
State and explain the triangle law of vector addition.
Answer
495.3k+ views
Hint: Vector addition is the process of adding two or more vectors together into a vector sum. It is defined as the geometrical sum of two or more vectors. They do not follow any rules and regulations of algebra. There are two laws of vector addition one of which is the triangle law of vector addition and the other is the parallelogram law of vector addition. We are going to see about the triangle law of vector addition in detail.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The triangle law of vector addition says that “Consider two vectors as the two sides of the triangle of the order of same magnitude and the direction, then the third side of the triangle will represent the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector”.
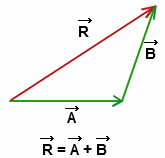
Explanation of the law:
If we have two vectors, \[\vec A\] and \[\vec B\]. We can find the resultant vector as follows. We can refer to the two vectors in the below diagram
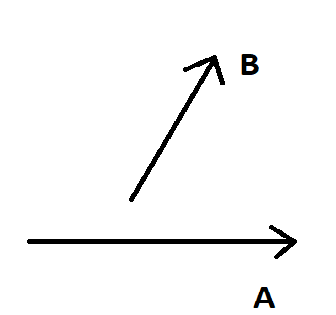
These two vectors \[\vec A\] and \[\vec B\] will both have the same magnitude and direction. If we move \[\vec B\] parallel such that the tail of \[\vec B\] coincides with the head of \[\vec A\].
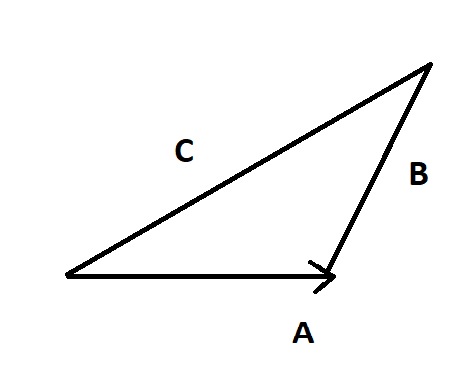
Therefore the vector addition of \[\vec A\] and \[\vec B\] will be the third side that is \[\vec C\]. This is what is known as the triangle law of vector addition.
Note: We should know some basic conditions in vector addition. They are as follows. One is scalars and vectors can never be added. For any two scalars to be added they must be of the same nature and similarly for any two vectors to be added they must have the same nature. The triangle law of vectors can be used in both acute and obtuse angles.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The triangle law of vector addition says that “Consider two vectors as the two sides of the triangle of the order of same magnitude and the direction, then the third side of the triangle will represent the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector”.

Explanation of the law:
If we have two vectors, \[\vec A\] and \[\vec B\]. We can find the resultant vector as follows. We can refer to the two vectors in the below diagram

These two vectors \[\vec A\] and \[\vec B\] will both have the same magnitude and direction. If we move \[\vec B\] parallel such that the tail of \[\vec B\] coincides with the head of \[\vec A\].

Therefore the vector addition of \[\vec A\] and \[\vec B\] will be the third side that is \[\vec C\]. This is what is known as the triangle law of vector addition.
Note: We should know some basic conditions in vector addition. They are as follows. One is scalars and vectors can never be added. For any two scalars to be added they must be of the same nature and similarly for any two vectors to be added they must have the same nature. The triangle law of vectors can be used in both acute and obtuse angles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




