
State Pythagoras Theorem?
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: This theorem is applied in a right angle triangle only, it states that the square of sum of two adjacent sides is equal to the sum of the largest third side.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we have to state Pythagoras theorem.
Pythagoras' theorem states that for all right-angled triangles, 'The square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides'. The hypotenuse is the longest side and it's always opposite the right angle.
Diagram:
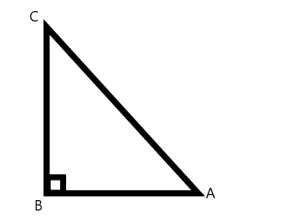
Hence, we can see that the two adjacent sides here are AB, BC and the hypotenuse is AC.
Hence, we can write that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of both adjacent sides.
Hence, it can be given as \[A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}\] .
Thus, above is the Pythagoras theorem.
Additional Information:
Pythagoras theorem is also used in Architecture and Construction. Given two straight lines, the Pythagorean Theorem allows you to calculate the length of the diagonal connecting them. This application is frequently used in architecture, woodworking, or other physical construction projects.
Engineers and astronomers use the Pythagorean Theorem to calculate the paths of spacecraft, including rockets and satellites. Architects use the Pythagorean Theorem to calculate the heights of buildings and the lengths of walls.
Note: In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides.
Pythagoras' theorem only works for right-angled triangles, so you can use it to test whether a triangle has a right angle or not.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we have to state Pythagoras theorem.
Pythagoras' theorem states that for all right-angled triangles, 'The square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides'. The hypotenuse is the longest side and it's always opposite the right angle.
Diagram:

Hence, we can see that the two adjacent sides here are AB, BC and the hypotenuse is AC.
Hence, we can write that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of both adjacent sides.
Hence, it can be given as \[A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}\] .
Thus, above is the Pythagoras theorem.
Additional Information:
Pythagoras theorem is also used in Architecture and Construction. Given two straight lines, the Pythagorean Theorem allows you to calculate the length of the diagonal connecting them. This application is frequently used in architecture, woodworking, or other physical construction projects.
Engineers and astronomers use the Pythagorean Theorem to calculate the paths of spacecraft, including rockets and satellites. Architects use the Pythagorean Theorem to calculate the heights of buildings and the lengths of walls.
Note: In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides.
Pythagoras' theorem only works for right-angled triangles, so you can use it to test whether a triangle has a right angle or not.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





