
Stack of lamellae found inside a plastid is
(a)Thylakoid
(b)Stroma
(c)Granum
(d)Oxysome
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: The name of the stack of lamellae found inside a plastid is a small town situated in Canada (South Alberta) and it was popularly known as ‘The village of leavings’. It is the place where the photosynthetic light reaction takes place in a plant cell.
Complete answer:
The Thylakoids are membrane-bound compartments that are present inside the chloroplasts. Thylakoids are the site where the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur. Thylakoids have a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. The thylakoid or lamellae discs stack to form a granum. Grana are connected as a single functional compartment by intergranal / stroma thylakoids which bind granum stacks together. When stacked, each thylakoid will increase its total surface area allowing more electron transport chains to be integrated into each thylakoid membrane.
Additional Information:
-In higher plants, thylakoids are arranged into an assembly of the granum-stroma membrane. A granum (plural: grana) is a set of discs of thylakoids. Chloroplasts can have between 10 and 100 grana. Grana is connected by stroma thylakoids, also known as intergranal thylakoids or lamellae. Grana thylakoids and stroma thylakoids can be differentiated by their different composition of proteins. Grana leads to a high surface to volume ratio of the chloroplasts.
-The thylakoids are the location for light-dependent photosynthetic reactions. These include light-driven water oxidation and oxygen evolution, pumping protons across thylakoid membranes coupled with the photosystem electron transport chain and cytochrome complex, and ATP synthesis using the proton gradient generated by the ATP synthase.
-The first step involved in the light-driven reduction of water is to provide the electrons for the photosynthetic electron transport chains as well as protons for the establishment of a proton gradient. The water-splitting reaction takes place on the lumenal side of the thylakoid membrane and is guided by the light energy the photosystems absorb. This water oxidation produces the waste product O2 which is essential for cellular respiration of various life forms. The molecular oxygen resulting from the reaction is released into the atmosphere.
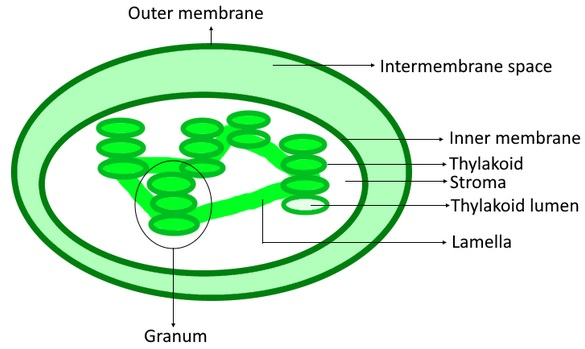
So, the correct answer is ‘Granum’.
Note: Most cyanobacteria (a photosynthetic bacteria), have chloroplasts, thylakoid, and have an internal membrane system where the photosynthetic apparatus is located. These species do not show significant stacking of grana lamellae. Like cyanobacteria, most algae do not contain stacks of grana.
Complete answer:
The Thylakoids are membrane-bound compartments that are present inside the chloroplasts. Thylakoids are the site where the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur. Thylakoids have a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. The thylakoid or lamellae discs stack to form a granum. Grana are connected as a single functional compartment by intergranal / stroma thylakoids which bind granum stacks together. When stacked, each thylakoid will increase its total surface area allowing more electron transport chains to be integrated into each thylakoid membrane.
Additional Information:
-In higher plants, thylakoids are arranged into an assembly of the granum-stroma membrane. A granum (plural: grana) is a set of discs of thylakoids. Chloroplasts can have between 10 and 100 grana. Grana is connected by stroma thylakoids, also known as intergranal thylakoids or lamellae. Grana thylakoids and stroma thylakoids can be differentiated by their different composition of proteins. Grana leads to a high surface to volume ratio of the chloroplasts.
-The thylakoids are the location for light-dependent photosynthetic reactions. These include light-driven water oxidation and oxygen evolution, pumping protons across thylakoid membranes coupled with the photosystem electron transport chain and cytochrome complex, and ATP synthesis using the proton gradient generated by the ATP synthase.
-The first step involved in the light-driven reduction of water is to provide the electrons for the photosynthetic electron transport chains as well as protons for the establishment of a proton gradient. The water-splitting reaction takes place on the lumenal side of the thylakoid membrane and is guided by the light energy the photosystems absorb. This water oxidation produces the waste product O2 which is essential for cellular respiration of various life forms. The molecular oxygen resulting from the reaction is released into the atmosphere.

So, the correct answer is ‘Granum’.
Note: Most cyanobacteria (a photosynthetic bacteria), have chloroplasts, thylakoid, and have an internal membrane system where the photosynthetic apparatus is located. These species do not show significant stacking of grana lamellae. Like cyanobacteria, most algae do not contain stacks of grana.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




