
State Charles law at constant pressure and constant volume.
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: The announcement of Charles' law is as per the following: the volume (V) of a given mass of a gas, at the steady weight (P), is straightforwardly relative to its temperature (T).
Complete answer:
Charles' law, or the law of volumes, was found in 1787 by Jacques Charles.
It expresses that, for a given mass of a perfect gas at a consistent weight, the volume is straightforwardly relative to its outright temperature, expecting in a shut framework.
As a numerical condition, Charles' law is composed as either:
\[V\propto T,\]
\[or\,V/T={{k}_{2}}\]
\[or\,{{V}_{1}}/{{T}_{1}}={{V}_{2}}/{{T}_{2}}\]
where the volume of a gas is the supreme temperature and \[{{k}_{2}}\]is a proportionality constant.
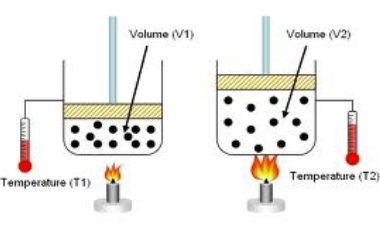
Paul's remark has it right. Charles' Law states "When the weight on an example of a dry gas is held steady, the Kelvin temperature and volume will be legitimately related."
The law says that by the chance that you organize things with the goal that the weight of the gas is fixed then you'll see that \[V\propto T\]. The temperature of the gas may change the weight or the volume, and by and large it's difficult to foresee which will occur.
Note:
We measure the volume of the gas and the temperature of the gas, we have the values \[{{V}_{1\,}}\] and \[{{T}_{1}}\]. Next, begin raising or bringing down the temperature of the gas. The volume should change, thus will the weight, yet once the heat stops again the weight will have returned to its unique worth yet the volume will have changed. Charles' Law says that whenever we do this, we will find that\[\dfrac{{{V}_{2}}}{{{V}_{1}}}=\dfrac{{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{1}}}\].
Complete answer:
Charles' law, or the law of volumes, was found in 1787 by Jacques Charles.
It expresses that, for a given mass of a perfect gas at a consistent weight, the volume is straightforwardly relative to its outright temperature, expecting in a shut framework.
As a numerical condition, Charles' law is composed as either:
\[V\propto T,\]
\[or\,V/T={{k}_{2}}\]
\[or\,{{V}_{1}}/{{T}_{1}}={{V}_{2}}/{{T}_{2}}\]
where the volume of a gas is the supreme temperature and \[{{k}_{2}}\]is a proportionality constant.

Paul's remark has it right. Charles' Law states "When the weight on an example of a dry gas is held steady, the Kelvin temperature and volume will be legitimately related."
The law says that by the chance that you organize things with the goal that the weight of the gas is fixed then you'll see that \[V\propto T\]. The temperature of the gas may change the weight or the volume, and by and large it's difficult to foresee which will occur.
Note:
We measure the volume of the gas and the temperature of the gas, we have the values \[{{V}_{1\,}}\] and \[{{T}_{1}}\]. Next, begin raising or bringing down the temperature of the gas. The volume should change, thus will the weight, yet once the heat stops again the weight will have returned to its unique worth yet the volume will have changed. Charles' Law says that whenever we do this, we will find that\[\dfrac{{{V}_{2}}}{{{V}_{1}}}=\dfrac{{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{1}}}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




