
State Hooke's Law, with graphical representation.
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint:Hooke's Law, or law of elasticity is the fundamental principle behind spring scale, the manometer, balance wheel of the mechanical clock and many other crucial things in mechanics.
Complete step by step answer:
1. Hooke’s Law was given by the scientist Robert Hooke.
2. It states that within the elastic limit, stress developed is directly proportional to the strain produced in the body. Hence, Stress = k × strain, where k is the proportionality constant, and is called modulus of elasticity.
3. For instance, consider a body on which we apply an external force. As a result, stress is developed in the body, which in turn develops a strain (deformation) in the body.
4. Hence, because of stress, strain is consequently produced in the body. According to Hooke's Law, if strain increases, then the stress will increase and vice versa.
5. This law is applicable to all elastic materials. It is not applicable to plastic deformation.
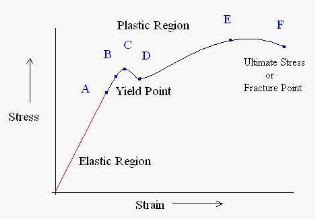
This is the graphical representation of Hooke’s Law-
6. As stated above, Hooke’s law is followed up to the point C. That is, strain and stress are directly proportional to each other.
7. After that point, plasticity comes into play, hence Hooke’s Law I not followed there. The point F is the ultimate fracture point, where the material breaks.
Note:Most of the students get confused between Hooke’s law and restoring force so always remember that Hooke’s law is one of the types of restoring force and always remember it’s formula. It helps in solving various numerical problems.
Complete step by step answer:
1. Hooke’s Law was given by the scientist Robert Hooke.
2. It states that within the elastic limit, stress developed is directly proportional to the strain produced in the body. Hence, Stress = k × strain, where k is the proportionality constant, and is called modulus of elasticity.
3. For instance, consider a body on which we apply an external force. As a result, stress is developed in the body, which in turn develops a strain (deformation) in the body.
4. Hence, because of stress, strain is consequently produced in the body. According to Hooke's Law, if strain increases, then the stress will increase and vice versa.
5. This law is applicable to all elastic materials. It is not applicable to plastic deformation.
This is the graphical representation of Hooke’s Law-
6. As stated above, Hooke’s law is followed up to the point C. That is, strain and stress are directly proportional to each other.
7. After that point, plasticity comes into play, hence Hooke’s Law I not followed there. The point F is the ultimate fracture point, where the material breaks.

Note:Most of the students get confused between Hooke’s law and restoring force so always remember that Hooke’s law is one of the types of restoring force and always remember it’s formula. It helps in solving various numerical problems.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




