermic conditions. Some of the strains are thermotolerant and may cause opportunistic infections. They may cause autolysis of infected cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




