
State the law of conservation of momentum and derive related expression.
Answer
603.6k+ views
Hint: In this first we start with the rate of change in momentum of body A and body B that is $\dfrac{{\Delta P}}{{\Delta time}} = {F_{AB}} = \dfrac{{{M_A}{v_A} - {M_A}{u_A}}}{t}$ and $\dfrac{{\Delta P}}{{\Delta time}} = {F_{BA}} = \dfrac{{{M_B}{v_B} - {M_B}{u_B}}}{t}$ respectively and this rate of change in momentum is also equal to the force on one body by another body. Now using Newton's third law that every action has an equal and opposite reaction we can write \[{F_{AB}} = - {F_{BA}}\]. After substituting and rearranging we get \[{M_A}{u_A} + {M_B}{u_B} = {M_B}{v_B} + {M_A}{v_A}\] that is momentum after collision is equal to the momentum before collision if no external force is acting on the system.
Complete step-by-step answer:
According to the law of conservation of momentum when two bodies collide with one another, the sum of their linear momentum always remains unaffected; that is linear momentum after and linear momentum before the collision remains the same but this is true only when there is no external unbalanced force acting on the bodies.
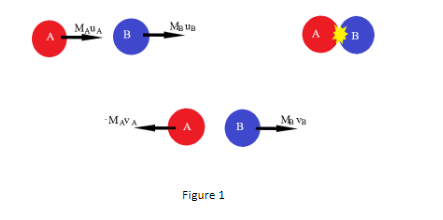
Now let assume the following variables according to figure 1
The mass of body A equals \[{M_A}\]
The mass of body B equals \[{M_B}\]
The force exerted by body A on Body B equals \[{F_{AB}}\]
The force exerted by body B on Body A equals \[{F_{BA}}\]
The velocity of Body A before collision be \[{u_A}\]
The velocity of Body B before collision be \[{u_B}\]
The velocity of Body A after collision be \[{v_A}\]
The velocity of Body B after collision be \[{v_B}\]
Now we will find the change in momentum body A that is
Change in momentum = Momentum of body A after the collision – Momentum of body A before the collision
$ \Rightarrow \Delta P = {M_A}{v_A} - {M_A}{u_A}$
Now we will find the rate of change of momentum for body A that is equal to change in momentum of body A with respect to time $t$.
$\dfrac{{\Delta P}}{{\Delta time}} = \dfrac{{{M_A}{v_A} - {M_A}{u_A}}}{t}$
We know that the rate of change in momentum is same as force exerted by body B on body A that is
$\dfrac{{\Delta P}}{{\Delta time}} = {F_{AB}} = \dfrac{{{M_A}{v_A} - {M_A}{u_A}}}{t}$----------------------------- (1)
Similarly, the rate of change of momentum of body B will be equal to the force exerted by body B on body A that is
$\dfrac{{\Delta P}}{{\Delta time}} = {F_{BA}} = \dfrac{{{M_B}{v_B} - {M_B}{u_B}}}{t}$----------------------------- (2)
Now applying Newton’s third law of motion which is every action has an equal and opposite reaction, we can write
\[{F_{AB}} = - {F_{BA}}\]------------------------------------------ (3)
Here negative sign indicates that one of the body starts moving in the opposite direction after the collision
Now substituting equation (1) and equation (2) in equation (3) we will get
$\dfrac{{{M_A}{v_A} - {M_A}{u_A}}}{t} = - \left[ {\dfrac{{{M_B}{v_B} - {M_B}{u_B}}}{t}} \right]$
$ \Rightarrow {M_A}{v_A} - {M_A}{u_A} = - \left( {{M_B}{v_B} - {M_B}{u_B}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {M_A}{v_A} - {M_A}{u_A} = - {M_B}{v_B} + {M_B}{u_B}$
Now after rearranging we will get
\[ \Rightarrow {M_A}{u_A} + {M_B}{u_B} = {M_B}{v_B} + {M_A}{v_A}\]
\[ \Rightarrow Initial Momentum = Final Momentum\]
Hence it is proved that the momentum after the collision is equal to the momentum before the collision if no external force is acting on the system.
Note: For these types of questions we need to have a clear understanding of all the three Newton’s laws of motion. We need to be clear with the concepts of forces, and momentum and how to calculate them. Since all these are vector quantities we need to be careful with the sign conventions.
Complete step-by-step answer:
According to the law of conservation of momentum when two bodies collide with one another, the sum of their linear momentum always remains unaffected; that is linear momentum after and linear momentum before the collision remains the same but this is true only when there is no external unbalanced force acting on the bodies.

Now let assume the following variables according to figure 1
The mass of body A equals \[{M_A}\]
The mass of body B equals \[{M_B}\]
The force exerted by body A on Body B equals \[{F_{AB}}\]
The force exerted by body B on Body A equals \[{F_{BA}}\]
The velocity of Body A before collision be \[{u_A}\]
The velocity of Body B before collision be \[{u_B}\]
The velocity of Body A after collision be \[{v_A}\]
The velocity of Body B after collision be \[{v_B}\]
Now we will find the change in momentum body A that is
Change in momentum = Momentum of body A after the collision – Momentum of body A before the collision
$ \Rightarrow \Delta P = {M_A}{v_A} - {M_A}{u_A}$
Now we will find the rate of change of momentum for body A that is equal to change in momentum of body A with respect to time $t$.
$\dfrac{{\Delta P}}{{\Delta time}} = \dfrac{{{M_A}{v_A} - {M_A}{u_A}}}{t}$
We know that the rate of change in momentum is same as force exerted by body B on body A that is
$\dfrac{{\Delta P}}{{\Delta time}} = {F_{AB}} = \dfrac{{{M_A}{v_A} - {M_A}{u_A}}}{t}$----------------------------- (1)
Similarly, the rate of change of momentum of body B will be equal to the force exerted by body B on body A that is
$\dfrac{{\Delta P}}{{\Delta time}} = {F_{BA}} = \dfrac{{{M_B}{v_B} - {M_B}{u_B}}}{t}$----------------------------- (2)
Now applying Newton’s third law of motion which is every action has an equal and opposite reaction, we can write
\[{F_{AB}} = - {F_{BA}}\]------------------------------------------ (3)
Here negative sign indicates that one of the body starts moving in the opposite direction after the collision
Now substituting equation (1) and equation (2) in equation (3) we will get
$\dfrac{{{M_A}{v_A} - {M_A}{u_A}}}{t} = - \left[ {\dfrac{{{M_B}{v_B} - {M_B}{u_B}}}{t}} \right]$
$ \Rightarrow {M_A}{v_A} - {M_A}{u_A} = - \left( {{M_B}{v_B} - {M_B}{u_B}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {M_A}{v_A} - {M_A}{u_A} = - {M_B}{v_B} + {M_B}{u_B}$
Now after rearranging we will get
\[ \Rightarrow {M_A}{u_A} + {M_B}{u_B} = {M_B}{v_B} + {M_A}{v_A}\]
\[ \Rightarrow Initial Momentum = Final Momentum\]
Hence it is proved that the momentum after the collision is equal to the momentum before the collision if no external force is acting on the system.
Note: For these types of questions we need to have a clear understanding of all the three Newton’s laws of motion. We need to be clear with the concepts of forces, and momentum and how to calculate them. Since all these are vector quantities we need to be careful with the sign conventions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




