
State the differences between Nucleus and Nucleolus.
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: In a prokaryotic cell, the nucleus and nucleolus are not present. Their presence is a characteristic feature of a eukaryotic cell. A prokaryotic cell is identified by the absence of any well-defined structure for its genome, opposite to a eukaryotic cell.
Complete answer:
Difference between nucleus and nucleolus:
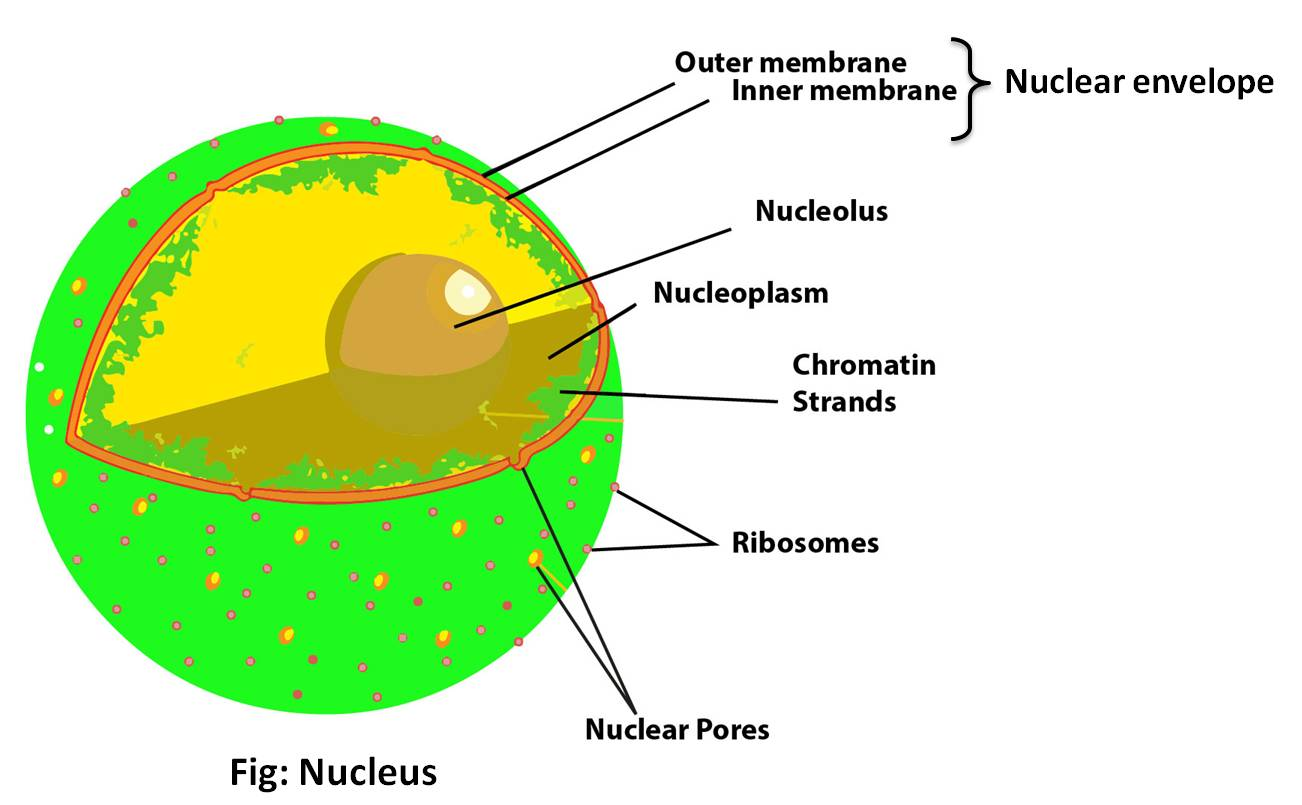
Additional Information: A nucleus has four components: nuclear envelope, nucleolus, nuclear matrix, and chromosomes.
Nuclear envelope: It consists of two concentric membranes called the inner and outer nuclear membranes separating the contents of the nucleus or the nucleoplasm from the cytoplasm. Transport of any protein or molecule occurs through the nuclear pores.
Nuclear matrix: it is a network of protein filaments that provides a structural framework for the organized chromatin while facilitating replication and transcription. It provides mechanical strength and shape to the nucleus.
Nucleolus: It is a naked, round or irregular structure produced by Nucleolar Organizing Regions of a chromosome (NOR) which is termed as a nucleolar organizing chromosome. They are ribosome synthesizing machinery.
Chromosome: A single dsDNA is coiled and with the help of histones and condensed to form chromatin in eukaryotes. Chromatin and chromosome are the same things. Chromatin is less condensed and extended DNA than chromosomes.
Note: DNA bears genes which are a particular set of nucleotide sequences that later produces proteins. Two types of regions are observed on chromosomes:
- Heterochromatin: These are the highly condensed and darkly stained region of chromosomes. They are transcriptionally silent and do not produce proteins.
- Euchromatin: It is a less condensed and lightly stained region of the chromosome that is transcriptionally active.
Complete answer:
Difference between nucleus and nucleolus:
| Property | Nucleus | Nucleolus |
| Location | It is located centrally in an animal cell while in a plant cell, it is located on the periphery. | It is located in the central or periphery region of the nucleus. |
| Membrane | It is encircled with a prominent nuclear envelope. | It is a non-membrane bound structure. |
| Components | It is rich in DNA which is associated with histones( a type of positively charged proteins). | These are rich in RNA and ribosomal proteins. |
| Function | It contains hereditary information in the form of genes arranged on DNA and controls a cell division and metabolism, expression, and production of protein. | It contains the information regarding the transcription of the gene producing ribosomal RNA and assembly of ribosomes. |

Additional Information: A nucleus has four components: nuclear envelope, nucleolus, nuclear matrix, and chromosomes.
Nuclear envelope: It consists of two concentric membranes called the inner and outer nuclear membranes separating the contents of the nucleus or the nucleoplasm from the cytoplasm. Transport of any protein or molecule occurs through the nuclear pores.
Nuclear matrix: it is a network of protein filaments that provides a structural framework for the organized chromatin while facilitating replication and transcription. It provides mechanical strength and shape to the nucleus.
Nucleolus: It is a naked, round or irregular structure produced by Nucleolar Organizing Regions of a chromosome (NOR) which is termed as a nucleolar organizing chromosome. They are ribosome synthesizing machinery.
Chromosome: A single dsDNA is coiled and with the help of histones and condensed to form chromatin in eukaryotes. Chromatin and chromosome are the same things. Chromatin is less condensed and extended DNA than chromosomes.
Note: DNA bears genes which are a particular set of nucleotide sequences that later produces proteins. Two types of regions are observed on chromosomes:
- Heterochromatin: These are the highly condensed and darkly stained region of chromosomes. They are transcriptionally silent and do not produce proteins.
- Euchromatin: It is a less condensed and lightly stained region of the chromosome that is transcriptionally active.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




