
State and explain Kepler’s law of planetary motion. Draw diagrams to illustrate these laws.
Answer
493.5k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we should know that all the planets revolve around the sun, and it was kepler who first introduced three basic laws which tells us about the nature of motion of these planets around the sun, here we will discuss each law one by one and their statements which are known as Kepler’s law of planetary motion.
Complete step by step answer:
There are three laws of kepler’s planetary motion which are stated as:
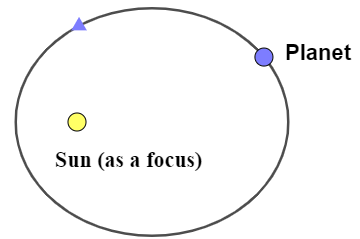
Kepler’s first law: This law states that. all the planets revolve around the sun in an elliptical orbit with the sun as their one of the focus. And as we know the ellipse is a locus of all points whose sum of distance from both the focus always remain constant. Kepler’s first law can be shown in diagram as, sun as one of the focus of the elliptical orbit of a planet revolving around it.
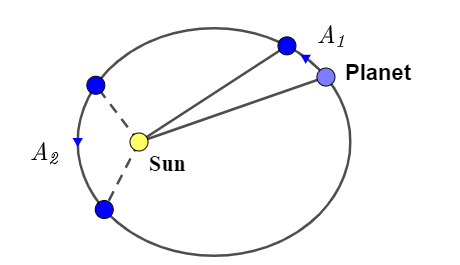
Kepler’s second law: This law states that, planet covers equal area in equal periods of time. which means the areal velocity of a planet is constant. From diagram we can see that, when planet if far from sun then it covers some area say ${A_1}$ in time t and when planet is near the sun it covers area of ${A_2}$ in period of time t, then both the areas will be equal ${A_1} = {A_2}$
Kepler’s Third law: This law states that, The square of time period of revolution of a planet is directly proportional to the cube of the radius of its orbit. Mathematically if T be the time period of a planet and R be the radius of the orbit then this law can be written as
${T^2} \propto {R^3}.$
Hence, these three laws are known as Kepler’s law of planetary motion.
Note: It should be remembered that, due to strong gravitational field of sun when planet passes close to it the velocity of a planet is large as compared to the case when planet is far away from the sun, this is the reason of covering large area near the sun in short period of time.
Complete step by step answer:
There are three laws of kepler’s planetary motion which are stated as:
Kepler’s first law: This law states that. all the planets revolve around the sun in an elliptical orbit with the sun as their one of the focus. And as we know the ellipse is a locus of all points whose sum of distance from both the focus always remain constant. Kepler’s first law can be shown in diagram as, sun as one of the focus of the elliptical orbit of a planet revolving around it.

Kepler’s second law: This law states that, planet covers equal area in equal periods of time. which means the areal velocity of a planet is constant. From diagram we can see that, when planet if far from sun then it covers some area say ${A_1}$ in time t and when planet is near the sun it covers area of ${A_2}$ in period of time t, then both the areas will be equal ${A_1} = {A_2}$

Kepler’s Third law: This law states that, The square of time period of revolution of a planet is directly proportional to the cube of the radius of its orbit. Mathematically if T be the time period of a planet and R be the radius of the orbit then this law can be written as
${T^2} \propto {R^3}.$
Hence, these three laws are known as Kepler’s law of planetary motion.
Note: It should be remembered that, due to strong gravitational field of sun when planet passes close to it the velocity of a planet is large as compared to the case when planet is far away from the sun, this is the reason of covering large area near the sun in short period of time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




