
State the principle of an electric generator.
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: An electric generator is an electronic device which converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy. The electric generators are operated on electrostatic principles, based on the phenomenon of the electromagnetic induction.
Complete answer:
The electric generator is an application of electromagnetic induction. Electromagnetic induction is defined as the process in which a conductor is fixed in a particular position and the magnetic field keeps varying or instead the magnetic field is stationary and the conductor keeps moving. This process results in the production of a voltage or electromotive force (EMF) across the electrical conductor.
The electric generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction, in which when a straight conductor moves in a magnetic field, then the current is induced in the conductor.
For better understand of the working of an electric generator let us see the diagram of an electric generator:
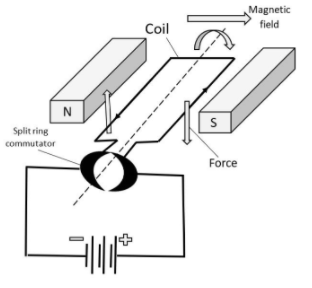
In an electric generator a rectangular coil is made to rotate rapidly in the magnetic field between the poles of a horseshoe type magnet. When the coil rotates it cuts the magnetic field lines because of which the current is produced in the coil.
The electric generators are further classified as:
AC generators: These are known as single – phase generators.
DC generators: These generators are further divided in three categories, i.e. shunt, series and compound wound.
There are various uses of an electric generator:
1) These are used for driving motors.
2) Small scale electric generators provide a good backup for household power needs.
3) It is energy efficient as it reduces the fuel consumption.
Hence, the principle of an electric generator is based on electromagnetic induction.
Note:
Students tend to get confused between electric generators and electric motors. An electric motor works on the reverse conversion of electrical energy to mechanical energy. Both electric motors and electric generators have many similarities.
Complete answer:
The electric generator is an application of electromagnetic induction. Electromagnetic induction is defined as the process in which a conductor is fixed in a particular position and the magnetic field keeps varying or instead the magnetic field is stationary and the conductor keeps moving. This process results in the production of a voltage or electromotive force (EMF) across the electrical conductor.
The electric generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction, in which when a straight conductor moves in a magnetic field, then the current is induced in the conductor.
For better understand of the working of an electric generator let us see the diagram of an electric generator:

In an electric generator a rectangular coil is made to rotate rapidly in the magnetic field between the poles of a horseshoe type magnet. When the coil rotates it cuts the magnetic field lines because of which the current is produced in the coil.
The electric generators are further classified as:
AC generators: These are known as single – phase generators.
DC generators: These generators are further divided in three categories, i.e. shunt, series and compound wound.
There are various uses of an electric generator:
1) These are used for driving motors.
2) Small scale electric generators provide a good backup for household power needs.
3) It is energy efficient as it reduces the fuel consumption.
Hence, the principle of an electric generator is based on electromagnetic induction.
Note:
Students tend to get confused between electric generators and electric motors. An electric motor works on the reverse conversion of electrical energy to mechanical energy. Both electric motors and electric generators have many similarities.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




