
State whether true or false:
In a convergent beam of light all the light rays meet at a point.
A. True
B. False
Answer
600k+ views
Hint: As the name suggests convergent beam will converge and meet at a point known as focus. Concave mirror and a concave lens are used to converge light into one point. With the light ray diagrams of the concave mirror and convex lens, we can define the convergent beam of light rays.
Complete step by step answer:
Convergent beams of light rays will come together at a single point and known as focus.
For concave mirrors or converging mirrors, the path of light rays is shown below.
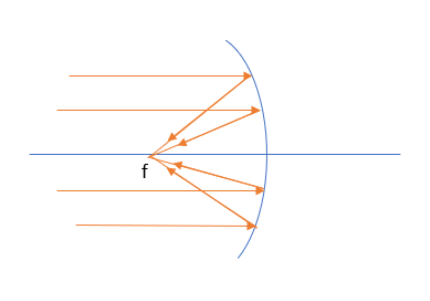
For convex lens or converging lens, the path of light rays is shown below.
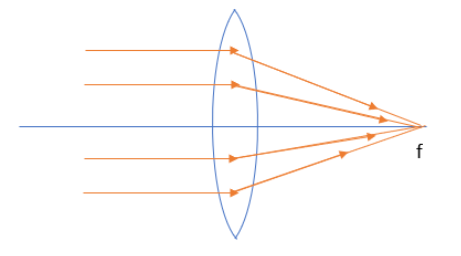
Both figures are showing the converging behaviour of light after the reflection or refraction from a converging mirror or converging lens. These converging beams of light meet at a point known as focus. So, the correct option is A.
Additional information:
A spherical mirror is a part of a reflective sphere. It has a centre of curvature, which corresponds to the centre of the sphere, a radius of curvature, which corresponds to the radius of the sphere and a focal point.
Focal length of spherical mirror is given by,
\[f=\dfrac{R}{2}\], where R is the radius of curvature.
This is an approximation. Only parabolic mirrors can really focus the parallel rays to a single focal point.
For spherical mirrors,
If the inside surface is reflective, then the mirror is concave.
If the outside surface is reflective, then the mirror is convex.
Concave mirrors can form either real or virtual images. While, convex mirrors can form only virtual images. A virtual image is formed because the light rays can be extended back to meet the image position, but they won’t go through the image position.
Note: Divergent beams of light are the light rays from a point source that travel in all directions. Parallel beams of light that incident on either convergent mirror or convergent lens will focus at one point after the reflection or refraction. It is better to remember optical instruments like lenses and mirrors used to converge or diverge the beam of light rays to explain these kinds of problems.
Complete step by step answer:
Convergent beams of light rays will come together at a single point and known as focus.
For concave mirrors or converging mirrors, the path of light rays is shown below.

For convex lens or converging lens, the path of light rays is shown below.

Both figures are showing the converging behaviour of light after the reflection or refraction from a converging mirror or converging lens. These converging beams of light meet at a point known as focus. So, the correct option is A.
Additional information:
A spherical mirror is a part of a reflective sphere. It has a centre of curvature, which corresponds to the centre of the sphere, a radius of curvature, which corresponds to the radius of the sphere and a focal point.
Focal length of spherical mirror is given by,
\[f=\dfrac{R}{2}\], where R is the radius of curvature.
This is an approximation. Only parabolic mirrors can really focus the parallel rays to a single focal point.
For spherical mirrors,
If the inside surface is reflective, then the mirror is concave.
If the outside surface is reflective, then the mirror is convex.
Concave mirrors can form either real or virtual images. While, convex mirrors can form only virtual images. A virtual image is formed because the light rays can be extended back to meet the image position, but they won’t go through the image position.
Note: Divergent beams of light are the light rays from a point source that travel in all directions. Parallel beams of light that incident on either convergent mirror or convergent lens will focus at one point after the reflection or refraction. It is better to remember optical instruments like lenses and mirrors used to converge or diverge the beam of light rays to explain these kinds of problems.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




