
What is stomatal apparatus? Explain the structure of stomata with a labelled diagram.
Answer
521.7k+ views
Hint:Stomata is defined as the minute pores that is present in the leaves and stems of the plants. These are the organs of the transpiration in which the water is lost through it. This is also called the stomata apparatus which helps in the water and gaseous exchange.
Complete answer:
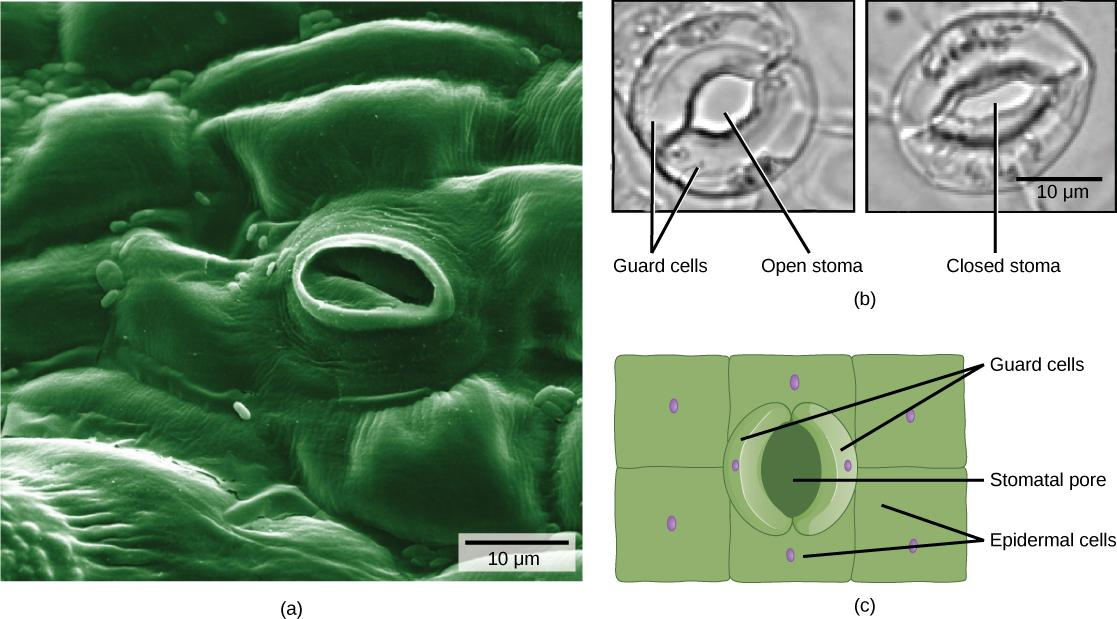
Guard cells are the bean shaped cells present in the leaves and have the potassium ions in it. But in grasses the guard cells are dumb- bell shaped. The pore space formed within these cells is called stomata. Transpiration is the process by which the water is lost through the stomatal openings. This opening and the closing of the stomata is controlled by the guard cells surrounding the pores of the stomata in the leaves. Transport of potassium in the guard cells maintains the turgor pressure in the guard cells, this helps in the opening or the closing of the stomata.
(1) Opening of stomata
Guard cells are full of potassium ions and in order to balance it, water from the nearby guard cells enters into these guard cells. As the water enters, the guard cell becomes bulge and swollen. This process is called endosmosis. This increases the turgor pressure and makes the stomatal pores open.
(2) Closing of stomata
This occurs when the water from the guard cell moves out and the turgor pressure gets reduced. At this time guard cells become flaccid and the pores of the stomata closes. Transport of the potassium ion is responsible for the changes in the stomata opening and closing mechanism.
Note: Opening of stomata mainly occurs at the presence of sunlight and when the photosynthesis takes place. And the closing of the stomata is the opposite of the opening phenomenon. And the closing occurs at the time of night where there is absence of sunlight.
Complete answer:
Guard cells are the bean shaped cells present in the leaves and have the potassium ions in it. But in grasses the guard cells are dumb- bell shaped. The pore space formed within these cells is called stomata. Transpiration is the process by which the water is lost through the stomatal openings. This opening and the closing of the stomata is controlled by the guard cells surrounding the pores of the stomata in the leaves. Transport of potassium in the guard cells maintains the turgor pressure in the guard cells, this helps in the opening or the closing of the stomata.
(1) Opening of stomata
Guard cells are full of potassium ions and in order to balance it, water from the nearby guard cells enters into these guard cells. As the water enters, the guard cell becomes bulge and swollen. This process is called endosmosis. This increases the turgor pressure and makes the stomatal pores open.
(2) Closing of stomata
This occurs when the water from the guard cell moves out and the turgor pressure gets reduced. At this time guard cells become flaccid and the pores of the stomata closes. Transport of the potassium ion is responsible for the changes in the stomata opening and closing mechanism.

Note: Opening of stomata mainly occurs at the presence of sunlight and when the photosynthesis takes place. And the closing of the stomata is the opposite of the opening phenomenon. And the closing occurs at the time of night where there is absence of sunlight.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




