
State the laws of reflection.
Answer
611.1k+ views
Hint – In this question think about the incident ray of the light incident upon a surface present in the same medium, eventually it will get reflected back so reflected ray also needs to be taken into consideration. There is one another parameter that is the angle of incident and the angle of reflection. This concept will help to state the laws of reflection.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
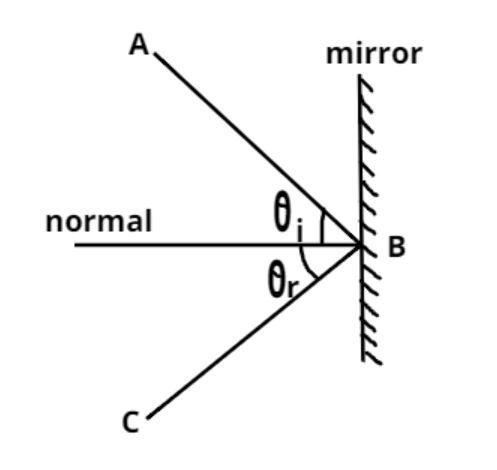
The laws of reflection are as follows:
$\left( 1 \right)$ The incident ray.
$\left( 2 \right)$ The reflected ray.
$\left( 3 \right)$ And the normal to the reflection at that point of the incidence.
So these all lie in the same plane, and the angle which the incident ray makes with the normal is equal to the angle which the reflected ray makes to the same normal as shown in the figure.
In the diagram, a light ray AB strikes a vertical mirror at point B, and the reflected ray is BC, by projecting an imaginary line through point B perpendicular to the mirror, known as the normal so the law of reflection says incident angle is equal to the reflected angle.
Let ${\theta _i}$ be the incident angle and ${\theta _r}$ be the reflection angle so according to above rule
$ \Rightarrow {\theta _i} = {\theta _r}$
So this is the required answer.
Note – There lies a great bit of confusion between reflection and refraction. If a light, radio wave etc, is being deflected in passing through the interface between one medium and another or through a medium of varying density then it is refraction. The laws of reflection only hold true for mediums in the same medium, however if medium is different then there are separate laws governing this phenomena.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:

The laws of reflection are as follows:
$\left( 1 \right)$ The incident ray.
$\left( 2 \right)$ The reflected ray.
$\left( 3 \right)$ And the normal to the reflection at that point of the incidence.
So these all lie in the same plane, and the angle which the incident ray makes with the normal is equal to the angle which the reflected ray makes to the same normal as shown in the figure.
In the diagram, a light ray AB strikes a vertical mirror at point B, and the reflected ray is BC, by projecting an imaginary line through point B perpendicular to the mirror, known as the normal so the law of reflection says incident angle is equal to the reflected angle.
Let ${\theta _i}$ be the incident angle and ${\theta _r}$ be the reflection angle so according to above rule
$ \Rightarrow {\theta _i} = {\theta _r}$
So this is the required answer.
Note – There lies a great bit of confusion between reflection and refraction. If a light, radio wave etc, is being deflected in passing through the interface between one medium and another or through a medium of varying density then it is refraction. The laws of reflection only hold true for mediums in the same medium, however if medium is different then there are separate laws governing this phenomena.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




